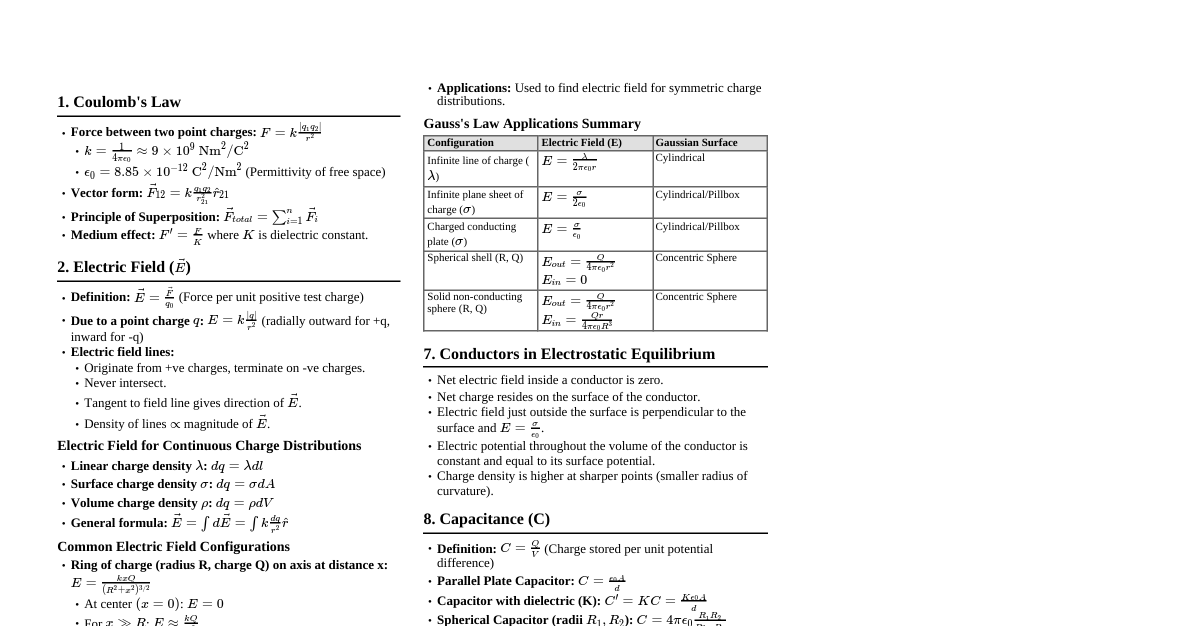
Electrostatics 1. Coulomb's Law Force between two point charges: $F = k \frac{|q_1 q_2|}{r^2}$, where $k = \frac{1}{4\pi\epsilon_0} \approx 9 \times 10^9 \text{ N m}^2/\text{C}^2$. $\epsilon_0$ is permittivity of free space. 2. Electric Field Electric field due to a point charge $q$: $E = k \frac{q}{r^2}$ (radially outward for positive $q$). Electric field lines: originate from positive charges, terminate on negative charges, never cross. Electric dipole moment: $\vec{p} = q(2\vec{a})$ (from negative to positive charge). Torque on a dipole in uniform E-field: $\vec{\tau} = \vec{p} \times \vec{E}$. Potential energy of a dipole in uniform E-field: $U = -\vec{p} \cdot \vec{E}$. 3. Electric Potential Electric potential difference: $\Delta V = -\int \vec{E} \cdot d\vec{l}$. Potential due to a point charge $q$: $V = k \frac{q}{r}$. Potential energy of a system of two charges: $U = k \frac{q_1 q_2}{r}$. Equipotential surfaces: Perpendicular to electric field lines. 4. Gauss's Law $\Phi_E = \oint \vec{E} \cdot d\vec{A} = \frac{Q_{enc}}{\epsilon_0}$. Applications: Infinite line charge: $E = \frac{\lambda}{2\pi\epsilon_0 r}$. Infinite plane sheet: $E = \frac{\sigma}{2\epsilon_0}$. Charged spherical shell: $E_{in}=0$, $E_{out}=k\frac{Q}{r^2}$. Solid non-conducting sphere: $E_{in}=k\frac{Qr}{R^3}$, $E_{out}=k\frac{Q}{r^2}$. Capacitance 1. Capacitor Basics Capacitance: $C = \frac{Q}{V}$. Unit: Farad (F). Parallel plate capacitor: $C = \frac{\epsilon_0 A}{d}$. Spherical capacitor: $C = 4\pi\epsilon_0 \frac{ab}{b-a}$. Cylindrical capacitor: $C = \frac{2\pi\epsilon_0 L}{\ln(b/a)}$. 2. Capacitors in Combination Series: $\frac{1}{C_{eq}} = \frac{1}{C_1} + \frac{1}{C_2} + \dots$. Charge is same. Parallel: $C_{eq} = C_1 + C_2 + \dots$. Voltage is same. 3. Energy Stored in a Capacitor $U = \frac{1}{2}CV^2 = \frac{Q^2}{2C} = \frac{1}{2}QV$. Energy density: $u = \frac{1}{2}\epsilon_0 E^2$. 4. Dielectrics With dielectric: $C' = KC = K \frac{\epsilon_0 A}{d}$. Induced electric field in dielectric: $E_{ind} = E_0(1 - 1/K)$. Current Electricity 1. Electric Current Current: $I = \frac{dQ}{dt}$. Unit: Ampere (A). Drift velocity: $v_d = \frac{eE\tau}{m}$. Relation between current and drift velocity: $I = nAev_d$. 2. Ohm's Law and Resistance $V = IR$. Unit of Resistance: Ohm ($\Omega$). Resistance: $R = \rho \frac{L}{A}$. $\rho$ is resistivity. Conductivity: $\sigma = 1/\rho$. Temperature dependence of resistance: $R_T = R_0(1 + \alpha(T-T_0))$. 3. Cells and Emf Emf ($\epsilon$): Potential difference across terminals when no current flows. Terminal voltage: $V = \epsilon - Ir$ (discharging), $V = \epsilon + Ir$ (charging). $r$ is internal resistance. Cells in series: $\epsilon_{eq} = \sum \epsilon_i$, $r_{eq} = \sum r_i$. Cells in parallel (identical cells): $\epsilon_{eq} = \epsilon$, $r_{eq} = r/n$. 