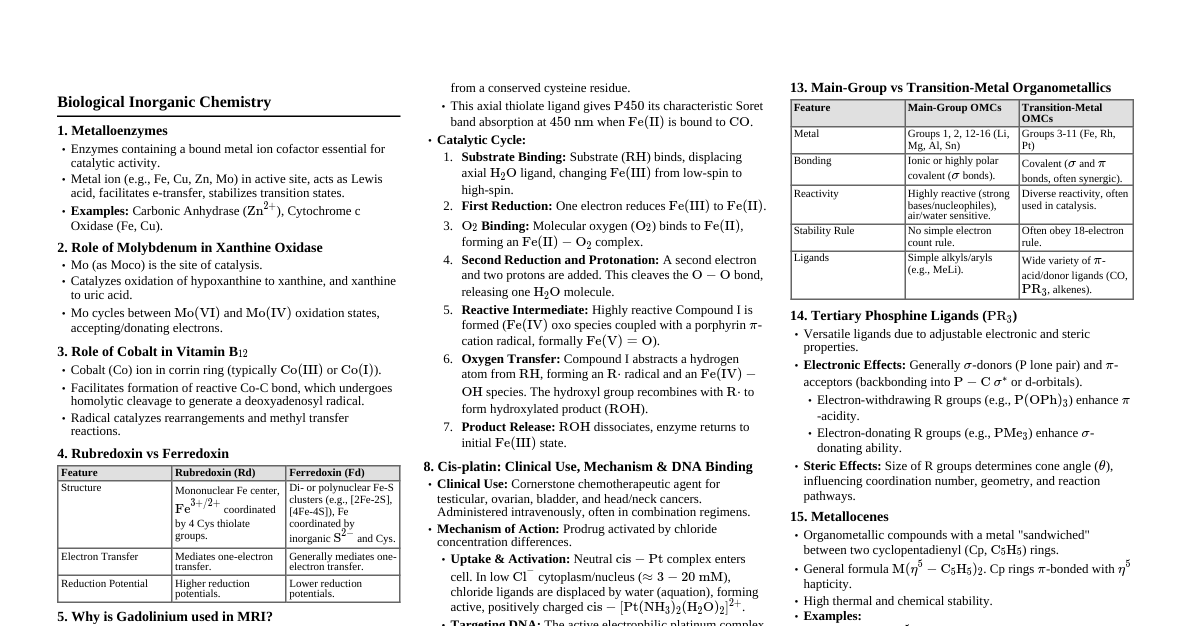
2. Qualitative Chemistry Formula Extraction Bohr's Angular Momentum: $mvr = \frac{nh}{2\pi}$ Emitted/Absorbed Energy: $\Delta E = E_2 - E_1 = hf$ Photon Energy: $E = hf = \frac{hc}{\lambda}$ De Broglie Wavelength: $\lambda = \frac{h}{mv} = \frac{h}{p}$ Rydberg Wavenumber: $\bar{\nu} = \frac{1}{\lambda} = R_H \left(\frac{1}{n_L^2} - \frac{1}{n_H^2} \right)$ Average Atomic Mass: $\text{Avg. Mass} = \frac{am_1+bm_2+cm_3}{100} \text{amu}$ Bohr Orbit Radius: $r_n = \frac{n^2\epsilon_0 h^2}{\pi m e^2}$ Hybridization Factor: $X = \frac{1}{2} (V + M - C + A)$ Bond Order (Molecular Orbital): $\text{Bond Order} = \frac{n_b - n_a}{2}$ Pattern Mapping Bohr's Angular Momentum: $n$ (principal quantum number) must be an integer (1, 2, 3,...). Photon Energy: Calculates quantized energy ($E$) based on measurable frequency ($f$) or wavelength ($\lambda$). Rydberg Wavenumber: $R_H$ is a constant ($109678 \text{ cm}^{-1}$). $n_L$ is the final energy level, $n_H$ is the initial level. Average Atomic Mass: Used to calculate weighted average atomic mass from percentage abundances and isotopic masses. Hybridization Factor: $C$ (cation charge) is subtracted; $A$ (anion charge) is added. $X$ values map directly to hybridization states (e.g., $X=4 \implies sp^3$). Bond Order: $n_b$ and $n_a$ derived from molecular orbital theory filling rules. Error Analysis Units: $R_H$ unit is $\text{cm}^{-1}$. Planck's constant ($h$) unit is J$\cdot$s (Joules $\cdot$ seconds). Bohr radius is often given in picometers (pm, $10^{-12} \text{ m}$). Signs (+/-): In the hybridization factor formula, use the positive magnitude for charge numbers, and subtract cation charge while adding anion charge. Negative energy values in Bohr's model ($E_n$) imply the electron is bound to the nucleus. Assumptions/Traps: Bohr's model applies only to single-electron species ($\text{H}, \text{He}^+, \text{Li}^{2+}$). 48-Hour Sheet High-Risk Error List: For $K_{SP}$ calculation $A_x B_y$: Forgetting the powers $x^x y^y$ (e.g., $K_{SP} = 4S^3$ for $AB_2$ type, not $S^2$). Failing to correctly calculate $n_b$ and $n_a$ for heteronuclear diatomics (like CO or NO) for Bond Order. Misapplying the Hybridization Factor formula by incorrectly counting valence electrons ($V$), monovalent atoms ($M$), or misusing the sign of the charge ($C/A$). Confusing the use of $\Delta H$ vs $E_a$ (Enthalpy change vs Activation Energy) in temperature/rate relationships. Incorrect units for Rydberg equation ($R_H$ in $\text{cm}^{-1}$) when calculating $\lambda$. Instant Recall Formula Block: $X = \frac{1}{2} (V + M - C + A)$ $mvr = \frac{nh}{2\pi}$ $\bar{\nu} = R_H \left( \frac{1}{n_L^2} - \frac{1}{n_H^2} \right)$ $\text{B.O.