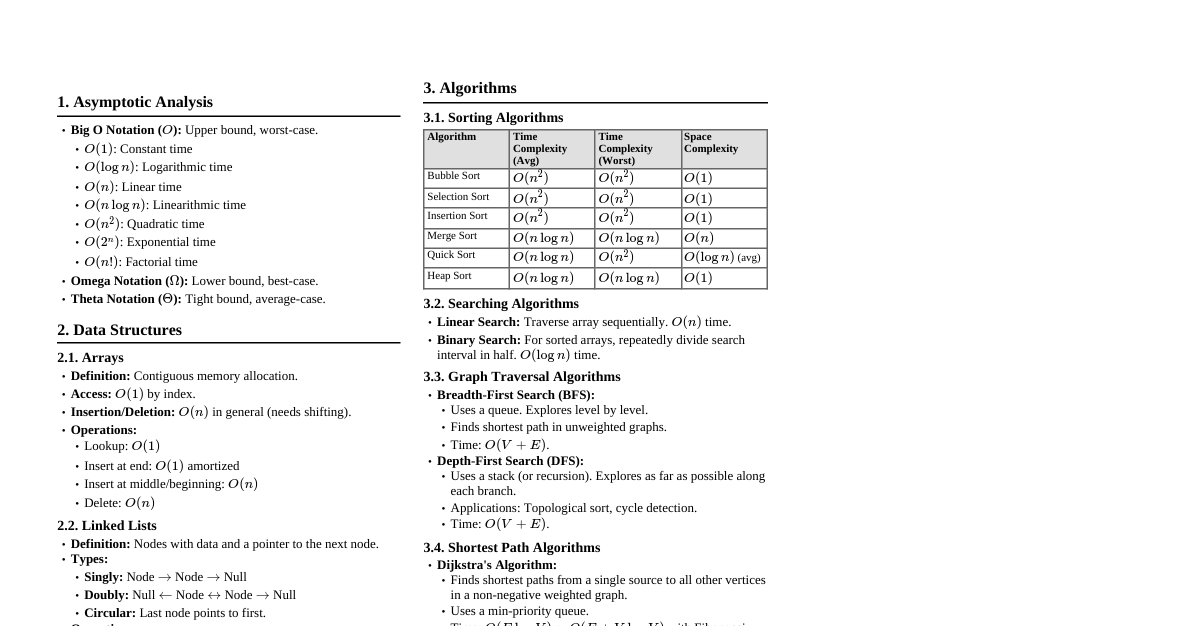
1. Asymptotic Analysis Big O Notation ($O$): Upper bound. $O(g(n))$ if $f(n) \le c \cdot g(n)$ for $n \ge n_0$. Big Omega Notation ($\Omega$): Lower bound. $\Omega(g(n))$ if $f(n) \ge c \cdot g(n)$ for $n \ge n_0$. Big Theta Notation ($\Theta$): Tight bound. $\Theta(g(n))$ if $c_1 \cdot g(n) \le f(n) \le c_2 \cdot g(n)$ for $n \ge n_0$. Common Complexities: $O(1) Space Complexity: Auxiliary space used by an algorithm. 2. Data Structures: Arrays & Strings Array: Contiguous memory allocation. $O(1)$ access, $O(n)$ insertion/deletion (shifting). Dynamic Array (ArrayList/Vector): Resizable array. Amortized $O(1)$ insertion. String: Immutable sequence of characters (often char array). Operations: Traversal, search, sort, reverse, substring, palindrome check. Techniques: Two pointers, sliding window, prefix sums. 3. Data Structures: Linked Lists Singly Linked List: Node (data, next). $O(1)$ insertion/deletion if prev known. $O(n)$ search. Doubly Linked List: Node (data, prev, next). $O(1)$ insertion/deletion if node known. Circular Linked List: Last node points to head. Operations: Insertion (head, tail, middle), deletion, traversal, reverse, cycle detection (Floyd's Tortoise and Hare). 4. Data Structures: Stacks & Queues Stack (LIFO): `push()`, `pop()`, `peek()`. Array or Linked List implementation. $O(1)$ for all. Queue (FIFO): `enqueue()`, `dequeue()`, `front()`. Array (circular) or Linked List implementation. $O(1)$ for all. Deque (Double-Ended Queue): Add/remove from both ends. Applications: Function call stack, expression evaluation, BFS (queue), DFS (stack/recursion), undo/redo. 5. Data Structures: Trees Tree: Hierarchical structure. Root, parent, child, leaf, depth, height. Binary Tree: Each node has at most two children. Binary Search Tree (BST): Left child Balanced BSTs (AVL, Red-Black Tree): Self-balancing, $O(\log n)$ for all operations. Traversal: Inorder (Left, Root, Right): Sorted output for BST. Preorder (Root, Left, Right): Used for copying/prefix expressions. Postorder (Left, Right, Root): Used for deleting/postfix expressions. Level Order (BFS): Using a queue. Heap (Priority Queue): Complete binary tree. Max-Heap (parent $\ge$ children), Min-Heap (parent $\le$ children). `insert()`, `deleteMax/Min()`: $O(\log n)$. `heapify()`: $O(n)$. Trie (Prefix Tree): Efficient for string prefix search. 6. Data Structures: Graphs Graph: Set of vertices (nodes) and edges. Directed/Undirected, Weighted/Unweighted. Representations: Adjacency Matrix: $A[i][j]=1$ if edge $(i,j)$ exists. $O(V^2)$ space. $O(1)$ edge check. Adjacency List: Array of linked lists. $O(V+E)$ space. $O(\text{deg}(V))$ edge check. Traversal: BFS (Breadth-First Search): Uses Queue. Finds shortest path in unweighted graphs. DFS (Depth-First Search): Uses Stack/Recursion. Detects cycles, topological sort. Topological Sort: Linear ordering of vertices for DAGs (Directed Acyclic Graphs). (Kahn's algorithm, DFS-based). Connected Components: Set of nodes where any two nodes are connected. Strongly Connected Components (SCC): For directed graphs (Kosaraju's, Tarjan's). 7. Algorithms: Sorting Comparison Sorts: Bubble Sort: $O(n^2)$ worst, $O(n^2)$ avg. Selection Sort: $O(n^2)$ worst, $O(n^2)$ avg. Insertion Sort: $O(n^2)$ worst, $O(n)$ best. Good for nearly sorted. Merge Sort: $O(n \log n)$ worst, $O(n \log n)$ avg. Stable. $O(n)$ space. Divide & Conquer. Quick Sort: $O(n^2)$ worst, $O(n \log n)$ avg. In-place (avg). Divide & Conquer. Heap Sort: $O(n \log n)$ worst, $O(n \log n)$ avg. In-place. Non-Comparison Sorts: Counting Sort: $O(n+k)$ for integers in range $[0, k]$. Stable. Radix Sort: $O(nk)$ for $n$ numbers with $k$ digits. Stable. Bucket Sort: $O(n^2)$ worst, $O(n+k)$ avg. (depends on distribution). 