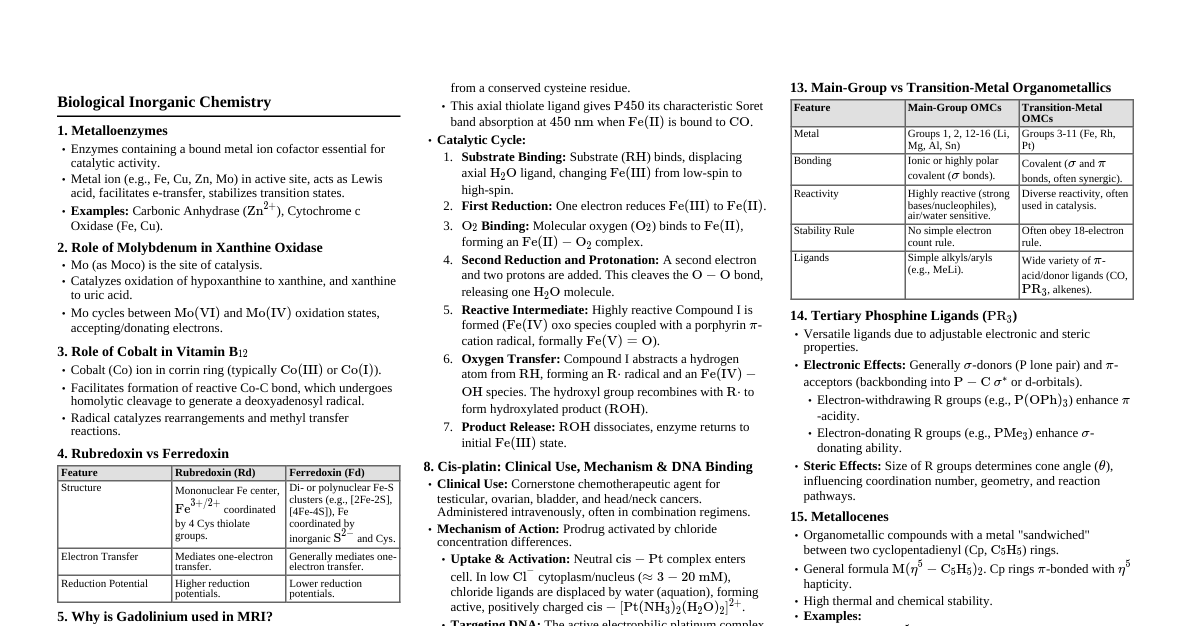
### Foundation and Fundamentals - **Chemistry:** Study of matter's composition, properties, and reactions. - **Basic Concepts:** - **Atoms:** Smallest unit of an element. - **Molecules:** Two or more atoms bonded together. - **Relative Atomic/Molecular Mass:** Mass relative to a standard (carbon-12). - **Atomic Mass Unit (amu):** $1/12$th the mass of a carbon-12 atom. - **Radicals:** A group of atoms with an unpaired electron. - **Molecular Formula:** Shows actual number of atoms of each element. - **Empirical Formula:** Simplest whole-number ratio of atoms in a compound. - **Percentage Composition:** $$\%\text{ Element} = \frac{\text{mass of element in compound}}{\text{molecular mass of compound}} \times 100$$ ### Stoichiometry - **Dalton's Atomic Theory:** 1. Elements are made of atoms. 2. Atoms of same element are identical. 3. Atoms cannot be created/destroyed. 4. Atoms combine in whole-number ratios. - **Laws of Stoichiometry:** Law of Conservation of Mass, Law of Definite Proportions, Law of Multiple Proportions. - **Avogadro's Law:** Equal volumes of gases at same T & P contain equal number of molecules. - **Deductions:** Molecular mass and vapor density ($M = 2 \times VD$), Molecular mass and volume of gas (1 mole = 22.4 L at STP), Molecular mass and number of particles (1 mole = $6.022 \times 10^{23}$ particles). - **Mole Concept:** - **Mole:** The amount of substance containing Avogadro's number of particles ($6.022 \times 10^{23}$). - **Relation:** Mass (g) = Moles $\times$ Molar Mass (g/mol); Volume (L) = Moles $\times$ 22.4 L (at STP); Number of particles = Moles $\times N_A$. - **Limiting Reactant:** Reactant completely consumed, determines max product. - **Excess Reactant:** Reactant left over after reaction. - **Yields:** - **Theoretical Yield:** Max product calculated from stoichiometry. - **Experimental Yield:** Actual product obtained in experiment. - **% Yield:** $(\text{Experimental Yield} / \text{Theoretical Yield}) \times 100$. - **Empirical/Molecular Formula from % Composition:** 1. Assume 100g sample. 2. Convert % to grams. 3. Convert grams to moles. 4. Divide by smallest mole value to get empirical formula ratio. 5. Calculate empirical formula mass. 6. Molecular Formula = $( \text{Empirical Formula} )_n$ where $n = \text{Molecular Mass} / \text{Empirical Formula Mass}$. ### Atomic Structure - **Rutherford's Atomic Model:** - Atom has a small, dense, positively charged nucleus. - Electrons orbit the nucleus. - **Limitations:** Could not explain stability of atom or atomic spectra. - **Bohr's Atomic Model Postulates:** 1. Electrons orbit in specific, quantized energy levels (stationary states). 2. Electrons do not radiate energy in these orbits. 3. Energy is absorbed/emitted when electrons move between levels ($E = h\nu$). - **Hydrogen Spectrum:** Explained by electron transitions between Bohr's energy levels. - **Defects of Bohr's Theory:** - Only worked for H-like atoms. - Could not explain fine structure of spectra or Zeeman/Stark effect. - **Elementary Quantum Mechanical Model:** - **de Broglie's Wave Equation:** $\lambda = h/mv$ (matter has wave-like properties). - **Heisenberg's Uncertainty Principle:** Cannot simultaneously know exact position and momentum of a particle. - **Concept of Probability:** Electron location described by probability distributions (orbitals). - **Quantum Numbers:** Describe electron state. - **Principal ($n$):** Energy level (1, 2, 3...). - **Azimuthal ($l$):** Subshell and shape (0 to $n-1$; $s, p, d, f$). - **Magnetic ($m_l$):** Orientation of orbital ($-l$ to $+l$). - **Spin ($m_s$):** Electron spin ($\pm 1/2$). - **Orbitals:** - **s-orbital:** Spherical. - **p-orbital:** Dumbbell-shaped (3 orientations: $p_x, p_y, p_z$). - **Electron Configuration Rules:** - **Aufbau Principle:** Fill lowest energy orbitals first. - **Pauli's Exclusion Principle:** Max 2 electrons per orbital, with opposite spins. - **Hund's Rule:** Fill degenerate orbitals singly with parallel spins before pairing. - **Electronic Configurations:** Up to atomic number 30. - Example: $C: 1s^2 2s^2 2p^2$, $Fe: [Ar] 4s^2 3d^6$. ### Classification of Elements and Periodic Table - **Modern Periodic Law:** Properties of elements are periodic functions of their atomic number. - **Modern