} = \frac{n_b - n_a}{2}$ 3. Periodic Properties of Elements and Chemical Bonding Formula Extraction Solubility Product ($K_{SP}$): $K_{SP} = [M^{q+}]^p \times [A^{p-}]^q$ $K_{SP}$ for $A_x B_y$: $K_{SP} = x^x y^y S^{x+y}$ Ionic Product ($Q$ or $K_{ip}$): $Q = [\text{cation}]^{\text{cation number}} \times [\text{anion}]^{\text{anion number}}$ Pattern Mapping $K_{SP}$ and $Q$ Application: Precipitation condition: $Q > K_{SP}$. Saturated condition: $Q = K_{SP}$. Unsaturated condition: $Q $K_{SP}$ vs $S$: These simplified forms relate molar solubility ($S$) directly to the solubility product ($K_{SP}$) for common salt stoichiometric types. Error Analysis Units: $K_{SP}$ unit depends on the stoichiometry, e.g., $\text{mol}^2 \text{L}^{-2}$ for AB type. Signs (+/-): Electronegativity difference ($\Delta EN$): Ionic character is high if $\Delta EN > 1.7$. Assumptions/Traps: $K_{SP}$ is constant only at constant temperature; solubility ($S$) can vary due to the common ion effect. In the presence of a common ion, solubility ($S$) decreases. Ionic compounds generally dissolve better in polar solvents (like $\text{H}_2\text{O}$) due to hydration energy. Covalency (Fajan's rule) increases with: smaller cation size, larger anion size, and higher charges. 48-Hour Sheet High-Risk Error List: $K_{SP}$ application: Incorrectly assuming precipitation occurs when $Q \neq K_{SP}$ (must be $Q > K_{SP}$). Hybridization of $\text{SnCl}_2$ (sp$^2$, V-shape, not tetrahedral sp$^3$). Hybridization of complex ions: Remembering coordination number = ligand count (e.g., $K_4[Fe(CN)_6]$ has coordination number 6). Highest Ionic Character: $\text{CsF}$ (due to largest cation/smallest anion). Bond Types: $NH_4CI$ contains all three types: ionic ($NH_4^+$ and $CI^-$), covalent ($N-H$ in $NH_3$), and coordinate ($N: \to H^+$) bonds. Instant Recall Formula Block: $K_{SP} \text{ for } A_x B_y = x^x y^y S^{x+y}$ $Q \text{ (Ionic Product) vs } K_{SP} \text{ (Solubility Product)}$ 4. Chemical Change Formula Extraction Reaction Rate (Instantaneous): $v = -\frac{1}{a} \frac{d[A]}{dt} = \frac{1}{c} \frac{d[C]}{dt}$ Rate Law (Order $n$): $v = -\frac{d[C]}{dt} = k \times C^n$ Zero Order Rate Constant: $v = k$ First Order Half-life: $t_{1/2} = \frac{\ln 2}{k} = \frac{0.693}{k}$ First Order Integrated Rate Law: $\log \frac{a}{a-x} = \frac{k t}{2.303}$ Arrhenius Equation (Log Form): $\ln k = \ln A - \frac{E_a}{RT}$ $K_P/K_C$ Relation: $K_P = K_C (RT)^{\Delta n}$ Enthalpy/Internal Energy Relation: $\Delta H = \Delta E + \Delta n RT$ pH: $\mathbf{pH = - \log[H^+]}$ Water Ion Product: $K_W = [H^+][OH^-] = 10^{-14}$ Henderson-Hasselbalch (Acidic): $\mathbf{pH = pK_a + \log \frac{[salt]}{[acid]}}$ Ostwald's Dilution Law (Weak Acid): $K_a = \alpha^2 c$ Pattern Mapping $K_P = K_C (RT)^{\Delta n}$: $\Delta n$ is the change in the total number of *moles of gaseous components*. If $\Delta n = 0$, then $K_P = K_C$. $\Delta H = \Delta E + \Delta n RT$: $\Delta H$ (heat at constant P) relates to $\Delta E$ (heat at constant V) via $\Delta n$. $t_{1/2} = 0.693/k$: Half-life is *independent* of initial concentration for first-order reactions. $\ln k = \ln A - E_a/RT$: Rate constant ($k$) increases exponentially with temperature ($T$) and inversely with activation energy ($E_a$). $\mathbf{pH = - \log[H^+]}$ and $\mathbf{K_W = 10^{-14}}$: Used inversely to find concentration from $\mathbf{pH/pOH}$ or vice versa. Error Analysis Units: Rate constant ($k$): $s^{-1}$ (for 1st order). Temperature ($T$): Must be in Kelvin for gas laws and Arrhenius equations. Signs (+/-): $\Delta H$ is negative for exothermic reactions (heat released). $\Delta H$ is positive for endothermic reactions (heat absorbed). Slope of $\ln k$ vs $1/T$ is negative for calculating $E_a$. Assumptions/Traps: Equilibrium: $K_P$ and $K_C$ are affected only by temperature . Pressure and catalysts do *not* change $K$. Le Chatelier's Principle: Increasing pressure favors the side with *fewer* moles of gas. Increasing temperature favors the *endothermic* reaction. $K_P/K_C$ (Heterogeneous): Solids and pure liquids (like $\text{H}_2\text{O}(l)$) are excluded from the equilibrium expressions. First Order: The half-life formula ($t_{1/2} = 0.693/k$) is applicable to all radioactive decay reactions, as they are universally first order. 48-Hour Sheet High-Risk Error List: Failing to convert concentrations/pressures to the correct base unit (Molar, atm) for $K_P/K_C$ calculations. Misidentifying the change in gas moles ($\Delta n$) for $\Delta H$ and $K_P$ calculations, especially neglecting solids/liquids. Exothermic reactions (like $\mathbf{N_2 + 3H_2 \rightleftharpoons 2NH_3}$) are favored by low temperature and high pressure . Confusing bond breaking ($\mathbf{E_{break} > 0}$, endothermic) vs bond formation ($\mathbf{E_{form} Incorrectly assigning the Henderson-Hasselbalch terms (Acid/Salt concentration ratio). Instant Recall Formula Block: $K_P = K_C (RT)^{\Delta n}$ $\Delta H = \Delta E + \Delta n RT$ $\mathbf{pH = pK_a + \log \frac{[salt]}{[acid]}}$ $t_{1/2} = \frac{0.693}{k} \text{ (1st Order)}$ $\mathbf{K_W = 10^{-14}}$ 5. Applied Chemistry Formula Extraction Urea Production (General reaction): $2NH_3(g) + CO_2(g) \xrightarrow{\Delta, P} H_2NCONH_2$ Fermentation of Glucose: $C_6H_{12}O_6 \xrightarrow{Zymase} 2C_2H_5OH + 2CO_2$ Decarboxylation (Alkane prep.): $\mathbf{R - COONa + NaOH(CaO) \xrightarrow{\Delta} R - H + Na_2CO_3}$ Wurtz Reaction (Alkane prep.): $\mathbf{2R - X + 2Na \xrightarrow{\text{Dry} \ \text{ether}} R - R + 2NaX}$ Tollen's Test (Aldehyde Detection): $R-CHO + 2[Ag(NH_3)_2]OH \xrightarrow{\Delta} \mathbf{2Ag \downarrow} + RCOONH_4 + 3NH_3 + H_2O$ $K_{SP}$ calculation for $Al(OH)_3$: $K_{SP} = 27S^4$ Pattern Mapping Decarboxylation/Wurtz: Used to manipulate carbon chain length in alkanes. $\mathbf{CaO}$ acts as a dehydrating agent. Wurtz reaction yields higher alkanes with an even number of carbons. Tollen's Test: The formation of $\mathbf{Ag \downarrow}$ (silver mirror) confirms the presence of the aldehyde group ($\mathbf{-CHO}$). Fermentation: Catalyzed by $\mathbf{Zymase}$ (for Glucose to Ethanol) and $\mathbf{Invertase}$ (for Sucrose to Glucose/Fructose) enzymes. Methanol Synthesis (Industrial): Uses $\mathbf{ZnO + Cr_2O_3}$ as catalyst. Error Analysis Units/Values: Vinegar is $\mathbf{6\% - 10\%}$ Acetic Acid aqueous solution. Formalin is $\mathbf{40\%}$ Formaldehyde aqueous solution. Recommended safe $\mathbf{pH}$ range for drinking water: $6.5 - 8.5$. Signs (+/-): Not applicable to compositional data. Assumptions/Traps: Lucas Reagent Test: Only $\mathbf{3^\circ}$ alcohols give immediate turbidity (precipitate) at room temperature with Lucas reagent ($conc. \ HCl + anhydrous \ ZnCl_2$). Common Industrial Reactions: Remember specific conditions: Haber-Bosch ($\text{Fe/Mo}$, 450-550$^\circ$C, 200 atm); $\text{H}_2\text{SO}_4$ contact process ($\text{V}_2\text{O}_5$/Pt, 400-500$^\circ$C, 1.7 atm). Green Chemistry: Focuses on minimizing waste and hazard. Tollen's/Fehling's: These tests only distinguish aldehyde ($\mathbf{-CHO}$) from ketones/alcohols, but they DO NOT react with $3^\circ$ alcohols or regular alkanes/alkenes. $\mathbf{SO_2}$ and $\mathbf{NO_x}$ are the main precursors for acid rain. 48-Hour Sheet High-Risk Error List: Lucas Test Speed: Mixing up the reactivity speed of $1^\circ, 2^\circ, 3^\circ$ alcohols. Carbylamine Test: Forgetting the characteristic foul smell/isocyanide product ($R-N\equiv C$). Vinegar/Formalin Concentration: Misstating the percentage concentrations. Greenhouse Gases: Misidentifying $\mathbf{CO_2}$ (50%) as the largest contributor to the greenhouse effect. $\mathbf{H_2S}$ Hazard: Known to cause nerve inflammation. Instant Recall Formula Block: $C_6H_{12}O_6 \xrightarrow{Zymase} 2C_2H_5OH + 2CO_2$ $R - COONa \xrightarrow{NaOH(CaO)} R - H$ $\text{Lucas Reagent} = \text{conc.