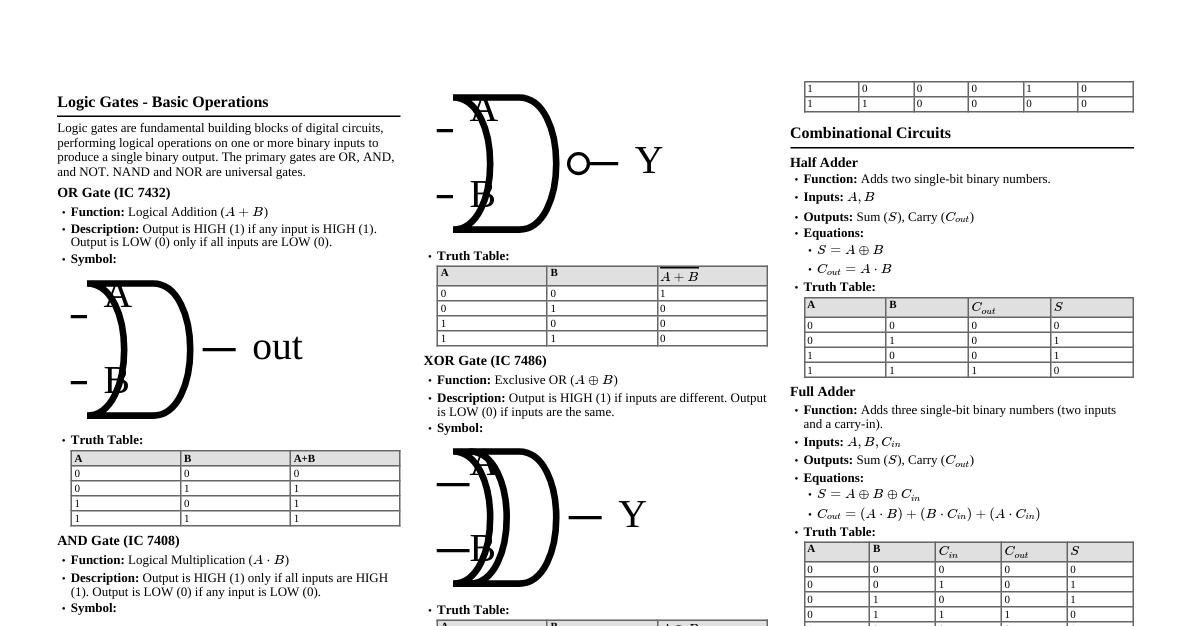
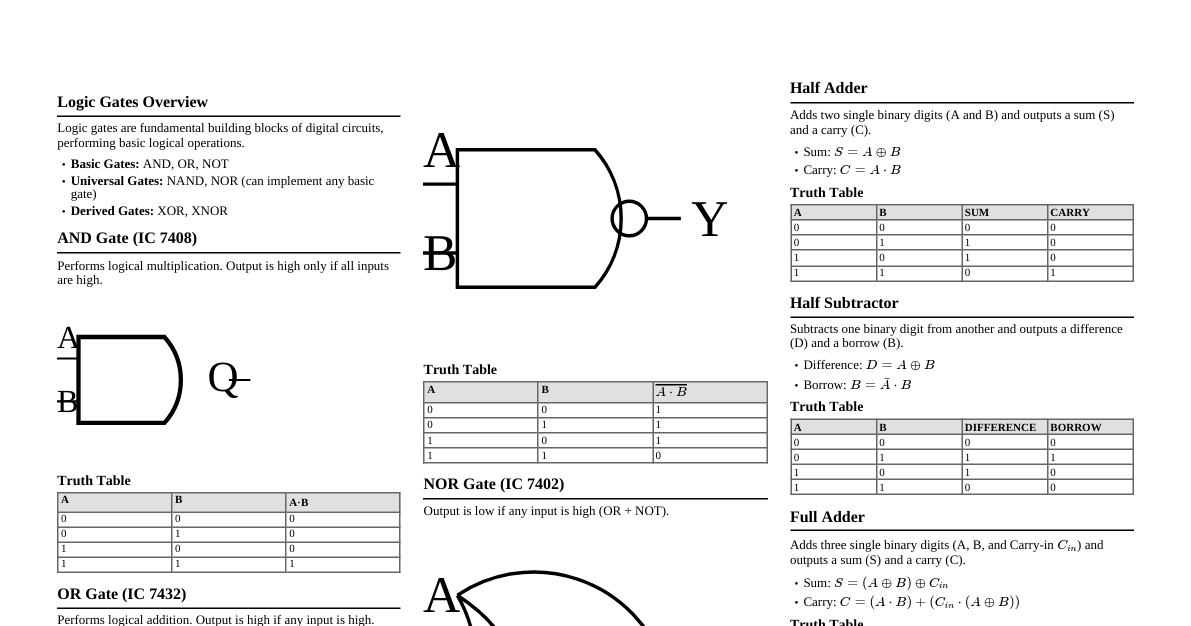
1. Basic Boolean Operations AND (Conjunction): $A \cdot B$ or $AB$. Output is 1 if both inputs are 1. A B A $\cdot$ B 0 0 0 0 1 0 1 0 0 1 1 1 OR (Disjunction): $A + B$. Output is 1 if at least one input is 1. A B A + B 0 0 0 0 1 1 1 0 1 1 1 1 NOT (Negation): $\bar{A}$ or $A'$. Output is the inverse of the input. A $\bar{A}$ 0 1 1 0 2. Boolean Algebra Postulates & Theorems Basic Postulates Commutative: $A+B = B+A$, $A \cdot B = B \cdot A$ Associative: $(A+B)+C = A+(B+C)$, $(A \cdot B) \cdot C = A \cdot (B \cdot C)$ Distributive: $A \cdot (B+C) = (A \cdot B) + (A \cdot C)$, $A + (B \cdot C) = (A+B) \cdot (A+C)$ Important Theorems Identity: $A+0=A$, $A \cdot 1=A$ Null/Dominance: $A+1=1$, $A \cdot 0=0$ Idempotence: $A+A=A$, $A \cdot A=A$ Complementation: $A+\bar{A}=1$, $A \cdot \bar{A}=0$ Involution: $\overline{\bar{A}} = A$ Absorption: $A + (A \cdot B) = A$, $A \cdot (A+B) = A$ Consensus: $(A \cdot B) + (\bar{A} \cdot C) + (B \cdot C) = (A \cdot B) + (\bar{A} \cdot C)$ 3. De Morgan's Theorems $\overline{A+B} = \bar{A} \cdot \bar{B}$ (NOR is equivalent to inverted AND) $\overline{A \cdot B} = \bar{A} + \bar{B}$ (NAND is equivalent to inverted OR) 4. Logic Gates Symbols & Truth Tables AND Gate Symbol: A B Y A B Y = A $\cdot$ B 0 0 0 0 1 0 1 0 0 1 1 1 OR Gate Symbol: A B Y A B Y = A + B 0 0 0 0 1 1 1 0 1 1 1 1 NOT Gate (Inverter) Symbol: A Y A Y = $\bar{A}$ 0 1 1 0 NAND Gate Symbol: AND gate with an inversion bubble. Output $Y = \overline{A \cdot B}$. A B Y = $\overline{A \cdot B}$ 0 0 1 0 1 1 1 0 1 1 1 0 NOR Gate Symbol: OR gate with an inversion bubble. Output $Y = \overline{A + B}$. A B Y = $\overline{A + B}$ 0 0 1 0 1 0 1 0 0 1 1 0 XOR Gate (Exclusive OR) Symbol: OR gate with an additional curved line