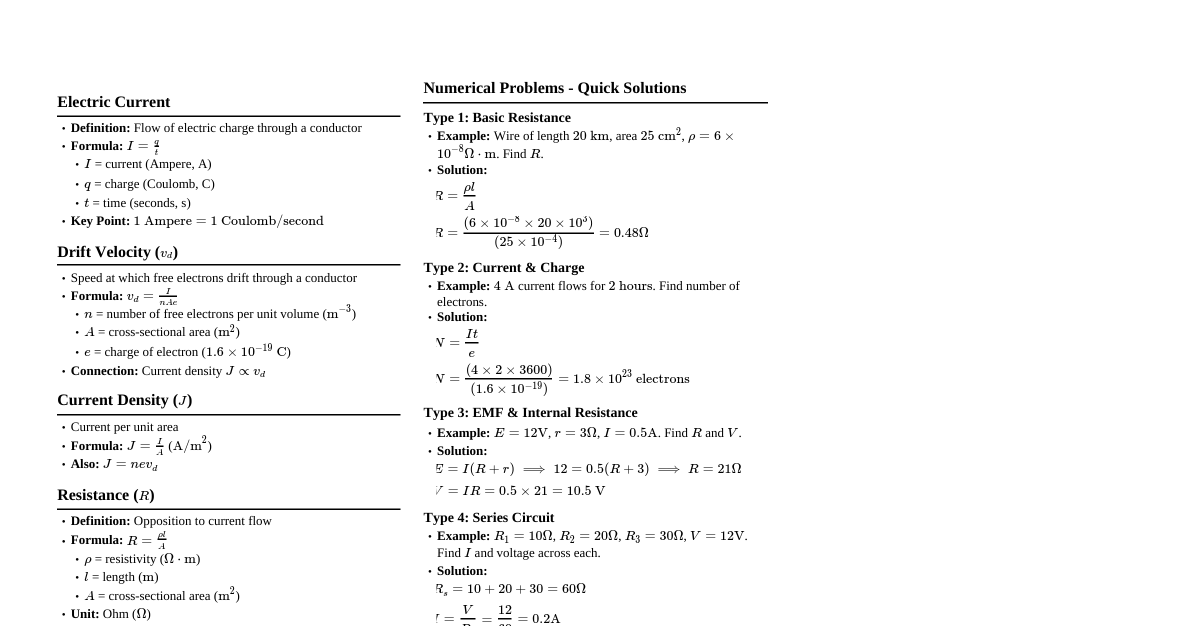
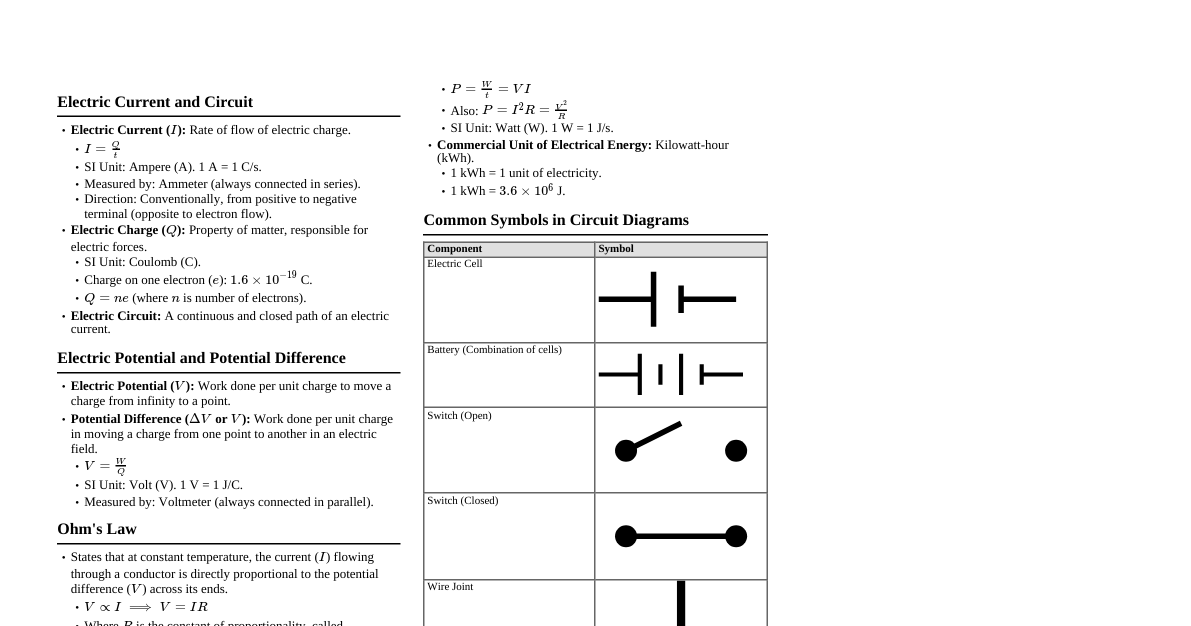
### Electric Current - **Definition:** The rate of flow of electric charge. - **Formula:** $I = \frac{dQ}{dt}$ - **Unit:** Ampere (A). 1 A = 1 C/s. - **Conventional Current:** Direction of flow of positive charge. - **Drift Velocity ($v_d$):** Average velocity acquired by free electrons in a conductor under an electric field. - $I = n e A v_d$, where $n$ is number density of electrons, $e$ is charge of electron, $A$ is cross-sectional area. - $v_d = \frac{e E \tau}{m}$, where $E$ is electric field, $\tau$ is relaxation time, $m$ is mass of electron. ### Ohm's Law - **Statement:** At constant temperature, the current flowing through a conductor is directly proportional to the potential difference across its ends. - **Formula:** $V = I R$ - **Resistance ($R$):** Opposition to the flow of current. - **Unit:** Ohm ($\Omega$). - **Factors affecting R:** $R = \rho \frac{L}{A}$, where $\rho$ is resistivity, $L$ is length, $A$ is area. - **Resistivity ($\rho$):** Intrinsic property of material. Unit: Ohm-meter ($\Omega \cdot m$). - **Conductance ($G$):** Reciprocal of resistance. $G = \frac{1}{R}$. Unit: Siemens (S) or mho ($\mho$). - **Conductivity ($\sigma$):** Reciprocal of resistivity. $\sigma = \frac{1}{\rho}$. Unit: Siemens/meter (S/m). - **Temperature Dependence of Resistance:** - $R_T = R_0 (1 + \alpha (T - T_0))$, where $\alpha$ is temperature coefficient of resistance. ### Series and Parallel Combinations #### Series Combination - **Current:** Same through each resistor. $I_{total} = I_1 = I_2 = ...$ - **Voltage:** Sum of individual voltages. $V_{total} = V_1 + V_2 + ...$ - **Equivalent Resistance:** $R_{eq} = R_1 + R_2 + ...$ #### Parallel Combination - **Current:** Sum of individual currents. $I_{total} = I_1 + I_2 + ...$ - **Voltage:** Same across each resistor. $V_{total} = V_1 = V_2 = ...$ - **Equivalent Resistance:** $\frac{1}{R_{eq}} = \frac{1}{R_1} + \frac{1}{R_2} + ...