Periodic Table:** Arranges elements by increasing atomic number. - **Classification:** - **Groups (Columns):** Similar chemical properties (due to same valence electrons). - **Periods (Rows):** Number of electron shells. - **Blocks (s, p, d, f):** Based on orbital being filled. - **IUPAC Classification:** Groups 1-18. - **Nuclear Charge:** Number of protons in the nucleus. - **Effective Nuclear Charge ($Z_{eff}$):** Net positive charge experienced by valence electrons. - **Periodic Trend and Periodicity:** - **Atomic Radii:** Decreases across a period (increased $Z_{eff}$), increases down a group (new shells). - **Ionic Radii:** Cations smaller than parent atom, anions larger. Trends similar to atomic radii. - **Ionization Energy:** Energy required to remove an electron. Increases across a period, decreases down a group. - **Electron Affinity:** Energy change when an electron is added. Generally increases across a period. - **Electronegativity:** Atom's ability to attract electrons in a bond. Increases across a period, decreases down a group. - **Metallic Characters:** Decreases across a period, increases down a group. ### Chemical Bonding and Shapes of Molecules - **Valence Shell:** Outermost electron shell. - **Valence Electrons:** Electrons in the valence shell. - **Octet Theory:** Atoms tend to gain, lose, or share electrons to achieve 8 valence electrons. - **Ionic Bond:** Electrostatic attraction between oppositely charged ions (metal + nonmetal). - **Properties:** High melting/boiling points, soluble in polar solvents, conducts electricity when molten/dissolved. - **Covalent Bond:** Sharing of electrons between two nonmetal atoms. - **Coordinate Covalent Bond (Dative Bond):** One atom provides both shared electrons. - **Properties of Covalent Compounds:** Lower melting/boiling points, less soluble in water, poor conductors. - **Lewis Dot Structure:** Diagram showing valence electrons and bonds. - **Resonance:** Delocalization of electrons, represented by multiple Lewis structures. - **VSEPR Theory (Valence Shell Electron Pair Repulsion):** Electron pairs repel each other, determining molecular geometry. - **Shapes:** - BeF$_2$: Linear - BF$_3$: Trigonal Planar - CH$_4$: Tetrahedral - CH$_3$Cl: Tetrahedral (distorted) - PCl$_5$: Trigonal Bipyramidal - SF$_6$: Octahedral - H$_2$O: Bent - NH$_3$: Trigonal Pyramidal - CO$_2$: Linear - H$_2$S: Bent - PH$_3$: Trigonal Pyramidal - **Valence Bond Theory (Elementary Idea):** Covalent bonds form by overlap of atomic orbitals. - **Hybridization (s and p orbitals):** Mixing of atomic orbitals to form new hybrid orbitals. - $sp$ (linear), $sp^2$ (trigonal planar), $sp^3$ (tetrahedral). - **Bond Characteristics:** - **Bond Length:** Distance between nuclei of two bonded atoms. - **Ionic Character:** Degree of polarity in a covalent bond. - **Dipole Moment:** Measure of net molecular polarity. - **Intermolecular Forces:** - **Van der Waals Forces:** Weak attractive forces (London dispersion, dipole-dipole). - **Molecular Solids:** Held by weak intermolecular forces. - **Hydrogen Bonding:** Strong dipole-dipole attraction involving H bonded to F, O, or N. - **Metallic Bonding:** Delocalized electrons shared among a lattice of metal ions. - **Properties of Metallic Solids:** Good conductors, malleable, ductile, lustrous. ### Oxidation and Reduction - **General Concept:** - **Oxidation:** Gain of oxygen, loss of hydrogen, loss of electrons. - **Reduction:** Loss of oxygen, gain of hydrogen, gain of electrons. - **Electronic Concept:** - **Oxidation:** Loss of electrons (increase in oxidation number). - **Reduction:** Gain of electrons (decrease in oxidation number). - **Oxidation Number:** Hypothetical charge an atom would have if all bonds were ionic. - **Rules:** Assign based on electronegativity, common values for elements, sum equals overall charge. - **Balancing Redox Reactions:** - **Oxidation Number Method:** Track changes in oxidation numbers. - **Ion-Electron (Half-Reaction) Method:** Separate into oxidation and reduction half-reactions, balance atoms and charge. - **Electrolysis:** Chemical change driven by electrical energy. - **Qualitative Aspect:** Predicting products at electrodes. - **Quantitative Aspect (Faraday's Laws):** 1. Mass of substance deposited is proportional to charge passed. 