at input. Output $Y = A \oplus B = A\bar{B} + \bar{A}B$. A B Y = A $\oplus$ B 0 0 0 0 1 1 1 0 1 1 1 0 XNOR Gate (Exclusive NOR) Symbol: XOR gate with an inversion bubble. Output $Y = \overline{A \oplus B} = A B + \bar{A}\bar{B}$. A B Y = $\overline{A \oplus B}$ 0 0 1 0 1 0 1 0 0 1 1 1 5. Minterms and Maxterms Minterm (Standard Product): A product term containing all variables in either complemented or uncomplemented form. Denoted $m_i$. E.g., for 2 variables (A, B): $m_0 = \bar{A}\bar{B}$, $m_1 = \bar{A}B$, $m_2 = A\bar{B}$, $m_3 = AB$. Maxterm (Standard Sum): A sum term containing all variables in either complemented or uncomplemented form. Denoted $M_i$. E.g., for 2 variables (A, B): $M_0 = A+B$, $M_1 = A+\bar{B}$, $M_2 = \bar{A}+B$, $M_3 = \bar{A}+\bar{B}$. Relationship: $\overline{m_i} = M_i$ and $\overline{M_i} = m_i$. Sum of Products (SOP): Boolean expression as a sum of minterms. E.g., $F(A,B) = \sum m(1,3) = \bar{A}B + AB$. Product of Sums (POS): Boolean expression as a product of maxterms. E.g., $F(A,B) = \prod M(0,2) = (A+B)(\bar{A}+B)$. 6. Canonical Forms Canonical SOP: A sum of minterms. Each term is a minterm. Canonical POS: A product of maxterms. Each term is a maxterm. Any Boolean function can be expressed in both canonical SOP and POS forms. 7. Universal Gates NAND Gate: Can implement any other logic gate. NOT: $\overline{A} = A \text{ NAND } A$ AND: $A \cdot B = (A \text{ NAND } B) \text{ NAND } (A \text{ NAND } B)$ OR: $A+B = (\bar{A} \text{ NAND } \bar{B}) = (A \text{ NAND } A) \text{ NAND } (B \text{ NAND } B)$ NOR Gate: Can implement any other logic gate. NOT: $\overline{A} = A \text{ NOR } A$ OR: $A+B = (A \text{ NOR } B) \text{ NOR } (A \text{ NOR } B)$ AND: $A \cdot B = (\bar{A} \text{ NOR } \bar{B}) = (A \text{ NOR } A) \text{ NOR } (B \text{ NOR } B)$