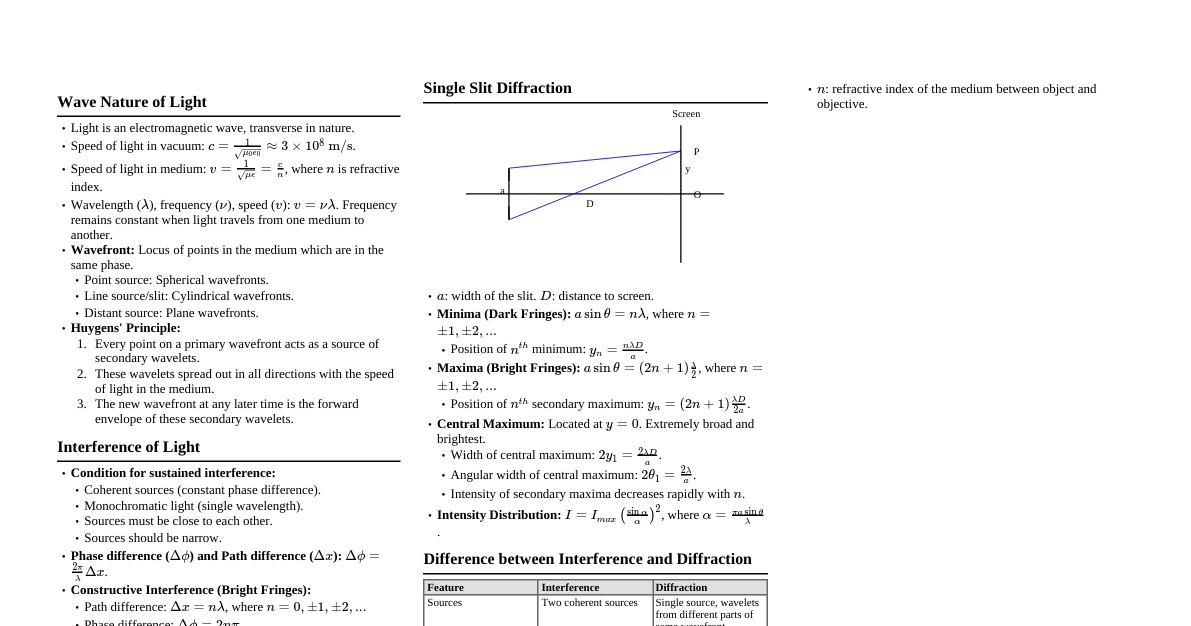
### Wavefronts & Huygens' Principle - **Wavefront:** Locus of points oscillating in the same phase. - **Types:** Spherical (point source), Cylindrical (line source), Plane (distant source). - **Huygens' Principle:** 1. Every point on a primary wavefront acts as a source of secondary wavelets. 2. These wavelets spread out in all directions with the speed of light. 3. The new wavefront at any instant is the forward envelope of these secondary wavelets. - **Laws of Reflection/Refraction from Huygens' Principle:** Explained by considering the time taken for wavelets to travel. ### Interference of Light - **Definition:** Superposition of two or more light waves resulting in a redistribution of energy. - **Conditions for Sustained Interference:** 1. Coherent sources (constant phase difference). 2. Monochromatic light (single wavelength). 3. Sources close to each other. 4. Sources of nearly equal amplitude. - **Constructive Interference:** - Path difference: $\Delta x = n\lambda$ - Phase difference: $\Delta\phi = 2n\pi$ - Intensity: $I_{max} = (\sqrt{I_1} + \sqrt{I_2})^2$ (If $I_1=I_2=I_0$, then $I_{max}=4I_0$) - **Destructive Interference:** - Path difference: $\Delta x = (2n+1)\frac{\lambda}{2}$ - Phase difference: $\Delta\phi = (2n+1)\pi$ - Intensity: $I_{min} = (\sqrt{I_1} - \sqrt{I_2})^2$ (If $I_1=I_2=I_0$, then $I_{min}=0$) ### Young's Double Slit Experiment (YDSE) - **Setup:** Two narrow slits (S1, S2) separated by distance 'd', illuminated by a monochromatic source. Screen at distance 'D' from slits. - **Fringe Position:** - Bright fringes (maxima): $y_n = \frac{n\lambda D}{d}$ - Dark fringes (minima): $y_n = \frac{(2n+1)\lambda D}{2d}$ - **Fringe Width ($\beta$):** Distance between two consecutive bright or dark fringes. - $\beta = \frac{\lambda D}{d}$ - **Angular Fringe Width ($\theta$):** $\theta = \frac{\beta}{D} = \frac{\lambda}{d}$ - **Intensity Distribution:** $I = I_{max}\cos^2(\frac{\phi}{2})$ where $\phi = \frac{2\pi}{\lambda}\Delta x$ ### Diffraction of Light - **Definition:** Bending of light waves around obstacles or spreading of light into the geometrical shadow region. - **Fraunhofer Diffraction (Single Slit):** - **Minima:** $d\sin\theta = n\lambda$ (where n = 1, 2, 3, ...) - **Maxima:** $d\sin\theta = (2n+1)\frac{\lambda}{2}$ (approximate, more complex for exact) - **Width of Central Maxima:** $2\theta = \frac{2\lambda}{d}$ (angular), $2y = \frac{2\lambda D}{d}$ (linear) - **Intensity:** Decreases rapidly from central maximum. ### Polarization of Light - **Definition:** Restriction of vibrations of light waves to a single plane. - **Unpolarized Light:** Vibrations in all possible planes perpendicular to propagation. - **Plane Polarized Light:** Vibrations confined to one plane. - **Polarizer:** Device used to produce plane polarized light. - **Malus's Law:** When plane polarized light of intensity $I_0$ passes through an analyzer, the transmitted intensity is $I = I_0\cos^2\theta$, where $\theta$ is the angle between the transmission axes of the polarizer and analyzer. - **Brewster's Law:** When unpolarized light is incident at Brewster's angle ($i_p$) on an interface, the reflected light is completely plane polarized. - $\tan i_p = n$ (where n is refractive index of the second medium). - At $i_p$, reflected and refracted rays are perpendicular to each other ($90^\circ$).