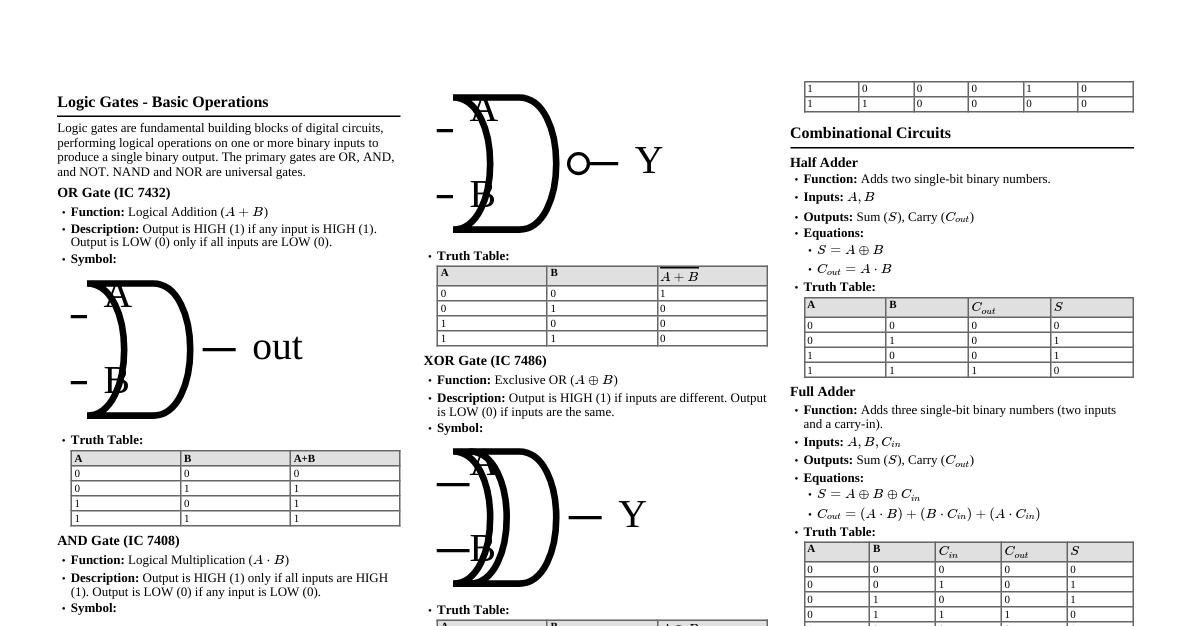
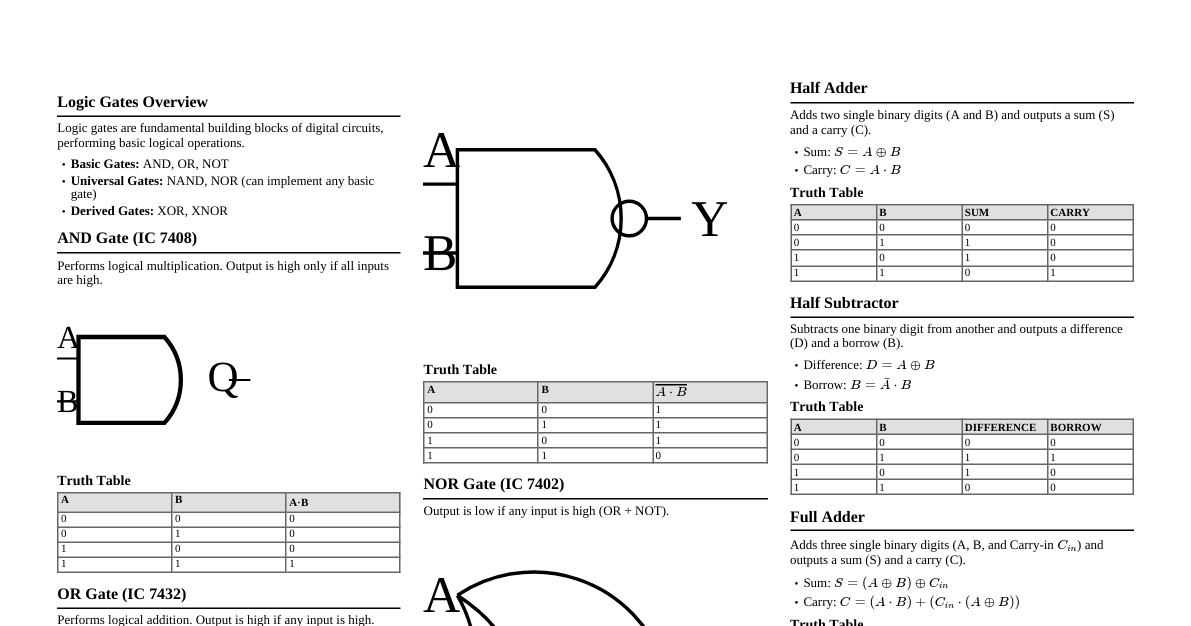
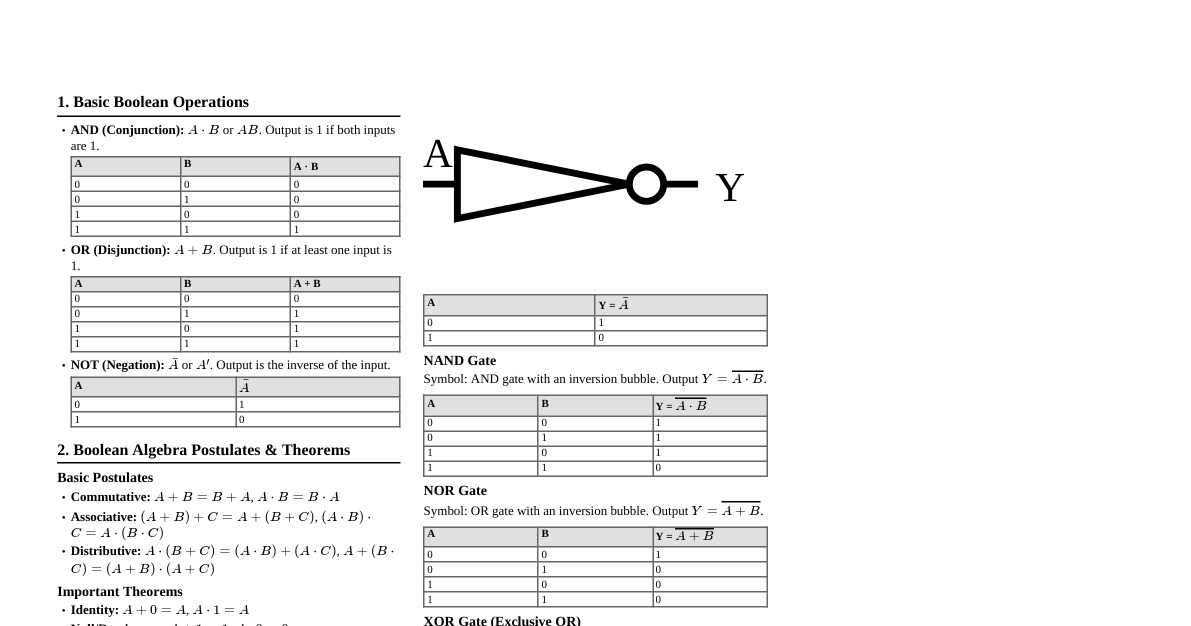
Multiplexer (MUX) A multiplexer is a combinational circuit that selects one of many input lines and directs it to a single output line. The selection is controlled by select lines. #### 2-to-1 MUX - **Truth Table:** | S | I1 | I0 | Y | |---|----|----|---| | 0 | X | 0 | 0 | | 0 | X | 1 | 1 | | 1 | 0 | X | 0 | | 1 | 1 | X | 1 | - **Boolean Expression:** $Y = S'I_0 + SI_1$ - **Logic Circuit:** ``` I0 ---| | I1 ---|--- MUX --- Y | S ----| ``` #### 4-to-1 MUX - **Truth Table:** | S1 | S0 | I3 | I2 | I1 | I0 | Y | |----|----|----|----|----|----|---| | 0 | 0 | X | X | X | 0 | 0 | | 0 | 0 | X | X | X | 1 | 1 | | 0 | 1 | X | X | 0 | X | 0 | | 0 | 1 | X | X | 1 | X | 1 | | 1 | 0 | X | 0 | X | X | 0 | | 1 | 0 | X | 1 | X | X | 1 | | 1 | 1 | 0 | X | X | X | 0 | | 1 | 1 | 1 | X | X | X | 1 | - **Boolean Expression:** $Y = S_1'S_0'I_0 + S_1'S_0I_1 + S_1S_0'I_2 + S_1S_0I_3$ - **Logic Circuit (Conceptual):** ``` I0 ---| I1 ---| I2 ---|--- 4-to-1 MUX --- Y I3 ---| | S1 ---| S0 ---| ``` Encoder An encoder is a combinational circuit that converts an active input signal into a coded output signal (e.g., binary, BCD). It performs the inverse operation of a decoder. #### 4-to-2 Binary Encoder - **Truth Table:** | D3 | D2 | D1 | D0 | A1 | A0 | |----|----|----|----|----|----| | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 | | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 | - **Boolean Expressions (assuming only one input is high at a time):** - $A_1 = D_3 + D_2$ - $A_0 = D_3 + D_1$ - **Logic Circuit:** ``` D1 ---| |--- OR -- A0 D3 ---| D2 ---| |--- OR -- A1 D3 ---| ``` - **K-Map for A1:** | D1\D0 | 00 | 01 | 11 | 10 | |-------|----|----|----|----| | 00 | X | 0 | X | X | | 01 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 | | 11 | 1 | X | X | X | | 10 | 1 | X | X | X | (Note: K-maps for encoders are typically simplified assuming