4. Kirchhoff's Laws Junction Rule (KCL): $\sum I = 0$ (algebraic sum of currents at a junction is zero). Loop Rule (KVL): $\sum V = 0$ (algebraic sum of potential changes around any closed loop is zero). 5. Measuring Instruments Wheatstone Bridge: $\frac{R_1}{R_2} = \frac{R_3}{R_4}$ for balanced bridge. Meter Bridge: $\frac{R}{S} = \frac{l}{100-l}$. Potentiometer: Compares emfs, measures internal resistance. Principle: potential drop across a wire is proportional to its length. Magnetic Effects of Current and Magnetism 1. Biot-Savart Law $d\vec{B} = \frac{\mu_0}{4\pi} \frac{I d\vec{l} \times \vec{r}}{r^3}$. Magnetic field at center of circular loop: $B = \frac{\mu_0 I}{2R}$. Magnetic field on axis of circular loop: $B = \frac{\mu_0 I R^2}{2(R^2+x^2)^{3/2}}$. 2. Ampere's Circuital Law $\oint \vec{B} \cdot d\vec{l} = \mu_0 I_{enc}$. Magnetic field due to infinite straight wire: $B = \frac{\mu_0 I}{2\pi r}$. Magnetic field inside a solenoid: $B = \mu_0 nI$. Magnetic field inside a toroid: $B = \frac{\mu_0 N I}{2\pi r}$. 3. Lorentz Force Force on a charge $q$: $\vec{F} = q(\vec{E} + \vec{v} \times \vec{B})$. Force on a current-carrying conductor: $\vec{F} = I(\vec{L} \times \vec{B})$. Magnetic force between two parallel currents: $F/L = \frac{\mu_0 I_1 I_2}{2\pi d}$. Torque on a current loop: $\vec{\tau} = \vec{M} \times \vec{B}$, where $\vec{M}$ is magnetic dipole moment ($M = NIA$). 4. Moving Coil Galvanometer Deflection $\phi \propto I$. $I = \frac{C}{NAB}\phi$. Conversion to Ammeter: Low resistance shunt in parallel. Conversion to Voltmeter: High resistance in series. 5. Magnetism and Matter Magnetic field lines: form closed loops, emerge from N-pole, enter S-pole. Earth's magnetism: Angle of declination, angle of dip. Magnetic properties of materials: Diamagnetic ($\chi 0$), Ferromagnetic ($\chi \gg 0$). Electromagnetic Induction and AC 1. Faraday's Laws of EMI Induced EMF: $\epsilon = -\frac{d\Phi_B}{dt}$. Magnetic Flux: $\Phi_B = \int \vec{B} \cdot d\vec{A}$. Lenz's Law: Induced current opposes the change in magnetic flux that produced it. 2. Motional EMF $\epsilon = (B l v) \sin\theta$. Energy consideration: Mechanical power $=$ Electrical power. 3. Self and Mutual Inductance Self-inductance: $\Phi_B = LI \implies \epsilon = -L \frac{dI}{dt}$. Unit: Henry (H). Energy stored in inductor: $U = \frac{1}{2}LI^2$. Mutual inductance: $\Phi_{21} = M_{21} I_1 \implies \epsilon_2 = -M_{21} \frac{dI_1}{dt}$. 