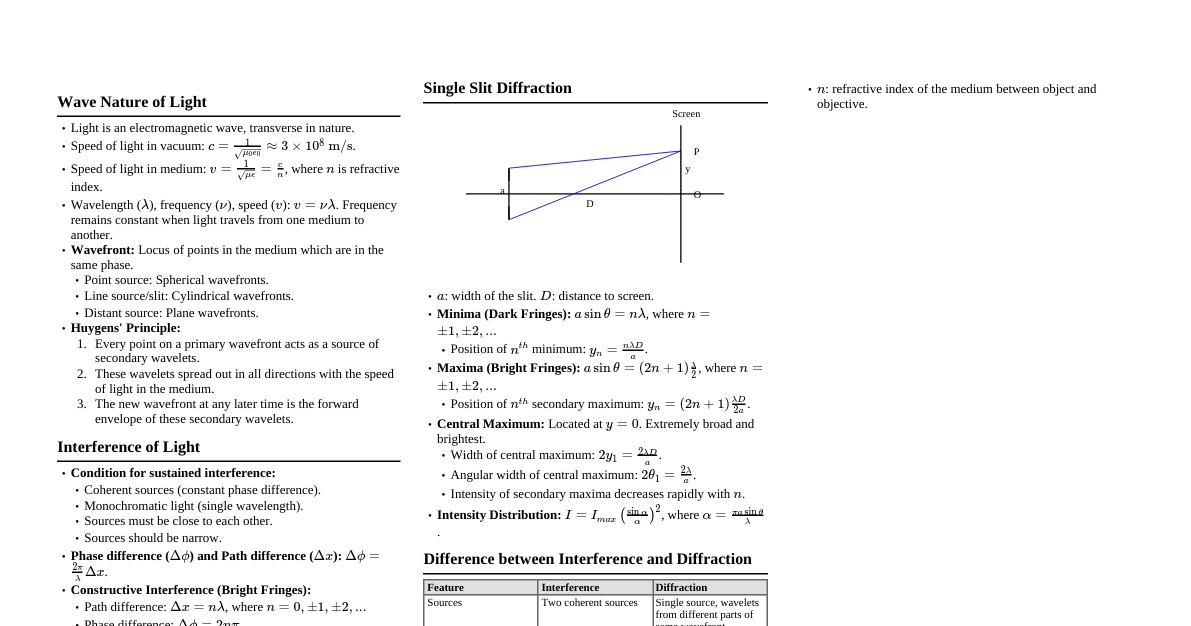
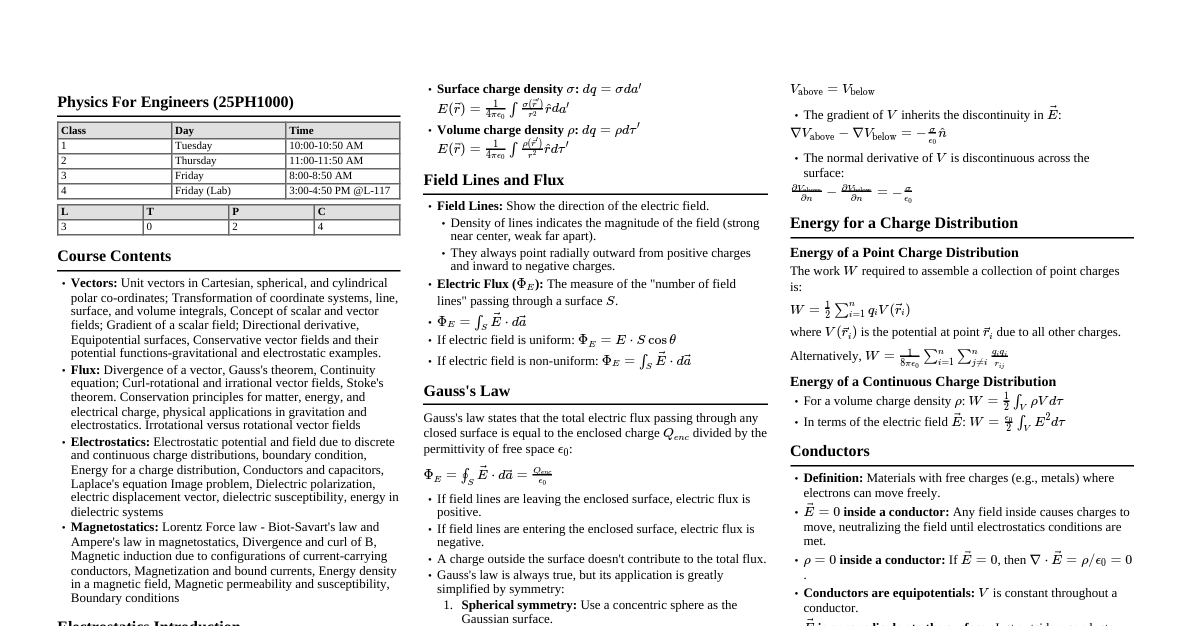
### Photoelectric Effect - **Key Concepts:** Emission of electrons when light shines on a material. - **Einstein's Photoelectric Equation:** $KE_{max} = h\nu - \phi_0$ - $KE_{max}$: Maximum kinetic energy of emitted electrons. - $h$: Planck's constant ($6.626 \times 10^{-34}$ J·s). - $\nu$: Frequency of incident light. - $\phi_0 = h\nu_0$: Work function (minimum energy required to eject an electron). - $\nu_0$: Threshold frequency. - **Stopping Potential ($V_s$):** $eV_s = KE_{max}$ - **Important Points:** - Instantaneous process. - $KE_{max}$ depends on frequency, not intensity. - Current depends on intensity. ### de Broglie Wavelength - **Wave-Particle Duality:** All matter exhibits wave-like properties. - **Formula:** $\lambda = \frac{h}{p} = \frac{h}{mv}$ - $\lambda$: de Broglie wavelength. - $p$: Momentum of the particle. - $m$: Mass of the particle. - $v$: Velocity of the particle. - **For an electron accelerated through potential V:** $\lambda = \frac{h}{\sqrt{2meV}} = \frac{12.27}{\sqrt{V}}$ Å ### Bohr Model of Hydrogen Atom - **Postulates:** 1. Electrons revolve in stable orbits without radiating energy. 2. Angular momentum is quantized: $L = mvr = n\frac{h}{2\pi}$, where $n = 1, 2, 3, ...$ (principal quantum number). 3. Energy is emitted or absorbed only when electrons jump between orbits. - **Radius of nth orbit ($r_n$):** $r_n = 0.529 \frac{n^2}{Z}$ Å (for H-like atoms) - **Energy of nth orbit ($E_n$):** $E_n = -13.6 \frac{Z^2}{n^2}$ eV - **Rydberg Formula for Wavelength:** $\frac{1}{\lambda} = RZ^2 \left(\frac{1}{n_f^2} - \frac{1}{n_i^2}\right)$ - $R$: Rydberg constant ($1.097 \times 10^7$ m$^{-1}$). - $n_i, n_f$: Initial and final principal quantum numbers. - **Spectral Series (for H-atom, Z=1):** - **Lyman Series:** $n_f=1$, $n_i=2,3,4,...$ (UV region) - **Balmer Series:** $n_f=2$, $n_i=3,4,5,...$ (Visible region) - **Paschen Series:** $n_f=3$, $n_i=4,5,6,...$ (Infrared region) - **Brackett Series:** $n_f=4$, $n_i=5,6,7,...$ (Infrared region) - **Pfund Series:** $n_f=5$, $n_i=6,7,8,...