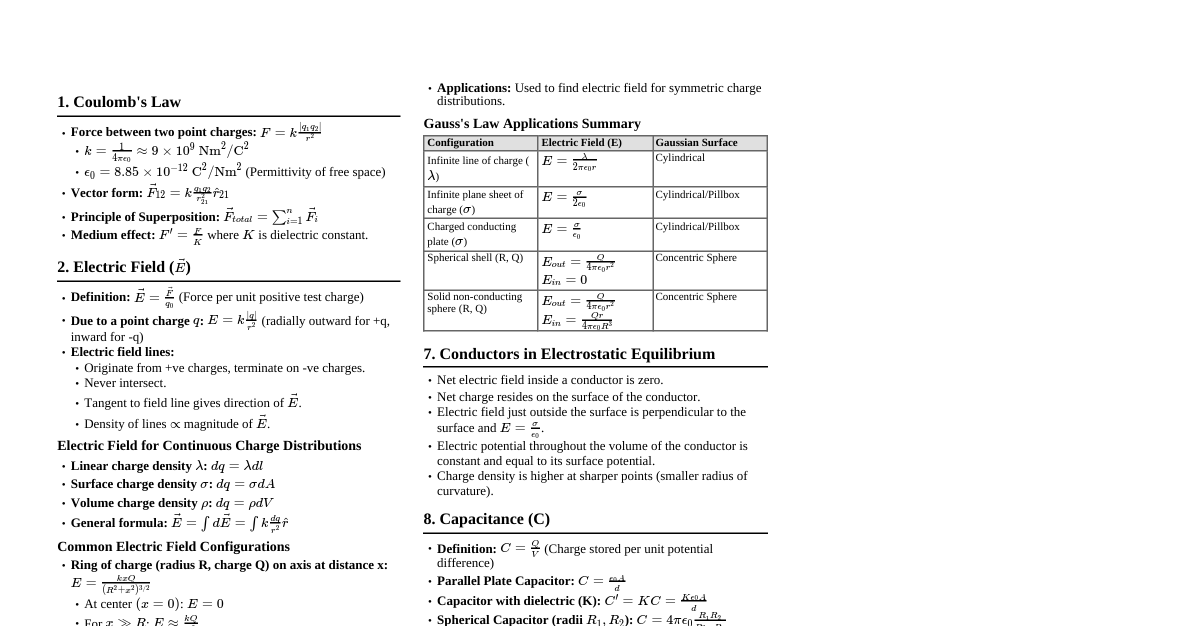
1. Basic Ratios & Identities $\sin \theta = \frac{\text{Opposite}}{\text{Hypotenuse}}$, $\cos \theta = \frac{\text{Adjacent}}{\text{Hypotenuse}}$, $\tan \theta = \frac{\text{Opposite}}{\text{Adjacent}}$ $\csc \theta = \frac{1}{\sin \theta}$, $\sec \theta = \frac{1}{\cos \theta}$, $\cot \theta = \frac{1}{\tan \theta}$ $\sin^2 \theta + \cos^2 \theta = 1$ $1 + \tan^2 \theta = \sec^2 \theta$ $1 + \cot^2 \theta = \csc^2 \theta$ 2. Angle Conversions Degrees to Radians: $x \text{ degrees} = x \times \frac{\pi}{180} \text{ radians}$ Radians to Degrees: $x \text{ radians} = x \times \frac{180}{\pi} \text{ degrees}$ 3. Allied Angles $\sin(-\theta) = -\sin \theta$, $\cos(-\theta) = \cos \theta$, $\tan(-\theta) = -\tan \theta$ $\sin(90^\circ - \theta) = \cos \theta$, $\cos(90^\circ - \theta) = \sin \theta$ $\sin(90^\circ + \theta) = \cos \theta$, $\cos(90^\circ + \theta) = -\sin \theta$ $\sin(180^\circ - \theta) = \sin \theta$, $\cos(180^\circ - \theta) = -\cos \theta$ $\sin(180^\circ + \theta) = -\sin \theta$, $\cos(180^\circ + \theta) = -\cos \theta$ For $n \in \mathbb{Z}$: $\sin(n\pi \pm \theta) = (-1)^n \sin \theta$, $\cos(n\pi \pm \theta) = (-1)^n \cos \theta$ For $n \in \mathbb{Z}$: $\sin((2n+1)\frac{\pi}{2} \pm \theta) = \pm \cos \theta$, $\cos((2n+1)\frac{\pi}{2} \pm \theta) = \mp \sin \theta$ 4. Compound Angle Formulas $\sin(A \pm B) = \sin A \cos B \pm \cos A \sin B$ $\cos(A \pm B) = \cos A \cos B \mp \sin A \sin B$ $\tan(A \pm B) = \frac{\tan A \pm \tan B}{1 \mp \tan A \tan B}$ $\cot(A \pm B) = \frac{\cot A \cot B \mp 1}{\cot B \pm \cot A}$ 5. Multiple Angle Formulas $\sin 2A = 2 \sin A \cos A = \frac{2 \tan A}{1 + \tan^2 A}$ $\cos 2A = \cos^2 A - \sin^2 A = 2 \cos^2 A - 1 = 1 - 2 \sin^2 A = \frac{1 - \tan^2 A}{1 + \tan^2 A}$ $\tan 2A = \frac{2 \tan A}{1 - \tan^2 A}$ $\sin 3A = 3 \sin A - 4 \sin^3 A$ $\cos 3A = 4 \cos^3 A - 3 \cos A$ $\tan 3A = \frac{3 \tan A - \tan^3 A}{1 - 3 \tan^2 A}$ 6. Half Angle Formulas $\sin A = 2 \sin \frac{A}{2} \cos \frac{A}{2}$ $\cos A = \cos^2 \frac{A}{2} - \sin^2 \frac{A}{2}$ $1 - \cos A = 2 \sin^2 \frac{A}{2} \implies \sin \frac{A}{2} = \pm \sqrt{\frac{1 - \cos A}{2}}$ $1 + \cos A = 2 \cos^2 \frac{A}{2} \implies \cos \frac{A}{2} = \pm \sqrt{\frac{1 + \cos A}{2}}$ $\tan \frac{A}{2} = \pm \sqrt{\frac{1 - \cos A}{1 + \cos A}} = \frac{1 - \cos A}{\sin A} = \frac{\sin A}{1 + \cos A}$ 7. Product-to-Sum & Sum-to-Product Product-to-Sum $2 \sin A \cos B = \sin(A+B) + \sin(A-B)$ $2 \cos A \sin B = \sin(A+B) - \sin(A-B)$ $2 \cos A \cos B = \cos(A+B) + \cos(A-B)$ $2 \sin A \sin B = \cos(A-B) - \cos(A+B)$ Sum-to-Product $\sin C + \sin D = 2 \sin \left(\frac{C+D}{2}\right) \cos \left(\frac{C-D}{2}\right)$ $\sin C - \sin D = 2 \cos \left(\frac{C+D}{2}\right) \sin \left(\frac{C-D}{2}\right)$ $\cos C + \cos D = 2 \cos \left(\frac{C+D}{2}\right) \cos \left(\frac{C-D}{2}\right)$ $\cos C - \cos D = -2 \sin \left(\frac{C+D}{2}\right) \sin \left(\frac{C-D}{2}\right)$ 8. Trigonometric Equations: General Solutions $\sin \theta = \sin \alpha \implies \theta = n\pi + (-1)^n \alpha$, where $n \in \mathbb{Z}$ $\cos \theta = \cos \alpha \implies \theta = 2n\pi \pm \alpha$, where $n \in \mathbb{Z}$ $\tan \theta = \tan \alpha \implies \theta = n\pi + \alpha$, where $n \in \mathbb{Z}$ $\sin^2 \theta = \sin^2 \alpha \implies \theta = n\pi \pm \alpha$, where $n \in \mathbb{Z}$ $\cos^2 \theta = \cos^2 \alpha \implies \theta = n\pi \pm \alpha$, where $n \in \mathbb{Z}$ $\tan^2 \theta = \tan^2 \alpha \implies \theta = n\pi \pm \alpha$, where $n \in \mathbb{Z}$ 9. Inverse Trigonometric Functions Domain & Range Function