2. Masses of different substances deposited by same charge are proportional to their equivalent masses. $$m = \frac{ItE}{F}$$ where $m$ = mass, $I$ = current, $t$ = time, $E$ = equivalent weight, $F$ = Faraday constant ($96485 \text{ C/mol e}^-$). ### States of Matter #### Gaseous State - **Kinetic Theory of Gas Postulates:** 1. Gases consist of tiny particles in constant, random motion. 2. Volume of particles negligible compared to container volume. 3. No intermolecular forces. 4. Collisions are elastic. 5. Average kinetic energy $\propto$ absolute temperature. - **Gas Laws:** - **Boyle's Law:** $P_1V_1 = P_2V_2$ (constant T, n). - **Charles' Law:** $V_1/T_1 = V_2/T_2$ (constant P, n). - **Avogadro's Law:** $V_1/n_1 = V_2/n_2$ (constant T, P). - **Combined Gas Equation:** $(P_1V_1)/T_1 = (P_2V_2)/T_2$. - **Dalton's Law of Partial Pressure:** $P_{total} = P_1 + P_2 + ...$ - **Graham's Law of Diffusion:** $rate_1/rate_2 = \sqrt{M_2/M_1}$. - **Ideal Gas Equation:** $PV = nRT$. - **Universal Gas Constant (R):** $0.0821 \text{ L atm/mol K}$ or $8.314 \text{ J/mol K}$. - **Deviation of Real Gas from Ideality:** Occurs at high pressure and low temperature (intermolecular forces and finite particle volume become significant). #### Liquid State - **Physical Properties of Liquids:** - **Evaporation:** Liquid to gas below boiling point. - **Condensation:** Gas to liquid. - **Vapor Pressure:** Pressure exerted by vapor in equilibrium with liquid. - **Boiling Point:** Temperature where vapor pressure equals external pressure. - **Surface Tension:** Force acting on surface of liquid, minimizing surface area. - **Viscosity:** Resistance to flow. - **Liquid Crystals:** States of matter with properties between conventional liquids and solid crystals. #### Solid State - **Types of Solids:** - **Amorphous Solids:** Disordered structure (e.g., glass). - **Crystalline Solids:** Ordered, repeating lattice structure. - **Efflorescent Solids:** Lose water of hydration to atmosphere. - **Deliquescent Solids:** Absorb moisture from atmosphere to form solution. - **Hygroscopic Solids:** Absorb moisture without forming solution. - **Crystallization:** Process of forming crystals. - **Water of Crystallization:** Water molecules incorporated into crystal structure. - **Unit Crystal Lattice:** 3D arrangement of lattice points. - **Unit Cell:** Smallest repeating unit of a crystal lattice. ### Chemical Equilibrium - **Physical Equilibrium:** Equilibrium between different physical states (e.g., liquid-vapor). - **Chemical Equilibrium:** State where forward and reverse reaction rates are equal, and net change in reactant/product concentrations is zero. - **Dynamic Nature:** Reactions still occur, but at equal rates. - **Law of Mass Action:** For $aA + bB \rightleftharpoons cC + dD$, rate $\propto [A]^a[B]^b$. - **Equilibrium Constant ($K_c$ for concentrations, $K_p$ for partial pressures):** $$K_c = \frac{[C]^c[D]^d}{[A]^a[B]^b}$$ - **Importance:** Indicates extent of reaction (large K = favors products, small K = favors reactants). - **Relationship between $K_p$ and $K_c$:** $$K_p = K_c (RT)^{\Delta n}$$ where $\Delta n$ = (moles of gaseous products) - (moles of gaseous reactants). - **Le Chatelier's Principle:** If a change of condition is applied to a system in equilibrium, the system will shift in a direction that relieves the stress. - **Factors:** Concentration, pressure (for gases), temperature. ### Chemistry of Non-metals #### Hydrogen, Oxygen and Ozone - **Hydrogen:** - **Atomic Hydrogen:** Highly reactive. - **Nascent Hydrogen:** Atomic hydrogen generated in situ. - **Isotopes:** Protium ($^1$H), Deuterium ($^2$H), Tritium ($^3$H). - **Uses:** Fuel, reducing agent, in synthesis of ammonia. - **Heavy Water (D$_2$O):** Used as moderator in nuclear reactors. - **Oxygen:** - **Allotropes:** Different structural forms of an element (e.g., O$_2$, O$_3$). - **Types of Oxides:** - **Acidic:** Nonmetal oxides (e.g., CO$_2$, SO$_2$). - **Basic:** Metal oxides (e.g., Na$_2$O, CaO). - **Neutral:** (e.g., CO, NO). - **Amphoteric:** Reacts with both acids and bases (e.g., Al$_2$O$_3$, ZnO). - **Peroxide:** Contains O$_2^{2-}$ (e.g., H$_2$O$_2$). - **Mixed:** Contains two simple oxides (e.g., Pb$_3$O$_4$). - **Hydrogen Peroxide (H$_2$O$_2$):** Oxidizing agent, bleaching