} \ \text{HCI} + \text{anhydrous} \ \text{ZnCl}_2$ $\text{Vinegar} = 6-10\% \ CH_3COOH$ 1. Environmental Chemistry Formula Extraction Boyle and Charles' Combined Law: $\mathbf{\frac{P_{1}V_{1}}{T_{1}} = \frac{P_{2}V_{2}}{T_{2}}}$ Ideal Gas Equation: $PV = nRT$ Molar Mass and Density: $M = \frac{mRT}{PV}$ and $d = \frac{PM}{RT}$ Dalton's Law of Partial Pressures: $P_{A} = X_{A} P_{Total}$ Graham's Law of Diffusion: $\mathbf{\frac{r_{1}}{r_{2}} = \sqrt{\frac{d_{2}}{d_{1}}} = \sqrt{\frac{M_{2}}{M_{1}}} = \frac{t_{2}}{t_{1}}}$ Kinetic Theory of Gases Pressure Equation: $P = \frac{1}{3}mnc^2$ Pattern Mapping Boyle and Charles' Combined Law: $T$ must be converted to Kelvin (K) . Ideal Gas Equation: Substitute $\frac{m}{M}$ (mass/molar mass) or $d V$ (density $\times$ volume) to find $M$ or $d$. Dalton's Law of Partial Pressures: Substitute $X_A = \frac{n_A}{n_{Total}}$ to find partial pressure. Graham's Law of Diffusion: Used to find unknown molar mass by comparing with a known gas. Error Analysis Units: Temperature ($T$): Must be in Kelvin . Gas constant ($R$): Value must be consistent with units of pressure and volume. Pressure conversion: $1 \text{ atm} \approx 101.325 \text{ kPa}$ or $1.01325 \times 10^5 \text{ Pa}$. Assumptions/Traps: STP vs SATP: STP: $0^{\circ}C$ and $1 \text{ atm}$. Molar volume $22.4 \text{ L/mol}$. SATP: $25^{\circ}C$ and $100 \text{ kPa}$. Molar volume $24.789 \text{ L/mol}$. 48-Hour Sheet High-Risk Error List: Failing to convert temperature from $^\circ C$ to K . Incorrectly using the value and units of $R$ for $K_p/K_c$ or $C_{rms}$ calculations. Using $\text{g}/\text{mol}$ (grams/mole) instead of $\text{kg}/\text{mol}$ (kilograms/mole) for molar mass in RMS speed calculations. Confusing STP and SATP conditions. Instant Recall Formula Block: $\mathbf{PV = nRT = \frac{mRT}{M} = \frac{dRT}{P}}$ $\mathbf{\frac{P_{1}V_{1}}{T_{1}} = \frac{P_{2}V_{2}}{T_{2}}}$ $\mathbf{C_{rms} = \sqrt{\frac{3RT}{M}}}$ $\mathbf{P_{A} = X_{A} P_{Total} \text{ where } X_A = \frac{n_A}{n_{Total}}}$ 2. Organic Chemistry Formula Extraction Alkanes (saturated) general formula: $C_nH_{2n+2}$ Alkenes (unsaturated) general formula: $C_nH_{2n}$ Alkynes (unsaturated) general formula: $C_nH_{2n-2}$ Alcohols (monohydric) general formula: $C_nH_{2n+1}OH$ Ethers general formula: $R - O - R'$ Carbocation/Carbanion stability order: $3^\circ > 2^\circ > 1^\circ$ (Carbocation) Free radical reactivity order: $1^\circ > 2^\circ > 3^\circ$ Alkyl halide nucleophilic substitution: $R-X + Z: \rightarrow R-Z + X^{-}$ Wurtz reaction: $2R - X + 2Na \xrightarrow{\text{dry ether}} R - R + 2NaX$ Wurtz-Fittig reaction: $Ar - X + 2Na + X - R \xrightarrow{\text{dry ether}} Ar - R + 2NaX$ Tautomerism (Keto-enol): $\text{CH}_3\text{COCH}_3 \rightleftharpoons \text{CH}_3\text{C}(\text{OH})=\text{CH}_2$ Haloform reaction (Ethanol): $\text{CH}_3\text{CH}_2\text{OH} + 4\text{I}_2 + 6\text{NaOH} \rightarrow \text{CHI}_3 + \text{HCOONa} + 5\text{Nal} + 5\text{H}_2\text{O}$ Cannizzaro reaction (Formaldehyde): $2\text{HCHO} \xrightarrow{50\%\text{ NaOH}} \text{CH}_3\text{OH} + \text{HCOONa}$ Polymerization (Polyethylene): $n(\text{CH}_2 = \text{CH}_2) \xrightarrow{1000-1200 \text{ atm}, 200^\circ C, O_2} [-\text{CH}_2 - \text{CH}_2 -]_n$ Hybridization: $X = \frac{1}{2} [\text{V}+\text{M}-\text{C}+\text{A}]$ Pattern Mapping General Formulas: Identify the class of compound (Alkane/Alkene/Alkyne) from the molecular formula. $S_N1/S_N2$ Reactions: Determine reaction rate based on the type of $R-X$. Wurtz/Wurtz-Fittig: Always produces alkanes or alkylbenzenes with an even number of carbons if $R$ and $R'$ are the same. Tautomerism: Keto form requires $\alpha$-hydrogen. Cannizzaro reaction: Reactants must lack $\alpha$-hydrogen. Hybridization: Calculate $X$ to determine the number of hybrid orbitals and shape (e.g., $X=4 \implies sp^3 \implies$ tetrahedral). Error Analysis Units: Not applicable, but pay attention to reaction temperature and catalyst conditions. Signs (+/-): Carbocation/Carbanion stability: Positive charged carbocation stability $3^\circ > 2^\circ > 1^\circ$. Assumptions/Traps: Cannizzaro/Aldol: Be careful with concentrated $\text{NaOH}$ (Cannizzaro) versus dilute $\text{NaOH}$ (Aldol). $\text{S}_{\text{N}}1$ vs $\text{S}_{\text{N}}2$: $3^\circ$ alkyl halides show $S_N1$ reaction and $1^\circ$ alkyl halides show $S_N2$. Alkyl halides: Aqueous $\text{KOH}$ vs alcoholic $\text{KOH}$ leads to substitution vs elimination. 48-Hour Sheet High-Risk Error List: Lucas Reagent test: $3^\circ$ alcohols give immediate turbidity, $1^\circ$ do not at room temperature. Haloform reaction: Only compounds with $\mathbf{\text{CH}_3\text{CO}-}$ or $\mathbf{\text{CH}_3\text{CH}(\text{OH})-}$ groups give positive test. Wurtz reaction: Produces mixed alkanes if different alkyl halides are used. Hybridization calculation: Do not neglect lone pair electrons. Instant Recall Formula Block: Polymer: $n(\text{monomer}) \rightarrow [-\text{Polymer}-]_n$ Haloform: $\text{CH}_3\text{C(O)R} + 3\text{I}_2 + 4\text{NaOH} \rightarrow \text{CHI}_3 \downarrow$ Isomerism: $2^n$ (Chiral C count) Hybridization: $X = \frac{1}{2} [\text{V}+\text{M}-\text{C}+\text{A}]$