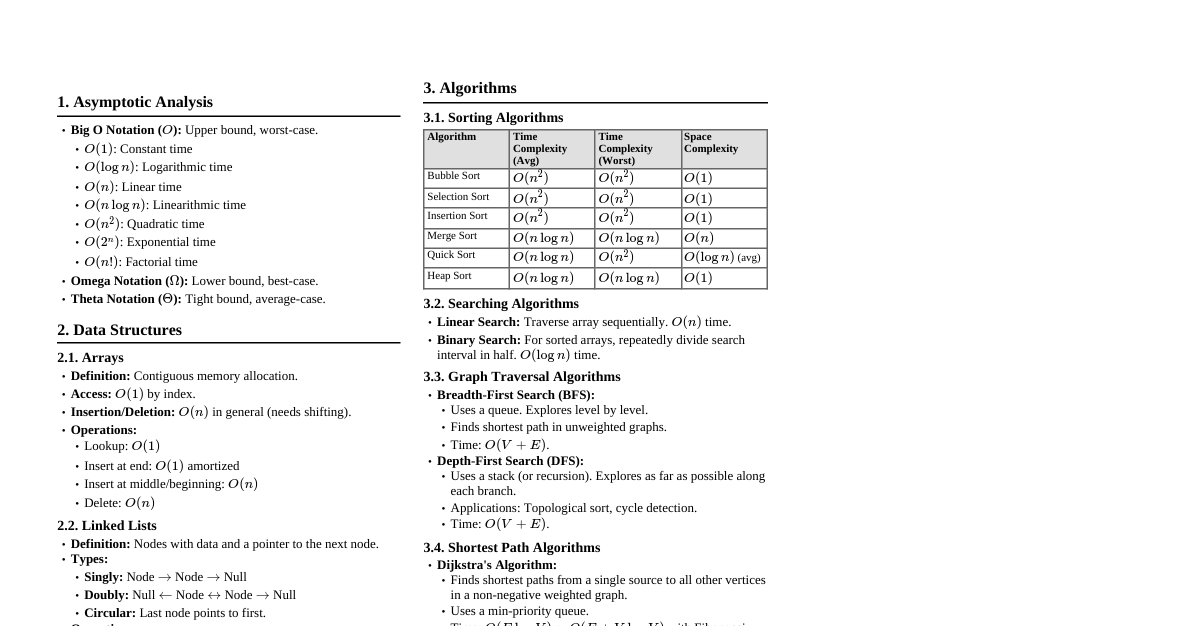
1. Asymptotic Analysis Big O Notation: Upper bound, worst-case. $O(g(n))$ if $f(n) \le c \cdot g(n)$ for $n \ge n_0$. Omega Notation: Lower bound, best-case. $\Omega(g(n))$ if $f(n) \ge c \cdot g(n)$ for $n \ge n_0$. Theta Notation: Tight bound, average-case. $\Theta(g(n))$ if $c_1 \cdot g(n) \le f(n) \le c_2 \cdot g(n)$ for $n \ge n_0$. Common Complexities: $O(1) 2. Arrays Definition: Contiguous memory allocation. Access: $O(1)$ by index. Insertion/Deletion: $O(n)$ in worst case (shifting elements). Dynamic Arrays (ArrayList/Vector): Resizes when capacity is full, $O(n)$ amortized $O(1)$ for append. 3. Linked Lists Singly Linked List: Node with data and `next` pointer. Insertion/Deletion: $O(1)$ if pointer to previous node is available, else $O(n)$. Search: $O(n)$. Doubly Linked List: Node with data, `next`, and `prev` pointers. Insertion/Deletion: $O(1)$ given the node. Circular Linked List: Last node points to first. 4. Stacks & Queues Stack (LIFO): Operations: `push()`, `pop()`, `peek()` - all $O(1)$. Applications: Function call stack, undo/redo, expression evaluation. Queue (FIFO): Operations: `enqueue()`, `dequeue()`, `front()` - all $O(1)$. Applications: BFS, print spooling, task scheduling. 5. Trees Binary Tree: Each node has at most two children. Binary Search Tree (BST): Left child $\le$ parent $\le$ right child. Search, Insertion, Deletion: $O(h)$ where $h$ is height. $O(\log n)$ average, $O(n)$ worst case. Balanced BSTs (AVL, Red-Black Trees): Maintain $O(\log n)$ height. Heaps (Priority Queue): Complete binary tree satisfying heap property. Max-Heap: parent $\ge$ children. Min-Heap: parent $\le$ children. `insert()`, `deleteMax/Min()`: $O(\log n)$. `peekMax/Min()`: $O(1)$. Trie (Prefix Tree): For efficient string retrieval. 6. Graphs Representation: Adjacency Matrix: $O(V^2)$ space. Check edge $O(1)$. Adjacency List: $O(V+E)$ space. Check edge $O(\deg(V))$. Traversal: BFS (Breadth-First Search): Uses Queue. Finds shortest path in unweighted graphs. $O(V+E)$. DFS (Depth-First Search): Uses Stack (or recursion). $O(V+E)$. Applications: Cycle detection, topological sort, connectivity. Minimum Spanning Tree (MST): Prim's Algorithm: $O(E \log V)$ with Fibonacci heap, $O(E \log V)$ with binary heap. Kruskal's Algorithm: $O(E \log E)$ or $O(E \log V)$ with Disjoint Set Union. Shortest Path: Dijkstra's Algorithm (non-negative weights): $O(E \log V)$ with binary heap. Bellman-Ford Algorithm (can handle negative weights): $O(VE)$. Detects negative cycles. Floyd-Warshall Algorithm (all-pairs shortest path): $O(V^3)$. Topological Sort: For DAGs. $O(V+E)$. 7. Hashing Hash Function: Maps keys to indices. Collision Resolution: Separate Chaining: Linked lists at each index. Open Addressing: Linear probing, quadratic probing, double hashing. Hash Table (Map/Dictionary): Average $O(1)$ for insert, delete, search. Worst $O(n)$. Applications: Caching, unique element lookup. 