Domain Range $\sin^{-1} x$ $[-1, 1]$ $[-\frac{\pi}{2}, \frac{\pi}{2}]$ $\cos^{-1} x$ $[-1, 1]$ $[0, \pi]$ $\tan^{-1} x$ $(-\infty, \infty)$ $(-\frac{\pi}{2}, \frac{\pi}{2})$ $\csc^{-1} x$ $(-\infty, -1] \cup [1, \infty)$ $[-\frac{\pi}{2}, 0) \cup (0, \frac{\pi}{2}]$ $\sec^{-1} x$ $(-\infty, -1] \cup [1, \infty)$ $[0, \frac{\pi}{2}) \cup (\frac{\pi}{2}, \pi]$ $\cot^{-1} x$ $(-\infty, \infty)$ $(0, \pi)$ Properties $\sin^{-1} x + \cos^{-1} x = \frac{\pi}{2}$, for $x \in [-1, 1]$ $\tan^{-1} x + \cot^{-1} x = \frac{\pi}{2}$, for $x \in \mathbb{R}$ $\csc^{-1} x + \sec^{-1} x = \frac{\pi}{2}$, for $|x| \ge 1$ $\tan^{-1} x + \tan^{-1} y = \tan^{-1} \left(\frac{x+y}{1-xy}\right)$, if $xy $\tan^{-1} x - \tan^{-1} y = \tan^{-1} \left(\frac{x-y}{1+xy}\right)$, if $xy > -1$ $2 \tan^{-1} x = \sin^{-1} \left(\frac{2x}{1+x^2}\right) = \cos^{-1} \left(\frac{1-x^2}{1+x^2}\right) = \tan^{-1} \left(\frac{2x}{1-x^2}\right)$ 10. Properties of Triangle (Sine Rule, Cosine Rule, Area) Sine Rule $\frac{a}{\sin A} = \frac{b}{\sin B} = \frac{c}{\sin C} = 2R$ (where $R$ is circumradius) Cosine Rule $a^2 = b^2 + c^2 - 2bc \cos A \implies \cos A = \frac{b^2+c^2-a^2}{2bc}$ $b^2 = a^2 + c^2 - 2ac \cos B \implies \cos B = \frac{a^2+c^2-b^2}{2ac}$ $c^2 = a^2 + b^2 - 2ab \cos C \implies \cos C = \frac{a^2+b^2-c^2}{2ab}$ Area of Triangle Area $= \frac{1}{2}bc \sin A = \frac{1}{2}ca \sin B = \frac{1}{2}ab \sin C$ Area $= \sqrt{s(s-a)(s-b)(s-c)}$ (Heron's Formula), where $s = \frac{a+b+c}{2}$ Area $= \frac{abc}{4R}$ 11. Important Values Angle $0^\circ$ $30^\circ$ $45^\circ$ $60^\circ$ $90^\circ$ $\sin \theta$ $0$ $\frac{1}{2}$ $\frac{1}{\sqrt{2}}$ $\frac{\sqrt{3}}{2}$ $1$ $\cos \theta$ $1$ $\frac{\sqrt{3}}{2}$ $\frac{1}{\sqrt{2}}$ $\frac{1}{2}$ $0$ $\tan \theta$ $0$ $\frac{1}{\sqrt{3}}$ $1$ $\sqrt{3}$ Undefined