agent, antiseptic. - **Applications of Oxygen:** Respiration, combustion, steel production. - **Ozone (O$_3$):** - **Occurrence:** Stratosphere (ozone layer). - **Preparation:** $3O_2 \xrightarrow{\text{electric discharge}} 2O_3$. - **Structure:** Bent, resonant structure. - **Test:** Turns starch iodide paper blue-black. - **Ozone Layer Depletion:** - **Causes:** CFCs, halons. - **Effects:** Increased UV radiation, skin cancer, crop damage. - **Control Measures:** Montreal Protocol (phasing out ODS). - **Uses:** Disinfectant, bleaching agent. #### Nitrogen - **Inertness of Nitrogen:** Due to strong triple bond in N$_2$. - **Active Nitrogen:** Highly reactive atomic nitrogen. - **Ammonia (NH$_3$) Chemical Properties:** - With CuSO$_4$: Forms deep blue complex $[Cu(NH_3)_4]^{2+}$. - With water: Weak base ($NH_3 + H_2O \rightleftharpoons NH_4^+ + OH^-$). - With FeCl$_3$: Forms Fe(OH)$_3$ precipitate. - With conc. HCl: Forms dense white fumes of NH$_4$Cl. - With mercurous nitrate paper: Turns black (detection). - With O$_2$: Burns to form N$_2$ and H$_2$O (or NO with catalyst). - **Applications of Ammonia:** Fertilizers, nitric acid production, refrigerants. - **Harmful Effects:** Respiratory irritant. - **Oxy-acids of Nitrogen:** Nitrous acid (HNO$_2$), Nitric acid (HNO$_3$). - **Nitric Acid (HNO$_3$) Chemical Properties:** - **As an acid:** Reacts with bases/metals (e.g., $Zn + 2HNO_3 \rightarrow Zn(NO_3)_2 + H_2$). - **As an oxidizing agent:** Reacts with metals (Zn, Mg, Fe, Cu), nonmetals (S, C), and reducing agents (SO$_2$, H$_2$S) producing NO$_2$, NO, or N$_2$. - **Ring Test for Nitrate Ion:** Brown ring at interface of conc. H$_2$SO$_4$ layer and solution containing nitrate and FeSO$_4$. #### Halogens (Cl$_2$, Br$_2$, I$_2$) - **General Characteristics:** Highly reactive nonmetals, form salts, high electronegativity. - **Comparative Study on Preparation:** (No diagram/description) - **Chemical Properties:** - **With water:** Form hydrohalic and hypohalous acids ($Cl_2 + H_2O \rightleftharpoons HCl + HOCl$). - **With alkali:** Form halides and hypohalites/halates. - **With ammonia:** Reacts to form N$_2$ and NH$_4$X. - **Oxidizing Character:** Decreases down the group (Cl > Br > I). - **Bleaching Action:** Due to formation of nascent oxygen (e.g., HOCl). - **Uses:** Disinfectants, bleaches, organic synthesis. - **Test for Cl$_2$, Br$_2$, I$_2$:** - Cl$_2$: Turns moist starch iodide paper blue/black. - Br$_2$: Decolorizes KI solution. - I$_2$: Turns starch solution blue/black. - **Haloacids (HCl, HBr, HI) Comparative Study:** - **Preparation:** (No diagram/description) - **Properties:** - **Reducing Strength:** Increases down the group (HI > HBr > HCl). - **Acidic Nature:** Increases down the group (HI > HBr > HCl). - **Solubility:** Highly soluble in water. - **Uses:** Strong acids, reducing agents. #### Carbon and Phosphorus - **Carbon:** - **Allotropes:** - **Crystalline:** Diamond, graphite, fullerenes (C$_{60}$, structure, properties, uses). - **Amorphous:** Coal, charcoal, coke. - **Carbon Monoxide (CO) Properties:** - **Reducing Action:** Reduces metal oxides (e.g., $Fe_2O_3 + 3CO \rightarrow 2Fe + 3CO_2$). - **Reaction with metals/nonmetals:** Forms carbonyls/carbides. - **Uses:** Fuel, reducing agent in metallurgy. - **Phosphorus:** - **Allotropes:** White, Red, Black phosphorus. - **Phosphine (PH$_3$) Preparation:** (No diagram/description) - **Properties:** - **Basic Nature:** Weak base, forms phosphonium salts. - **Reducing Nature:** Reduces metal salts. - **Action with halogens:** Forms PX$_3$ and PX$_5$. - **Action with oxygen:** Burns to form P$_4$O$_{10}$. - **Uses:** Fumigant, signal flares. #### Sulphur - **Allotropes of Sulphur:** Rhombic (alpha), Monoclinic (beta), Plastic. - **Uses of Sulphur:** Sulphuric acid production, vulcanization of rubber, fungicides. - **Hydrogen Sulphide (H$_2$S):** - **Preparation (Kipp's apparatus):** FeS + H$_2$SO$_4 \rightarrow FeSO_4 + H_2S$. - **Properties:** - **Acidic Nature:** Weak acid, forms sulphides. - **Reducing Nature:** Easily oxidized to S. - **Analytical Reagent:** Precipitates metal sulphides. - **Uses:** Analytical reagent. - **Sulphur Dioxide (SO$_2$) Properties:** - **Acidic Nature:** Forms sulphurous acid ($SO_2 + H_2O \rightleftharpoons H_2SO_3$). - **Reducing Nature:** Reduces