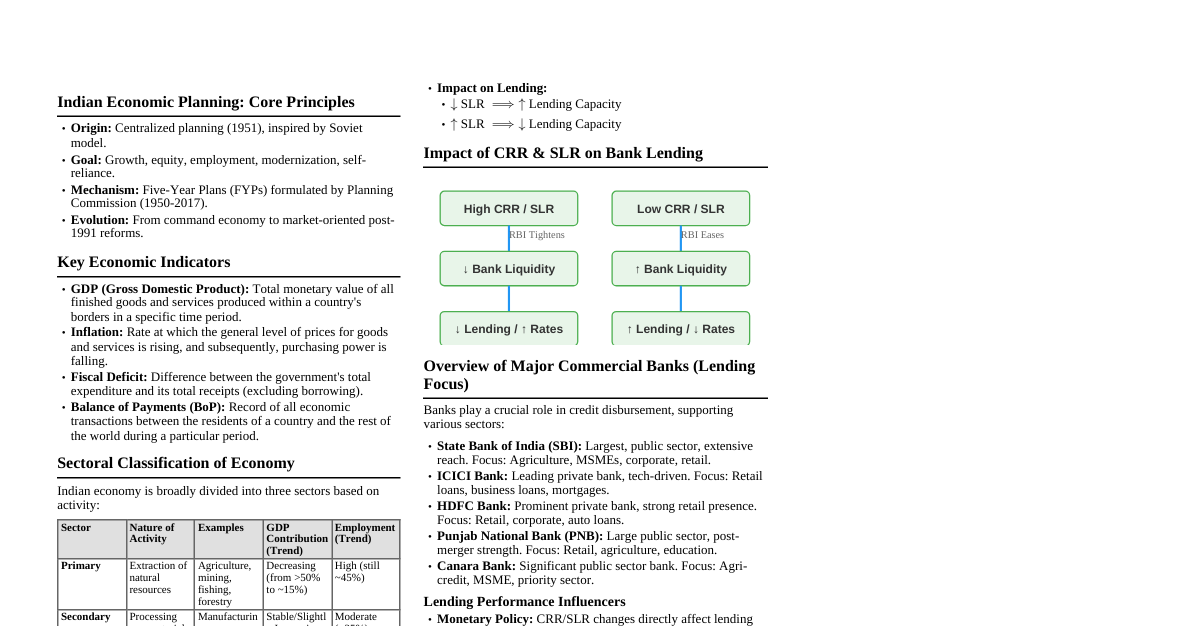
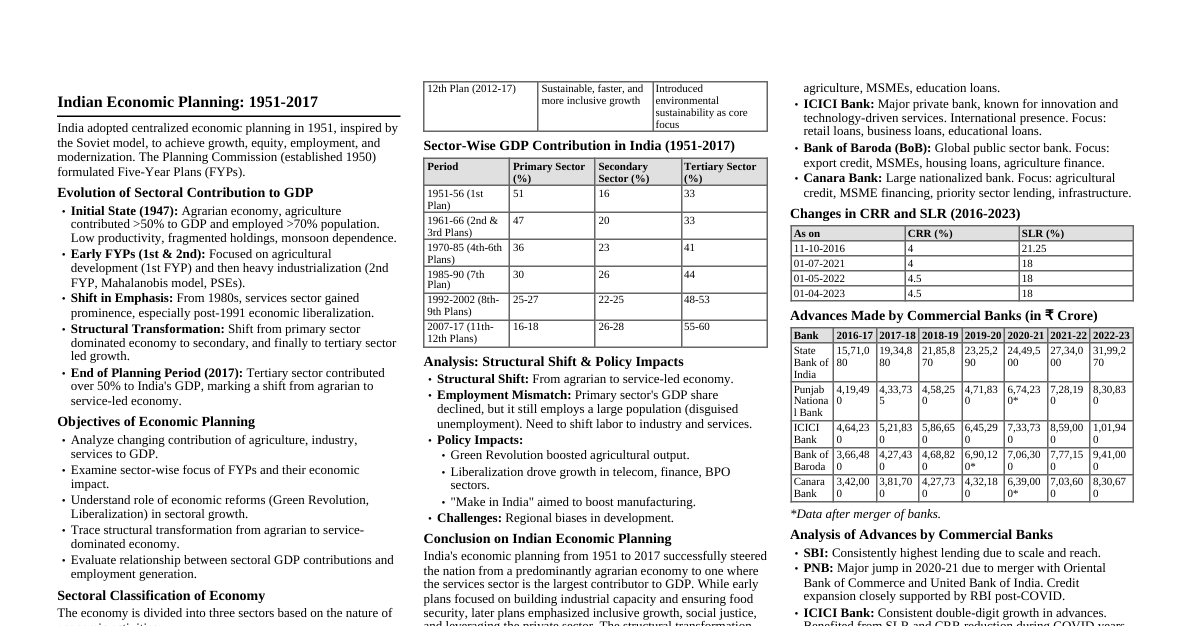
History of Indian Economy Thoughts Early economic thought influenced by Western thinkers. Raj Krishna's "Hindu rate of growth" (1978) for slow post-independence growth. Ancient Indian texts like Smriti, Arthashastra, Tirukkural, Sukranitisara, and Vedas reveal deep economic knowledge. Context from Dharmashastras Dharma: Central to Indian economic thought; righteousness, truthfulness, charity; influences objectives beyond monetary incentives (behavioural economics). Charity: Rig Veda: Voluntary act. Bhagwat Gita: Three types of charity (satwik, rajas, tamas) based on expectations. Modern economic parallel: Positive externality, boosts consumption during slowdowns. "Nudge economics" used by Indian government (e.g., LPG subsidy). Shukraniti Key Features: Authored at the decline of Indian kingdoms and rise of British colonial period. Prescribes administrative expenses $\leq 50\%$ of revenues; rest for public goods (roads, dams, education). Emphasizes judicious conduct for King and ministers. Advocates for maintaining buffer stocks (e.g., grains for crises). Warns against excessive taxation (Laffer curve concept). Scope of Shukraniti: Comprehensive administrative functions of the state. Checks on government functioning. Scientific punishment. Efficient army. Constitutional Monarchy. Well-knit judicial system. Deals with various aspects of society. Importance of Shukraniti: Advises the king on proper administration. Efficient taxation system. Proper judicial administration. Valuable contribution to Hindu science of polity. Practical concept of power usage. Describes people's sovereignty. Context from Mahabharata (Economic Lessons) Monopoly & Oligopoly: Duryodhana's initial monopoly over Hastinapur after burning Pandavas' wax palace. Pressure from elders led to sharing the kingdom, establishing an oligopoly (Hastinapur and Indraprastha). Asymmetric Information & Adverse Selection: Shakuni rigged dice in Chaupar (gambling game). Yudhishthir's unwitting acceptance led to adverse selection and Pandavas' defeat. Diminishing Marginal Product: Kauravas continued gambling, offering Draupadi, leading to war. Draupadi became the diminishing marginal product for the Kauravas. Equilibrium & Evolution: Krishna convinces Arjuna to fight: Restore equilibrium when disrupted. Analogy to Big Bang Theory: Stagnation is unsustainable, conflict (Big Bang) leads to evolution. Unconscious Manager: Krishna's role in guiding Arjuna; living in the present, letting go of past/future anxieties for effortless, intuitive action. Arthashastra: Kautilya's Economic Thoughts Kautilya (Vishnugupta/Chanakya): Teacher, contemporary of Aristotle. Author of 'Arthashastra,' a book on state management, wealth procurement, and preservation. Definition of Economics: Man's behavior/livelihood is Artha; land with man is Artha. Science developing such land is economics. Uses