$ ### Kirchhoff's Laws #### 1. Kirchhoff's Current Law (KCL) / Junction Rule - **Statement:** The algebraic sum of currents entering a junction is equal to the algebraic sum of currents leaving the junction. (Conservation of Charge) - **Formula:** $\sum I_{in} = \sum I_{out}$ or $\sum I = 0$ at a junction. #### 2. Kirchhoff's Voltage Law (KVL) / Loop Rule - **Statement:** The algebraic sum of changes in potential around any closed loop in a circuit is zero. (Conservation of Energy) - **Formula:** $\sum \Delta V = 0$ in a closed loop. ### Wheatstone Bridge - **Principle:** Used to measure an unknown resistance. - **Condition for Balance:** $\frac{P}{Q} = \frac{R}{S}$, where P, Q, R, S are resistances. - **Application:** Meter bridge (practical application for measuring unknown resistance). ### Potentiometer - **Principle:** A device used to measure potential difference, compare EMFs of cells, and measure internal resistance of a cell. - **Working:** Based on the principle that when a constant current flows through a wire of uniform cross-section, the potential drop across any length of the wire is directly proportional to its length ($V \propto L$). - **Comparison of EMFs:** $\frac{E_1}{E_2} = \frac{L_1}{L_2}$, where $L_1$ and $L_2$ are balancing lengths. - **Internal Resistance of a Cell ($r$):** $r = R \left( \frac{L_1}{L_2} - 1 \right)$, where $L_1$ is balancing length for open circuit, $L_2$ for closed circuit with resistance $R$. ### Electric Power and Energy - **Electric Power ($P$):** Rate at which electrical energy is dissipated or consumed in a circuit. - **Formulas:** - $P = V I$ - $P = I^2 R$ - $P = \frac{V^2}{R}$ - **Unit:** Watt (W). 1 W = 1 J/s. - **Electric Energy ($E$):** $E = P \times t = V I t = I^2 R t = \frac{V^2}{R} t$ - **Unit:** Joule (J). Commercial unit: kilowatt-hour (kWh). 1 kWh = $3.6 \times 10^6$ J. ### Cells, EMF, and Internal Resistance - **Electromotive Force (EMF, $E$):** The potential difference across the terminals of a cell when no current is drawn from it (open circuit). - **Terminal Potential Difference ($V$):** The potential difference across the terminals of a cell when current is drawn from it (closed circuit). - **Internal Resistance ($r$):** The resistance offered by the electrolyte and electrodes of a cell to the flow of current. - **Relationship:** $V = E - I r$ (for discharge) - **Combination of Cells:** - **Series:** $E_{eq} = E_1 + E_2 + ...$, $r_{eq} = r_1 + r_2 + ...$ - **Parallel:** For identical cells: $E_{eq} = E$, $\frac{1}{r_{eq}} = \frac{1}{r_1} + \frac{1}{r_2} + ...$