oxidizing agents (e.g., K$_2$Cr$_2$O$_7$). - **Oxidizing Nature:** Oxidizes strong reducing agents (e.g., H$_2$S). - **Bleaching Action:** Temporary bleaching of delicate fabrics. - **Uses:** Preservative, bleaching agent, SO$_3$ production. - **Sulphuric Acid (H$_2$SO$_4$) Properties:** - **Acidic Nature:** Strong diprotic acid. - **Oxidizing Nature:** Oxidizes metals and nonmetals (hot, conc. H$_2$SO$_4$). - **Dehydrating Nature:** Removes water from compounds (e.g., sugars). - **Uses:** Fertilizers, detergents, dyes, dehydrating agent. - **Sodium Thiosulphate (Na$_2$S$_2$O$_3$):** Used in photography (fixer) and as an anti-chlor. ### Chemistry of Metals #### Metals and Metallurgical Principles - **Metallurgy:** Science and technology of extracting metals from their ores. - **Hydrometallurgy:** Extraction using aqueous solutions. - **Pyrometallurgy:** Extraction using high temperatures. - **Electrometallurgy:** Extraction using electrolysis. - **Ores:** Naturally occurring minerals from which metals can be profitably extracted. - **Gangue/Matrix:** Unwanted earthy impurities in ore. - **Flux:** Substance added to remove gangue (forms slag). - **Slag:** Fusible product formed by reaction of flux with gangue. - **Alloy:** Mixture of two or more metals (or metal + nonmetal). - **Amalgam:** Alloy of mercury with another metal. - **General Principles of Extraction:** 1. **Concentration (Beneficiation):** Removal of gangue (e.g., gravity separation, froth flotation, magnetic separation, leaching). 2. **Calcination:** Heating ore in absence of air (removes volatile impurities, decomposes carbonates/hydroxides). 3. **Roasting:** Heating ore in presence of air (converts sulfides to oxides). 4. **Smelting:** Heating ore with reducing agent and flux to obtain molten metal. 5. **Reduction:** - **Carbon Reduction:** Using C or CO (e.g., Fe). - **Thermite Reduction:** Using Al powder (e.g., Cr, Mn). - **Electrochemical Reduction:** Electrolysis (e.g., Al, Na). - **Refining of Metals:** Purification of crude metal. - **Poling:** For metals containing oxides (e.g., Cu, Sn). - **Electro-refinement:** Electrolysis for high purity (e.g., Cu, Ag, Au). #### Alkali and Alkaline Earth Metals - **Alkali Metals (Group 1):** - **General Characteristics:** Highly reactive, low ionization energy, soft, low density, form +1 ions, basic oxides. - **Sodium (Na):** - **Extraction:** Down's process (electrolysis of molten NaCl). - **Properties:** - Action with O$_2$: Forms Na$_2$O, Na$_2$O$_2$. - Action with water: Reacts vigorously to form NaOH and H$_2$. - Action with acids: Reacts vigorously to form salt and H$_2$. - Action with nonmetals: Forms halides, sulfides. - Action with NH$_3$: Forms sodamide (NaNH$_2$). - **Uses:** Coolant in reactors, street lamps. - **Sodium Hydroxide (NaOH) Properties:** - **Precipitation Reactions:** Precipitates metal hydroxides. - **Action with CO:** No direct reaction, but used in some CO-related processes. - **Uses:** Soap, paper, rayon industries. - **Sodium Carbonate (Na$_2$CO$_3$) Properties:** - **Action with CO$_2$:** Forms NaHCO$_3$. - **Action with SO$_2$:** Forms Na$_2$SO$_3$. - **Action with water:** Hydrolyzes to give alkaline solution. - **Precipitation Reactions:** Precipitates metal carbonates. - **Uses:** Glass, soap, detergents. - **Alkaline Earth Metals (Group 2):** - **General Characteristics:** Reactive, higher ionization energy than alkali metals, harder, denser, form +2 ions, basic oxides. - **Molecular Formula and Uses:** - Quick lime (CaO): Cement. - Bleaching powder (CaOCl$_2$): Bleaching agent, disinfectant. - Magnesia (MgO): Refractory material, antacid. - Plaster of Paris (CaSO$_4 \cdot 1/2 H_2O$): Casts, plastering. - Epsom salt (MgSO$_4 \cdot 7 H_2O$): Laxative. - **Solubility of Hydroxides, Carbonates, Sulphates:** - **Hydroxides:** Solubility increases down the group ($Mg(OH)_2$ sparingly soluble, $Ba(OH)_2$ more soluble). - **Carbonates:** Solubility decreases down the group. - **Sulphates:** Solubility decreases down the group ($BaSO_4$ insoluble). - **Stability of Carbonates and Nitrates:** - **Thermal stability:** Increases down the group (larger cation polarizes anion less). ### Bio-inorganic Chemistry - **Introduction:** Study of the role of metals in biological systems. - **Micro and Macro