8. Sorting Algorithms Comparison Sorts (Lower Bound $\Omega(n \log n)$): Merge Sort: $O(n \log n)$ time, $O(n)$ space. Stable. Heap Sort: $O(n \log n)$ time, $O(1)$ space. Unstable. Quick Sort: $O(n \log n)$ average, $O(n^2)$ worst. $O(\log n)$ space average. Unstable. Non-Comparison Sorts: Counting Sort: $O(n+k)$ time, $O(n+k)$ space. For integers in range $[0, k]$. Stable. Radix Sort: $O(d(n+k))$ time. For integers with $d$ digits. Stable. Bucket Sort: $O(n+k)$ average. Divides into buckets, sorts each. 9. Searching Algorithms Linear Search: $O(n)$ time. For unsorted arrays. Binary Search: $O(\log n)$ time. For sorted arrays. Ternary Search: $O(\log_3 n)$ time. For unimodal functions. 10. Dynamic Programming Principle: Solve subproblems once and store solutions (memoization or tabulation). Properties: Optimal substructure, overlapping subproblems. Steps: Identify subproblems. Define recurrence relation. Identify base cases. Decide order of computation (memoization top-down, tabulation bottom-up). Examples: Fibonacci, Knapsack, Longest Common Subsequence. 11. Greedy Algorithms Principle: Make locally optimal choices hoping to reach global optimum. Properties: Optimal substructure, greedy choice property. Examples: Dijkstra's, Prim's, Kruskal's, Activity Selection. 12. Backtracking & Branch & Bound Backtracking: Explores all potential solutions incrementally. If a path doesn't lead to a solution, backtrack. Examples: N-Queens, Sudoku Solver, Permutations. Branch & Bound: Optimization technique for combinatorial problems. Prunes branches that cannot lead to an optimal solution. 13. Disjoint Set Union (DSU) Operations: `makeSet(x)`: Creates a new set containing $x$. `find(x)`: Returns representative of set containing $x$. (Path compression for optimization) `union(x, y)`: Merges sets containing $x$ and $y$. (Union by rank/size for optimization) Complexity: Nearly constant amortized time, $O(\alpha(n))$ where $\alpha$ is inverse Ackermann function. Applications: Kruskal's MST, connected components. 14. String Algorithms Rabin-Karp: Uses hashing for pattern matching. Average $O(m+n)$, worst $O(mn)$. KMP (Knuth-Morris-Pratt): Uses LPS array to avoid re-matching characters. $O(m+n)$. Z-Algorithm: Finds all occurrences of a pattern in a text. $O(m+n)$. Manacher's Algorithm: Finds longest palindromic substring in $O(n)$. 15. Bit Manipulation AND (`&`): $x \& 1$ checks if $x$ is odd. OR (`|`): Sets a bit. XOR (`^`): Swaps numbers without temp, finds unique number. NOT (`~`): Flips bits. Left Shift (` $x Right Shift (`>>`): $x >> k$ is $x / 2^k$ (integer division). Set $k$-th bit: $num | (1 Clear $k$-th bit: $num \& \sim(1 Toggle $k$-th bit: $num \oplus (1