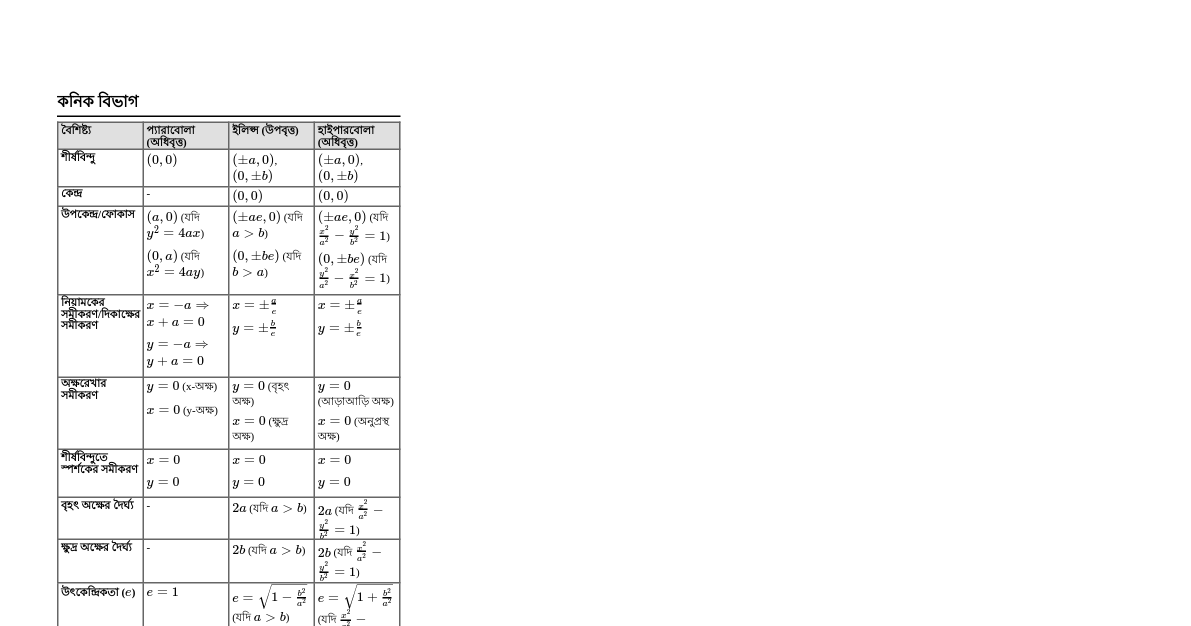
### Sequences & Series #### Arithmetic Progression (AP) - **nth term:** $a_n = a + (n-1)d$ - **Sum of n terms:** $S_n = \frac{n}{2}(2a + (n-1)d) = \frac{n}{2}(a + a_n)$ #### Geometric Progression (GP) - **nth term:** $a_n = ar^{n-1}$ - **Sum of n terms:** $S_n = \frac{a(r^n - 1)}{r-1}$ (for $r \neq 1$) - **Sum to infinity:** $S_\infty = \frac{a}{1-r}$ (for $|r| ### Trigonometry #### Basic Identities - $\sin^2\theta + \cos^2\theta = 1$ - $\sec^2\theta - \tan^2\theta = 1$ - $\csc^2\theta - \cot^2\theta = 1$ #### Angle Sum/Difference - $\sin(A \pm B) = \sin A \cos B \pm \cos A \sin B$ - $\cos(A \pm B) = \cos A \cos B \mp \sin A \sin B$ - $\tan(A \pm B) = \frac{\tan A \pm \tan B}{1 \mp \tan A \tan B}$ #### Double Angle Formulas - $\sin 2A = 2 \sin A \cos A$ - $\cos 2A = \cos^2 A - \sin^2 A = 2\cos^2 A - 1 = 1 - 2\sin^2 A$ - $\tan 2A = \frac{2 \tan A}{1 - \tan^2 A}$ #### Half Angle Formulas - $\sin^2 \frac{A}{2} = \frac{1 - \cos A}{2}$ - $\cos^2 \frac{A}{2} = \frac{1 + \cos A}{2}$ - $\tan^2 \frac{A}{2} = \frac{1 - \cos A}{1 + \cos A}$ #### Sine and Cosine Rule - **Sine Rule:** $\frac{a}{\sin A} = \frac{b}{\sin B} = \frac{c}{\sin C}$ - **Cosine Rule:** $c^2 = a^2 + b^2 - 2ab \cos C$ ### Derivatives #### Basic Rules - **Power Rule:** $\frac{d}{dx}(x^n) = nx^{n-1}$ - **Constant Rule:** $\frac{d}{dx}(c) = 0$ - **Constant Multiple Rule:** $\frac{d}{dx}(cf(x)) = c \frac{d}{dx}(f(x))$ - **Sum/Difference Rule:** $\frac{d}{dx}(f(x) \pm g(x)) = \frac{d}{dx}(f(x)) \pm \frac{d}{dx}(g(x))$ - **Product Rule:** $\frac{d}{dx}(f(x)g(x)) = f'(x)g(x) + f(x)g'(x)$ - **Quotient Rule:** $\frac{d}{dx}\left(\frac{f(x)}{g(x)}\right) = \frac{f'(x)g(x) - f(x)g'(x)}{(g(x))^2}$ - **Chain Rule:** $\frac{d}{dx}(f(g(x))) = f'(g(x)) \cdot g'(x)$ #### Derivatives of Common Functions - $\frac{d}{dx}(\sin x) = \cos x$ - $\frac{d}{dx}(\cos x) = -\sin x$ - $\frac{d}{dx}(\tan x) = \sec^2 x$ - $\frac{d}{dx}(e^x) = e^x$ - $\frac{d}{dx}(a^x) = a^x \ln a$ - $\frac{d}{dx}(\ln x) = \frac{1}{x}$ - $\frac{d}{dx}(\log_a x) = \frac{1}{x \ln a}$ ### Binomial Theorem #### For positive integer n - $(a+b)^n = \sum_{k=0}^n \binom{n}{k} a^{n-k} b^k$ - Where $\binom{n}{k} = \frac{n!