Nutrients:** - **Macronutrients:** Needed in large amounts (e.g., Na, K, Mg, Ca). - **Micronutrients:** Needed in trace amounts (e.g., Fe, Cu, Zn, Ni, Co, Cr). - **Importance of Metal Ions in Biological Systems:** - **Na, K:** Nerve impulse transmission, osmotic balance. - **Mg:** Chlorophyll, enzyme cofactor. - **Ca:** Bones, teeth, blood clotting, muscle contraction. - **Fe:** Hemoglobin (oxygen transport), enzyme cofactor. - **Cu:** Enzyme cofactor, electron transport. - **Zn:** Enzyme cofactor, immune function. - **Ni, Co, Cr:** Enzyme cofactors. - **Ion Pumps:** - **Sodium-Potassium Pump:** Maintains Na$^+$ and K$^+$ gradients across cell membranes, vital for nerve/muscle function. - **Sodium-Glucose Pump:** Co-transports Na$^+$ and glucose into cells. - **Metal Toxicity:** - **Iron:** Hemochromatosis (iron overload). - **Arsenic:** Multiple organ failure, cancer. - **Mercury:** Neurotoxicity, kidney damage. - **Lead:** Neurotoxicity, developmental issues. - **Cadmium:** Kidney damage, bone issues. ### Basic Concept of Organic Chemistry - **Introduction:** Chemistry of carbon compounds. - **Reasons for Separate Study:** - **Tetra-covalency of Carbon:** Forms four bonds. - **Catenation:** Ability of carbon atoms to form long chains and rings with themselves. - Vast number and diversity of organic compounds. - **Classification of Organic Compounds:** Aliphatic, aromatic, alicyclic, heterocyclic. - **Alkyl Groups:** Alkane minus one hydrogen (e.g., methyl, ethyl). - **Functional Groups:** Atom or group of atoms responsible for characteristic chemical properties (e.g., -OH, -COOH). - **Homologous Series:** Series of compounds with same functional group, similar chemical properties, and gradual change in physical properties. - **Structural Formula:** Shows arrangement of all atoms and bonds. - **Contracted Formula:** Abbreviated representation (e.g., CH$_3$CH$_2$CH$_3$). - **Bond Line Structural Formula:** Carbon atoms at vertices/ends, hydrogens implied. - **Preliminary Idea:** - **Cracking:** Breaking large hydrocarbons into smaller ones. - **Reforming:** Rearranging hydrocarbon structures to improve fuel quality. - **Quality of Gasoline:** Measured by octane number. - **Octane Number:** Rating of fuel's anti-knock properties. - **Cetane Number:** Rating of diesel fuel's ignition quality. - **Gasoline Additive:** Substances added to improve fuel performance. ### Fundamental Principles of Organic Chemistry - **IUPAC Nomenclature of Organic Compounds:** Systematic naming rules (up to 6 carbon atoms in chain). 1. Identify longest carbon chain (parent chain). 2. Number chain to give substituents lowest numbers. 3. Name substituents. 4. Alphabetize substituents. 5. Use prefixes (di, tri, tetra) for multiple identical substituents. 6. Functional groups take precedence. - **Qualitative Analysis of Organic Compounds (Lassaigne's Test):** - **Detection of N, S, Halogens:** Fuse organic compound with sodium metal, then test for NaCN, Na$_2$S, NaX. - N: Prussian blue color with FeSO$_4$/FeCl$_3$. - S: Violet color with Sodium nitroprusside. - Halogens: Precipitate with AgNO$_3$. - **Isomerism in Organic Compounds:** Compounds with same molecular formula but different structures. - **Classification:** Structural, Stereoisomerism. - **Structural Isomerism:** Different connectivity of atoms. - **Chain Isomerism:** Different carbon skeleton. - **Position Isomerism:** Different position of functional group/substituent. - **Functional Isomerism:** Different functional groups. - **Metamerism:** Different alkyl groups attached to same functional group. - **Tautomerism:** Rapid interconversion of two isomers (e.g., keto-enol). - **Stereoisomerism:** Same connectivity, different spatial arrangement. - **Geometrical Isomerism (cis & trans):** Restricted rotation around double bonds or in rings. - **Optical Isomerism (d & l form):** Non-superimposable mirror images (enantiomers), presence of chiral center. - **Preliminary Idea of Reaction Mechanism:** - **Homolytic Fission:** Bond breaks symmetrically, forming free radicals. - **Heterolytic Fission:** Bond breaks unsymmetrically, forming ions (carbocation, carbanion). - **Electrophiles:** Electron-deficient species, seek electrons. - **Nucleophiles:** Electron-rich species, seek positive centers. - **Free Radicals:** Species