4. Alternating Current (AC) Instantaneous AC voltage/current: $V = V_0 \sin(\omega t + \phi)$, $I = I_0 \sin(\omega t)$. RMS values: $V_{rms} = \frac{V_0}{\sqrt{2}}$, $I_{rms} = \frac{I_0}{\sqrt{2}}$. Reactance: Inductive reactance: $X_L = \omega L$. Capacitive reactance: $X_C = \frac{1}{\omega C}$. Impedance (Z): $Z = \sqrt{R^2 + (X_L - X_C)^2}$. Phase angle: $\tan \phi = \frac{X_L - X_C}{R}$. Power in AC circuit: $P = V_{rms} I_{rms} \cos\phi$. $\cos\phi$ is power factor. Resonance: $X_L = X_C \implies \omega_0 = \frac{1}{\sqrt{LC}}$. $Z = R$. Transformer: $\frac{V_s}{V_p} = \frac{N_s}{N_p} = \frac{I_p}{I_s}$ (for ideal transformer). Electromagnetic Waves 1. Properties of EM Waves Propagate in vacuum with speed $c = \frac{1}{\sqrt{\mu_0 \epsilon_0}}$. Transverse nature: $\vec{E} \perp \vec{B} \perp \vec{v}$. Ratio of $E$ and $B$: $E_0/B_0 = c$. Energy density: $u = \frac{1}{2}\epsilon_0 E^2 + \frac{1}{2\mu_0} B^2 = \epsilon_0 E^2 = \frac{B^2}{\mu_0}$. Poynting vector: $\vec{S} = \frac{1}{\mu_0}(\vec{E} \times \vec{B})$. EM spectrum: Radio, Microwave, IR, Visible, UV, X-ray, Gamma ray (increasing freq, decreasing wavelength). Optics 1. Reflection of Light Laws of reflection: Angle of incidence = Angle of reflection. Incident ray, reflected ray, normal are coplanar. Mirror formula: $\frac{1}{f} = \frac{1}{v} + \frac{1}{u}$. Magnification: $m = -\frac{v}{u} = \frac{h_i}{h_o}$. Sign convention: Cartesian sign convention. 2. Refraction of Light Snell's Law: $n_1 \sin i = n_2 \sin r$. Refractive index: $n = c/v$. Critical angle: $\sin C = n_2/n_1$ ($n_1 > n_2$). Total Internal Reflection (TIR). Apparent depth: $h_{app} = \frac{h_{real}}{n_{relative}}$. Refraction at spherical surfaces: $\frac{n_2}{v} - \frac{n_1}{u} = \frac{n_2 - n_1}{R}$. Lens Maker's Formula: $\frac{1}{f} = (n-1)\left(\frac{1}{R_1} - \frac{1}{R_2}\right)$. Lens Formula: $\frac{1}{f} = \frac{1}{v} - \frac{1}{u}$. Power of lens: $P = 1/f$ (in dioptres if f in meters). Lenses in contact: $P = P_1 + P_2$, $\frac{1}{f} = \frac{1}{f_1} + \frac{1}{f_2}$. 3. Optical Instruments Human eye: defects (myopia, hypermetropia, presbyopia, astigmatism) and corrections. Simple microscope: $M = 1 + D/f$ (image at D), $M = D/f$ (image at $\infty$). Compound microscope: $M = M_o M_e = \left(\frac{L}{f_o}\right)\left(1 + \frac{D}{f_e}\right)$. Astronomical telescope: $M = -f_o/f_e$. Length $L = f_o + f_e$. 4. Wave Optics Huygens' Principle: Every point on a wavefront is a source of secondary wavelets. Interference: Young's Double Slit Experiment (YDSE): $\Delta x = d \sin\theta$. Path difference for constructive interference: $\Delta x = n\lambda$. Path difference for destructive interference: $\Delta x = (n+1/2)\lambda$. Fringe width: $\beta = \frac{\lambda D}{d}$. Diffraction: Single slit: First minima at $a \sin\theta = \lambda$. Width of central maximum: $2\theta \approx \frac{2\lambda}{a}$. Polarization: Malus's Law: $I = I_0 \cos^2\theta$. Brewster's Law: $\tan i_p = n$. Reflected light is completely polarized. Dual Nature of Radiation and Matter 1. Photoelectric Effect Einstein's Photoelectric Equation: $h\nu = \phi_0 + K_{max}$. Work function: $\phi_0 = h\nu_0$. $\nu_0$ is threshold frequency. Stopping potential: $eV_s = K_{max}$. 