priority or only one input active at a time to avoid invalid states) For $A_1 = D_3 + D_2$: | D3D2\D1D0 | 00 | 01 | 11 | 10 | |-----------|----|----|----|----| | 00 | X | 0 | 0 | 0 | | 01 | 1 | X | X | X | | 11 | X | X | X | X | | 10 | 1 | X | X | X | (Only the active input cases are considered) - **K-Map for A0:** For $A_0 = D_3 + D_1$: | D3D2\D1D0 | 00 | 01 | 11 | 10 | |-----------|----|----|----|----| | 00 | X | 0 | 1 | 0 | | 01 | 0 | X | X | X | | 11 | X | X | X | X | | 10 | 1 | X | X | X | Full Adder A full adder is a combinational circuit that performs the addition of three binary bits (two input bits and a carry-in bit). It produces a sum bit and a carry-out bit. - **Inputs:** A, B, Cin - **Outputs:** Sum (S), Carry Out (Cout) - **Truth Table:** | A | B | Cin | Sum | Cout | |---|---|-----|-----|------| | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 0 | | 0 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | | 0 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 | | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 1 | | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 | | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | - **Boolean Expressions:** - $Sum = A \oplus B \oplus Cin$ - $Cout = AB + ACin + BCin = AB + Cin(A \oplus B)$ - **Logic Circuit:** ``` A ---| |--- XOR ---| | | |--- XOR --- Sum B ---|--- XOR ---| | | | | Cin ---------------| A ---| |--- AND ---| B ---| | |--- OR --- Cout A ---| | |--- AND ---| Cin ---| | | B ---| | |--- AND ---| Cin ---| ``` - **K-Map for Sum:** | A\BCin | 00 | 01 | 11 | 10 | |--------|----|----|----|----| | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 1 | | 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | (This pattern is characteristic of XOR, hence $A \oplus B \oplus Cin$) - **K-Map for Cout:** | A\BCin | 00 | 01 | 11 | 10 | |--------|----|----|----|----| | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | | 1 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 