with unpaired electrons. - **Electronic Effects:** - **Inductive Effect:** Polarization of $\sigma$-bond due to electronegativity difference. - **+I Effect:** Electron-donating (e.g., alkyl groups). - **-I Effect:** Electron-withdrawing (e.g., halogens, -COOH). - **Resonance Effect (Mesomeric Effect):** Delocalization of $\pi$-electrons. - **+R Effect:** Electron-donating through resonance (e.g., -OH, -NH$_2$). - **-R Effect:** Electron-withdrawing through resonance (e.g., -NO$_2$, -CHO). ### Hydrocarbons #### Saturated Hydrocarbons (Alkanes) - **Preparation:** - From haloalkanes: - **Reduction:** $RX \xrightarrow{Zn/HCl} RH$. - **Wurtz Reaction:** $2RX + 2Na \rightarrow R-R + 2NaX$. - **Decarboxylation:** $RCOONa + NaOH \xrightarrow{CaO, \Delta} RH + Na_2CO_3$. - **Catalytic Hydrogenation of Alkene/Alkyne:** $R-CH=CH_2 + H_2 \xrightarrow{Ni/Pt} R-CH_2-CH_3$. - **Chemical Properties:** - **Substitution Reactions (Free Radical):** - **Halogenation:** $CH_4 + Cl_2 \xrightarrow{hv} CH_3Cl + HCl$. - **Nitration:** Reaction with HNO$_3$ at high temperature. - **Sulphonation:** Reaction with fuming H$_2$SO$_4$. - **Oxidation of Ethane:** Combustion ($2C_2H_6 + 7O_2 \rightarrow 4CO_2 + 6H_2O$). #### Unsaturated Hydrocarbons (Alkenes & Alkynes) #### Alkenes - **Preparation:** - **Dehydration of Alcohol:** $R-CH_2-CH_2-OH \xrightarrow{conc. H_2SO_4, \Delta} R-CH=CH_2 + H_2O$. - **Dehydrohalogenation:** $R-CH_2-CH_2-X + KOH(alc) \rightarrow R-CH=CH_2 + KX + H_2O$. - **Catalytic Hydrogenation of Alkyne:** $R-C \equiv C-H + H_2 \xrightarrow{Lindlar's catalyst} R-CH=CH_2$. - **Chemical Properties (Addition Reactions):** - **With HX:** - **Markovnikov's Addition:** H adds to carbon with more H, X adds to carbon with fewer H. - **Peroxide Effect (Anti-Markovnikov):** For HBr in presence of peroxides. - **With H$_2$O:** Hydration (acid-catalyzed) to form alcohols. - **With O$_3$ (Ozonolysis):** Cleavage of double bond to form aldehydes/ketones. - **With H$_2$SO$_4$:** Forms alkyl hydrogen sulfates. #### Alkynes - **Preparation:** - From carbon and hydrogen: $C_2 + H_2 \xrightarrow{\text{electric arc}} C_2H_2$. - From 1,2 dibromoethane: $Br-CH_2-CH_2-Br + 2KOH(alc) \rightarrow HC \equiv CH + 2KBr + 2H_2O$. - From chloroform/iodoform: $CHCl_3 + 6Ag + CHCl_3 \rightarrow HC \equiv CH + 6AgCl$. - **Chemical Properties:** - **Addition Reactions:** - **H$_2$:** Catalytic hydrogenation to alkanes (or alkenes with controlled catalyst). - **HX:** Forms haloalkenes, then dihaloalkanes (Markovnikov's rule). - **H$_2$O:** Hydration (HgSO$_4$/H$_2$SO$_4$) to form aldehydes/ketones. - **Acidic Nature:** Terminal alkynes react with strong bases/metals. - **Action with Sodium:** $2HC \equiv CH + 2Na \rightarrow 2HC \equiv C^-Na^+ + H_2$. - **Ammoniacal AgNO$_3$ (Tollens' reagent):** Forms white silver acetylide precipitate. - **Ammoniacal Cu$_2$Cl$_2$ (Ammoniacal cuprous chloride):** Forms red copper acetylide precipitate. - **Test of Unsaturation:** - **Bromine Water Test:** Decolorizes reddish-brown bromine water. - **Baeyer's Test:** Decolorizes cold, dilute, alkaline KMnO$_4$ (purple color disappears). - **Comparative Studies of Physical Properties:** Boiling points generally increase with chain length. Alkanes ### Aromatic Hydrocarbons - **Introduction and Characteristics:** Cyclic, planar, conjugated systems with delocalized $\pi$-electrons. - **Huckel's Rule of Aromaticity:** $(4n+2)\pi$ electrons (where n = 0, 1, 2...). - **Kekulé Structure of Benzene:** Alternating single and double bonds. - **Resonance:** Benzene is a resonance hybrid of two Kekulé structures and other minor contributors. - **Isomerism:** Positional isomerism for disubstituted benzenes (ortho, meta, para). - **Preparation of Benzene:** - **Decarboxylation of Sodium Benzoate:** $C_6H_5COONa + NaOH \xrightarrow{CaO, \Delta} C_6H_6 + Na_2CO_3$. - **From Phenol:** $C_6H_5OH + Zn \xrightarrow{\Delta} C_6H_6 + ZnO$. - **From Ethyne (Acetylene):** $3HC \equiv CH \xrightarrow{\text{red hot iron tube}} C_6H_6$. - **Physical Properties of Benzene:** Colorless liquid, characteristic odor, insoluble in water, soluble in organic solvents. - **Chemical Properties of Benzene:** Primarily undergoes electrophilic substitution reactions due to aromatic stability. - **Addition Reactions:** - **Hydrogen (Hydrogenation):** $C_6H_6 + 3H_2 \xrightarrow{Ni/\Delta} C_6H_{12}$ (cyclohexane). - **Halogen (e.g., Cl$_2$):** $C_6H_6 + 3Cl_2 \xrightarrow{hv} C_6H_6Cl_6$ (BHC). - **Electrophilic Substitution Reactions:** - **Orientation of Benzene Derivatives:** - **Ortho-para directors:** Electron-donating groups (e.g., -OH, -NH$_2$, -CH$_3$, -X). - **Meta directors:** Electron-withdrawing groups (e.g., -NO$_2$, -COOH, -CHO, -CN). - **Nitration:** Reaction with conc. HNO$_3$/H$_2$SO$_4$ to form nitrobenzene. - **Sulphonation:** Reaction with fuming H$_2$SO$_4$ to form benzenesulphonic acid. - **Halogenation:** Reaction with X$_2$/FeX$_3$ to form halobenzenes. - **Friedel-Crafts Reaction:** - **Alkylation:** With alkyl halide/AlCl$_3$ to form alkylbenzenes. - **Acylation:** With acyl halide/AlCl$_3$ to form acylbenzenes. - **Combustion of Benzene:** $2C_6H_6 + 15O_2 \rightarrow 12CO_2 + 6H_2O$ (sooty flame due to high carbon content). - **Uses:** Solvents, synthesis of dyes, drugs, plastics. ### Fundamentals of Applied Chemistry - **Chemical Industry:** Sector involved in producing chemicals and related products. - **Importance:** Essential for agriculture, medicine, manufacturing, energy. - **Stages in Producing a New Product:** Research & Development, Process Design, Pilot Plant, Commercial Production, Marketing. - **Economics of Production:** Cost analysis, profitability, market demand. - **Cash Flow in Production Cycle:** Managing expenses and revenue. - **Running a Chemical Plant:** Operations, safety, quality control. - **Designing a Chemical Plant:** Engineering, layout, equipment selection. - **Continuous Processing:** Raw materials continuously fed, products continuously removed. - **Batch Processing:** Discrete batches of raw materials processed. - **Environmental Impact:** Pollution, waste management, sustainability. ### Modern Chemical Manufactures - **Manufacture of Ammonia (Haber's Process):** - **Principle:** $N_2(g) + 3H_2(g) \rightleftharpoons 2NH_3(g)$ (Exothermic, reversible). - **Conditions:** High pressure (200 atm), moderate temperature (400-450$^\circ$C), iron catalyst. - **Flow Sheet Diagram:** (Conceptual understanding of steps: gas purification, compression, reaction, cooling, separation, recycling). - **Manufacture of Nitric Acid (Ostwald's Process):** - **Principle:** Catalytic oxidation of ammonia. - **Steps:** 1. $NH_3 + O_2 \xrightarrow{Pt/Rh \text{ catalyst}, 800^\circ C} NO + H_2O$. 2. $NO + O_2 \rightarrow NO_2$. 3. $NO_2 + H_2O + O_2 \rightarrow HNO_3$. - **Flow Sheet Diagram:** (Conceptual understanding of steps). - **Manufacture of Sulphuric Acid (Contact Process):** - **Principle:** Catalytic oxidation of SO$_2$. - **Steps:** 1. Burning S or roasting metal sulfides to get SO$_2$. 2. $2SO_2(g) + O_2(g) \rightleftharpoons 2SO_3(g)$ (Exothermic, reversible) with V$_2$O$_5$ catalyst, 450$^\circ$C. 3. $SO_3 + H_2SO_4 \rightarrow H_2S_2O_7$ (oleum). 4. $H_2S_2O_7 + H_2O \rightarrow 2H_2SO_4$. - **Flow Sheet Diagram:** (Conceptual understanding of steps). - **Manufacture of Sodium Hydroxide (Diaphragm Cell):** - **Principle:** Electrolysis of brine (aqueous NaCl). - **Anode:** $2Cl^-(aq) \rightarrow Cl_2(g) + 2e^-$. - **Cathode:** $2H_2O(l) + 2e^- \rightarrow H_2(g) + 2OH^-(aq)$. - **Overall:** $2NaCl(aq) + 2H_2O(l) \rightarrow Cl_2(g) + H_2(g) + 2NaOH(aq)$. - **Diaphragm:** Prevents mixing of NaOH and Cl$_2$. - **Flow Sheet Diagram:** (Conceptual understanding of cell components). - **Manufacture of Sodium Carbonate (Ammonia Soda or Solvay Process):** - **Principle:** Reaction of NaCl, NH$_3$, CO$_2$, and H$_2$O. - **Key Reactions:** 1. $NH_3 + H_2O + CO_2 \rightarrow NH_4HCO_3$. 2. $NH_4HCO_3 + NaCl \rightarrow NaHCO_3 \downarrow + NH_4Cl$. 3. $2NaHCO_3 \xrightarrow{\Delta} Na_2CO_3 + H_2O + CO_2$. - **Flow Sheet Diagram:** (Conceptual understanding of steps and recycling of NH$_3$). - **Fertilizers:** Substances added to soil to enhance plant growth. - **Chemical Fertilizers:** Synthetically produced (e.g., urea, DAP). - **Types:** Nitrogenous, Phosphatic, Potassic. - **Production of Urea:** - **Principle:** Reaction of ammonia and carbon dioxide. - $2NH_3 + CO_2 \rightleftharpoons NH_2COONH_4$ (ammonium carbamate). - $NH_2COONH_4 \xrightarrow{\Delta} NH_2CONH_2 + H_2O$ (urea). - **Flow Sheet Diagram:** (Conceptual understanding of steps).