Artha in religion, economy, sensual pleasure. Arthashastra and Economics: Demand and Supply: Kautilya understood demand, supply, and price determination. King should not arbitrarily fix prices; consideration of D&S for equilibrium. Aware of monopoly elements; profit limits (5-10% for domestic, up to 20% for imports). State intervention in glut situations to centralize sales and prevent price falls (price floor). International Trade: Believed in advantages of international trade for prosperity. Encouraged foreign trade, sent experts to study markets. Classified commodities into exportable/importable groups. Envisaged greater consumption possibilities but restricted foreign trade. Interest and Profit (Risk, Uncertainty, Productivity): Higher risk/uncertainty rewarded with higher profits/interests. Imports: Higher profit margin (up to 20%) due to higher risk (robbery/looting). Domestic: Lower profit margin (5-10%). Interest rates regulated by state, based on risk and capital productivity. Tax Structure: Fiscal prudence; taxes should be equitable, just, not heavy/excessive. Suggested tax rates: $1/6^{th}$ or $1/5^{th}$ (16-20%) of economic activities. Taxes beyond limit hamper economic activities and encourage evasion. Higher tax rates (up to 50%+) for harmful goods/services. Taxes mainly on land and commodities. Income tax rare, except for specific professions (singers, dancers, spies). Administration and Budget: Eighteen ministers for overall administration; two for taxation (sulka). 'Samaharta' (chief of tax collection, revenue, land income, tariff revenue monitoring). 'Samindhata' (construction/maintenance of state storehouses for products and food). 'Sulkadhyaksa' (chief of tariff department). Advocated for surplus budget. Emphasized balancing income and expenditure to avoid financial crises. Adequate treasury considered one of seven elements of state sovereignty. Arthashastra – Significance Explains theories and concepts of state governance. Kautilya's imperative: government, polity, politics, and progress tied to people's well-being. Nature and role of state in economic system consistent despite vocabulary changes. Relevant today for administration, politics, economics. Ideas still widely held in India. Valued foundation for economic science; insights on international commerce, taxation, government spending, agriculture, industry. Stability when rulers are responsive, responsible, removable. Avoided hefty taxes; high rates discourage payment. Focus on social welfare: State assists impoverished, contributes to residents' well-being. Emphasized human capital generation. Useful financial information; illustrates contemporary economic ideas. Proposed economic policy approaches for development. India and Global GDP: Ancient India Global R&D Hub: Significant government effort in scientific/technical infrastructure over 50 years. 