}{k!(n-k)!}$ is the binomial coefficient. #### General Term - The $(k+1)$th term is $T_{k+1} = \binom{n}{k} a^{n-k} b^k$. #### Properties - Number of terms is $n+1$. - Sum of powers of $a$ and $b$ in each term is $n$. - $\binom{n}{k} = \binom{n}{n-k}$ #### For any real number n (Generalized Binomial Theorem) - $(1+x)^n = 1 + nx + \frac{n(n-1)}{2!}x^2 + \frac{n(n-1)(n-2)}{3!}x^3 + \dots$ - Valid for $|x| ### Probability, Permutation & Combination #### Permutations (Order matters) - **Number of permutations of n distinct items taken r at a time:** $P(n,r) = {}_nP_r = \frac{n!}{(n-r)!}$ - **Number of permutations of n items where $p_1$ are of one type, $p_2$ of another, etc.:** $\frac{n!}{p_1! p_2! \dots p_k!}$ #### Combinations (Order does not matter) - **Number of combinations of n distinct items taken r at a time:** $C(n,r) = {}_nC_r = \binom{n}{r} = \frac{n!}{r!(n-r)!}$ - **Properties:** $\binom{n}{r} = \binom{n}{n-r}$ and $\binom{n}{r} + \binom{n}{r+1} = \binom{n+1}{r+1}$ #### Probability - **Definition:** $P(E) = \frac{\text{Number of favorable outcomes}}{\text{Total number of outcomes}}$ - **Range:** $0 \le P(E) \le 1$ - **Complementary Event:** $P(E') = 1 - P(E)$ - **Addition Rule (for any two events A and B):** $P(A \cup B) = P(A) + P(B) - P(A \cap B)$ - **Addition Rule (for mutually exclusive events A and B):** $P(A \cup B) = P(A) + P(B)$ - **Conditional Probability:** $P(A|B) = \frac{P(A \cap B)}{P(B)}$ (Probability of A given B) - **Multiplication Rule:** $P(A \cap B) = P(A)P(B|A) = P(B)P(A|B)$ - **Multiplication Rule (for independent events A and B):** $P(A \cap B) = P(A)P(B)$ #### Bayes' Theorem - $P(A_i|B) = \frac{P(B|A_i)P(A_i)}{\sum_{j=1}^n P(B|A_j)P(A_j)}$