2. Matter Waves (de Broglie) de Broglie wavelength: $\lambda = \frac{h}{p} = \frac{h}{mv}$. For electron accelerated by potential V: $\lambda = \frac{1.227}{\sqrt{V}}$ nm. 3. Davisson-Germer Experiment Experimental verification of wave nature of electrons. Atoms and Nuclei 1. Atomic Models Rutherford's model: Gold foil experiment, nucleus discovery. Bohr's model for hydrogen atom: Quantization of angular momentum: $L = n\frac{h}{2\pi}$. Radii of orbits: $r_n = a_0 n^2$, where $a_0 = 0.529 \text{ Å}$ (Bohr radius). Energy of orbits: $E_n = -\frac{13.6}{n^2}$ eV. Spectral series: Lyman, Balmer, Paschen, Brackett, Pfund. 2. Nuclei Composition: Protons and Neutrons (Nucleons). Mass defect: $\Delta m = [Z m_p + (A-Z) m_n] - m_{nucleus}$. Binding energy: $E_b = \Delta m c^2$. Binding energy per nucleon: Stability curve. Nuclear forces: Strongest fundamental force, short-range, charge-independent. 3. Radioactivity Laws of radioactive decay: $N = N_0 e^{-\lambda t}$. Half-life: $T_{1/2} = \frac{\ln 2}{\lambda} = \frac{0.693}{\lambda}$. Mean life: $\tau = 1/\lambda$. Alpha decay: $^A_Z X \to ^{A-4}_{Z-2} Y + ^4_2 He$. Beta decay: $^A_Z X \to ^A_{Z+1} Y + e^- + \bar{\nu}$ (beta-minus). $^A_Z X \to ^A_{Z-1} Y + e^+ + \nu$ (beta-plus). Gamma decay: Nucleus in excited state emits $\gamma$ photon. Nuclear fission: Heavy nucleus splits into lighter nuclei. Nuclear fusion: Light nuclei combine to form heavier nucleus. Semiconductor Electronics 1. Classification of Solids Conductors, Insulators, Semiconductors (based on band theory). Intrinsic semiconductors: Ge, Si. $n_e = n_h = n_i$. Extrinsic semiconductors: N-type: Doping with pentavalent impurities (e.g., P, As). Majority carriers: electrons. P-type: Doping with trivalent impurities (e.g., B, Al). Majority carriers: holes. 2. P-N Junction Diode Formation: Diffusion and drift currents, depletion region, barrier potential. Forward biasing: Reduces barrier, current flows. Reverse biasing: Increases barrier, negligible current (until breakdown). I-V characteristics. Rectifiers: Half-wave, Full-wave. Efficiency. 3. Special Purpose P-N Junction Diodes Zener diode: Voltage regulator (reverse bias breakdown). LED (Light Emitting Diode): Emits light in forward bias. Photodiode: Detects light (reverse bias). Solar cell: Converts light energy to electrical energy. 4. Transistors (BJT) NPN, PNP configurations. Emitter, Base, Collector. Operating regions: Cut-off, Active, Saturation. Amplifier characteristics: Common Emitter (CE) configuration. Current gain: $\beta = I_C/I_B$. Voltage gain: $A_v = \beta (R_C/R_{in})$. Power gain: $A_p = A_v \beta$. 5. Logic Gates Basic gates: AND, OR, NOT. Universal gates: NAND, NOR. Truth tables, Boolean expressions.