250+ universities, 1,500+ research institutions, 10,428+ higher-education institutes. Produces 200,000 engineers, 300,000 technically trained graduates annually. Many MNCs (GE, Microsoft, Bell Labs, Delphi, Hewlett-Packard) have R&D centers in India. India is second only to USA in R&D hubs. World Economy: Future Economic Power Shifts (2008-2040) (% Share of World GDP in PPP) Country 2008 2014 2020 2030 2040 Germany 4.2 3.8 3.4 2.8 2.3 USA 20.4 19.2 17.6 15.3 13.9 Japan 6.2 5.6 4.7 3.7 2.9 China 11.3 16.3 22.2 30.9 37.4 India 4.9 6.3 8.5 14.3 20.8 Black Money and Tax Havens Black Money: Funds on which taxes have not been paid. Undermines formal economy by promoting parallel economy (cash/illegal transactions). Effects: Affects financial system: Central bank cannot control money supply, leads to inflation, decreases currency value. Used for illegal activities (narcotics, drug dealing). Government loses significant tax revenue. Increases real estate prices, negatively affects country's credibility. Weakens financial institutions (reduces deposits, hampers lending, hinders growth). Erodes trust in government, weakens governance, fosters non-compliance, undermines tax systems and public administration. Tax Haven: Country or independent area with low taxes and financial secrecy for foreign individuals/corporate entities. Accepts nominal charge for services. Mechanism: Attracts foreign investors, controls supply/demand, earns profits, stabilizes prices. Where India Stands Globally: An Emerging Global Leader Global Leader Definition: Person leading a group/country, recognized as important globally. Influence: Ability to shape events, gain bargaining power, use incentives. Influential powers are states important to welfare/security of other countries. Soft power: Attracting others to want what you want, framing issues, setting agenda. Roots in human experience; skillful leaders understand attractiveness stems from credibility and legitimacy. Quest for Leadership: India's attraction for millennia due to spiritual, artistic, learning centers, religious ideas, culture. Long history, culture, civilization attract intellectuals and common folk. "A nation that doesn't honor its past has no future" - Johann Wolfgang von Goeth. Analytical Perspectives: Shift from Western global domination. Natural return of China and India as largest economies (historically from 1 to 1820 AD). World has shrunk into a "global village." India emerged as a major power in Asia. Bloomberg Report (2022): India is the world's $6^{th}$ largest economy, surpassing Britain. Incredible India (Soft Power): Spirituality is at the core of India's soft power. Swami Vivekananda: "If India is to die... religion might be wiped off... and with it Truth." Soft Power Initiatives: Vaccine Maitri: Humanitarian initiative during COVID-19, distributing vaccines globally. Space Diplomacy: Emerging area for dominance; space technology builds relations and achieves national interests. Satellite data and imagery used across