8. Algorithms: Searching Linear Search: $O(n)$ worst. Binary Search: $O(\log n)$ on sorted arrays. Ternary Search: $O(\log_3 n)$ for unimodal functions. Hashing: $O(1)$ average for search/insert/delete using hash tables. Worst case $O(n)$ (collisions). 9. Algorithms: Graph Algorithms Shortest Path: Dijkstra's Algorithm: Single source, non-negative weights. $O(E \log V)$ with min-priority queue. Bellman-Ford Algorithm: Single source, handles negative weights. Detects negative cycles. $O(VE)$. Floyd-Warshall Algorithm: All-pairs shortest path. $O(V^3)$. Minimum Spanning Tree (MST): Prim's Algorithm: $O(E \log V)$ with min-priority queue. Kruskal's Algorithm: $O(E \log E)$ with Disjoint Set Union. Cycle Detection: DFS for directed/undirected. BFS for undirected. Bipartite Check: BFS/DFS with 2-coloring. Flow Networks: Ford-Fulkerson, Edmonds-Karp. 10. Algorithms: Recursion & Backtracking Recursion: Function calls itself. Base case and recursive step. Tail Recursion: Optimization possible. Backtracking: Explores all potential solutions. If a path doesn't work, backtrack. Examples: N-Queens, Sudoku Solver, Permutations, Combinations, Subset Sum. Master Theorem: Solves recurrences of form $T(n) = aT(n/b) + f(n)$. 11. Algorithms: Dynamic Programming (DP) Principle: Overlapping subproblems and Optimal substructure. Techniques: Memoization (Top-down): Store results of expensive function calls. Tabulation (Bottom-up): Fill a table iteratively. Examples: Fibonacci, Longest Common Subsequence (LCS), Knapsack Problem, Coin Change, Edit Distance. 12. Algorithms: Greedy Algorithms Principle: Make locally optimal choices hoping to reach global optimum. Examples: Activity Selection Problem, Huffman Coding, Kruskal's/Prim's MST, Dijkstra's. Note: Not always optimal. Proof of correctness often required. 13. Bit Manipulation Operators: `&` (AND), `|` (OR), `^` (XOR), `~` (NOT), ` >` (Right Shift). Common Uses: Check $k$-th bit: `(num >> k) & 1` Set $k$-th bit: `num | (1 Clear $k$-th bit: `num & ~(1 Toggle $k$-th bit: `num ^ (1 Count set bits: Brian Kernighan's algorithm. Power of 2 check: `num > 0 && (num & (num - 1)) == 0` 14. Disjoint Set Union (DSU) / Union-Find Operations: `find(i)`: Returns representative of set containing $i$. `union(i, j)`: Merges sets containing $i$ and $j$. Optimizations: Path Compression (for `find`), Union by Rank/Size (for `union`). Complexity: Nearly constant time (inverse Ackermann function $\alpha(n)$). Applications: Kruskal's MST, connected components, cycle detection in undirected graphs. 15. Advanced Topics & Techniques Segment Tree: Range queries (sum, min, max) and point/range updates in $O(\log n)$. Fenwick Tree (BIT): Prefix sum queries and point updates in $O(\log n)$. Sliding Window Maximum (Deque): Find max/min in all subarrays of size $k$ in $O(n)$. Two Pointers: Efficiently iterate through arrays/lists (e.g., sorted array pair sum). Meet-in-the-Middle: Optimization for exponential problems by splitting into two halves. Manacher's Algorithm: Finds longest palindromic substring in $O(n)$. Rabin-Karp Algorithm: String matching using hashing. $O(m+n)$ average. KMP Algorithm: String matching using LPS array. $O(m+n)$ worst.