1 | Grouping: - Group of 4: (none) - Group of 2s: - $AB$ (from $A=1, B=1, Cin=0$ and $A=1, B=1, Cin=1$) - $ACin$ (from $A=1, B=0, Cin=1$ and $A=1, B=1, Cin=1$) - $BCin$ (from $A=0, B=1, Cin=1$ and $A=1, B=1, Cin=1$) Resulting in $Cout = AB + ACin + BCin$. Full Subtractor A full subtractor is a combinational circuit that performs subtraction of three binary bits (minuend, subtrahend, and borrow-in bit). It produces a difference bit and a borrow-out bit. - **Inputs:** A (Minuend), B (Subtrahend), Bin (Borrow In) - **Outputs:** Difference (D), Bout (Borrow Out) - **Truth Table:** | A | B | Bin | D | Bout | |---|---|-----|---|------| | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 1 | | 0 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 1 | | 0 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 | | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | - **Boolean Expressions:** - $D = A \oplus B \oplus Bin$ - $Bout = A'B + A'Bin + BBin = A'B + Bin(A' \oplus B)$ - **Logic Circuit:** ``` A ---| |--- XOR ---| | | |--- XOR --- D B ---|--- XOR ---| | | | | Bin --------------| A' ---| |--- AND ---| B ----| | |--- OR --- Bout A' ---| | |--- AND ---| Bin ---| | | B ----| | |--- AND ---| Bin ---| ``` - **K-Map for Difference (D):** | A\BBin | 00 | 01 | 11 | 10 | |--------|----|----|----|----| | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 1 | | 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | (This pattern is characteristic of XOR, hence $A \oplus B \oplus Bin$) - **K-Map for Borrow Out (Bout):** | A\BBin | 00 | 01 | 11 | 10 | |--------|----|----|----|----| | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 1 | | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | Grouping: - Group of 4: (none) - Group of 2s: - $A'B$ (from $A=0, B=1, Bin=0$ and $A=0, B=1, Bin=1$) - $A'Bin$ (from $A=0, B=0, Bin=1$ and $A=0, B=1, Bin=1$) - $BBin$ (from $A=0, B=1, Bin=1$ and $A=1, B=1, Bin=1$) Resulting in $Bout = A'B + A'Bin + BBin$.