sectors (agriculture, transport, weather, urban development). ISRO is a global leader: moon landing, Mars orbit, launching 104 satellites on single rocket. Education and Aid Diplomacy: Education as a soft power strategy to expand influence, shape opinions, and build relations. New Education Policy (NEP) 2020 emphasizes rich heritage, culture, knowledge, thought. Human capital is the new index of power. NEP 2020 provides blueprint for soft power in foreign policy. IIPA's Contribution (Indian Institute of Public Administration): Contributes to India's global leadership through capacity development programs under ITEC (Indian Technical and Economic Cooperation). Programs on Strategic Leadership, Project Management, Data Analytics, Risk Management. Trained participants from 90+ countries. Peacekeeping Operations: India has a long history of service in UN Peacekeeping, contributing more personnel than any other country. Began with participation in UN operation in Korea (1950s). India's mediatory role resolved stalemate over prisoners of war, leading to armistice. Disaster and Humanitarian Diplomacy (HADR): Respects sovereignty, adheres to 1994 Oslo Guidelines (Humanity, Impartiality, Neutrality). Coalition for Disaster Resilient Infrastructure (CDRI): Launched by PM Modi (2019). Partnership of governments, UN agencies, banks, private sector, knowledge institutions. Aims to promote resilience of infrastructure to climate/disaster risks. Boosts India's soft power, provides synergy between disaster risk reduction, SDGs, and Climate Accord. Funding Ecosystem: Rise of Unicorns: "Unicorns" are startups valued at $1 billion+. Indian Startup Ecosystem is $3^{rd}$ largest globally. As of May 2022, 100 unicorns with total valuation of $332.7$ billion. 2021 saw 44 startups become unicorns ($93$ billion valuation). Building Connectivity: Signed MoU with Afghanistan for Lalandar (Shatoot) Dam (Kabul River tributary) for drinking water and irrigation. Since 2001, New Delhi pledged $3$+ billion for development/reconstruction projects in Afghanistan. Built roads, dams, electricity networks, schools, and Afghan Parliament. Culinary Diplomacy: Indian diaspora has spread culinary traditions globally. Indian cuisines adapted to local tastes and influenced local cuisines worldwide. Many Indian restaurants in major global cities. Conclusion India's soft power components are diverse: films, Bollywood, yoga, ayurveda, political pluralism, religious diversity, openness to global influences. Successful export of cultural products raised awareness and modified stereotypes. Institutional model of democratic and plural political system inspired societies abroad. Soft power grew with economic liberalization, success, and rapid acquisition of military power. Growth in hard economic and military power reinforced confidence in projecting soft power. India is emerging as a global leader in the $21^{st}$ century due to all-round development.