$ (Infrared region) ### X-rays - **Production:** High-energy electrons strike a metal target. - **Continuous X-rays (Bremsstrahlung):** Produced by deceleration of electrons. - **Minimum Wavelength (Duane-Hunt Law):** $\lambda_{min} = \frac{hc}{eV}$ (where V is accelerating voltage). - **Characteristic X-rays:** Produced when electrons fill vacancies in inner shells. - **Moseley's Law:** $\sqrt{\nu} = a(Z-b)$ - $\nu$: Frequency of characteristic X-ray. - $Z$: Atomic number. - $a, b$: Constants. ### Nuclear Physics - **Atomic Nucleus:** Composed of protons and neutrons (nucleons). - **Atomic Number (Z):** Number of protons. - **Mass Number (A):** Number of protons + neutrons. - **Nuclear Size:** Radius $R = R_0 A^{1/3}$, where $R_0 \approx 1.2 \times 10^{-15}$ m (Fermi). - **Mass Defect ($\Delta m$):** Difference between the sum of masses of individual nucleons and the actual mass of the nucleus. - $\Delta m = (Zm_p + (A-Z)m_n) - M_{nucleus}$ - **Binding Energy ($BE$):** Energy equivalent of mass defect. - $BE = \Delta m c^2$ - **Binding Energy per Nucleon:** $BE/A$ (measures nuclear stability). - **Radioactivity:** Spontaneous disintegration of unstable nuclei. - **Law of Radioactive Decay:** $N = N_0 e^{-\lambda t}$ - $N$: Number of nuclei at time t. - $N_0$: Initial number of nuclei. - $\lambda$: Decay constant. - **Half-Life ($T_{1/2}$):** Time for half of the nuclei to decay. $T_{1/2} = \frac{\ln 2}{\lambda} = \frac{0.693}{\lambda}$ - **Mean Life ($\tau$):** Average lifetime of a radioactive nucleus. $\tau = \frac{1}{\lambda}$ - **Activity (R):** Rate of decay. $R = -\frac{dN}{dt} = \lambda N = R_0 e^{-\lambda t}$ - Units: Becquerel (Bq), Curie (Ci). - **Types of Decay:** - **Alpha ($\alpha$) decay:** Emission of $^4_2He$ nucleus. $^A_Z X \to ^{A-4}_{Z-2} Y + ^4_2 He$ - **Beta ($\beta$) decay:** - $\beta^-$ decay: Neutron converts to proton + electron + antineutrino. $^A_Z X \to ^A_{Z+1} Y + e^- + \bar{\nu}_e$ - $\beta^+$ decay: Proton converts to neutron + positron + neutrino. $^A_Z X \to ^A_{Z-1} Y + e^+ + \nu_e$ - **Gamma ($\gamma$) decay:** Emission of high-energy photon from excited nucleus. - **Nuclear Fission:** Heavy nucleus splits into lighter nuclei. - **Nuclear Fusion:** Light nuclei combine to form a heavier nucleus. ### Semiconductors - **Types:** - **Intrinsic:** Pure semiconductor (e.g., Si, Ge). - $n_e = n_h = n_i$ (electron concentration = hole concentration = intrinsic carrier concentration). - **Extrinsic:** Doped semiconductor. - **N-type:** Doped with pentavalent impurity (e.g., P, As). Majority carriers: electrons. - **P-type:** Doped with trivalent impurity (e.g., B, Al). Majority carriers: holes. - **P-N Junction Diode:** - **Forward Bias:** p-side connected to positive, n-side to negative. Depletion region width decreases, current flows. - **Reverse Bias:** p-side connected to negative, n-side to positive. Depletion region width increases, very small current flows. - **Diode Characteristics:** - **Breakdown Voltage:** Reverse voltage at which current increases sharply. - **Knee Voltage (Cut-in Voltage):** Forward voltage at which current starts to increase significantly. - **Rectifiers:** Convert AC to DC. - **Half-wave rectifier:** Uses one diode, rectifies half of the AC cycle. Efficiency $\approx 40.6\%$. - **Full-wave rectifier:** Uses two or four diodes (bridge), rectifies both halves of the AC cycle. Efficiency $\approx 81.2\%$. - **Zener Diode:** Heavily doped p-n junction, designed to operate in reverse breakdown region (voltage regulator). - **Transistor (BJT - Bipolar Junction Transistor):** - npn or pnp structure. - Emitter (E), Base (B), Collector (C). - **Current Gain:** - $\alpha = I_C/I_E$ (common base) - $\beta = I_C/I_B$ (common emitter) - Relation: $\beta = \frac{\alpha}{1-\alpha}$ and $\alpha = \frac{\beta}{1+\beta}$ - **Logic Gates:** - **Basic Gates:** AND, OR, NOT - **Universal Gates:** NAND, NOR (can implement any other logic function) - **Boolean Algebra:** - AND: $A \cdot B$ - OR: $A + B$ - NOT: $\bar{A}$ - De Morgan's Theorems: $\overline{A \cdot B} = \bar{A} + \bar{B}$, $\overline{A + B} = \bar{A} \cdot \bar{B}$