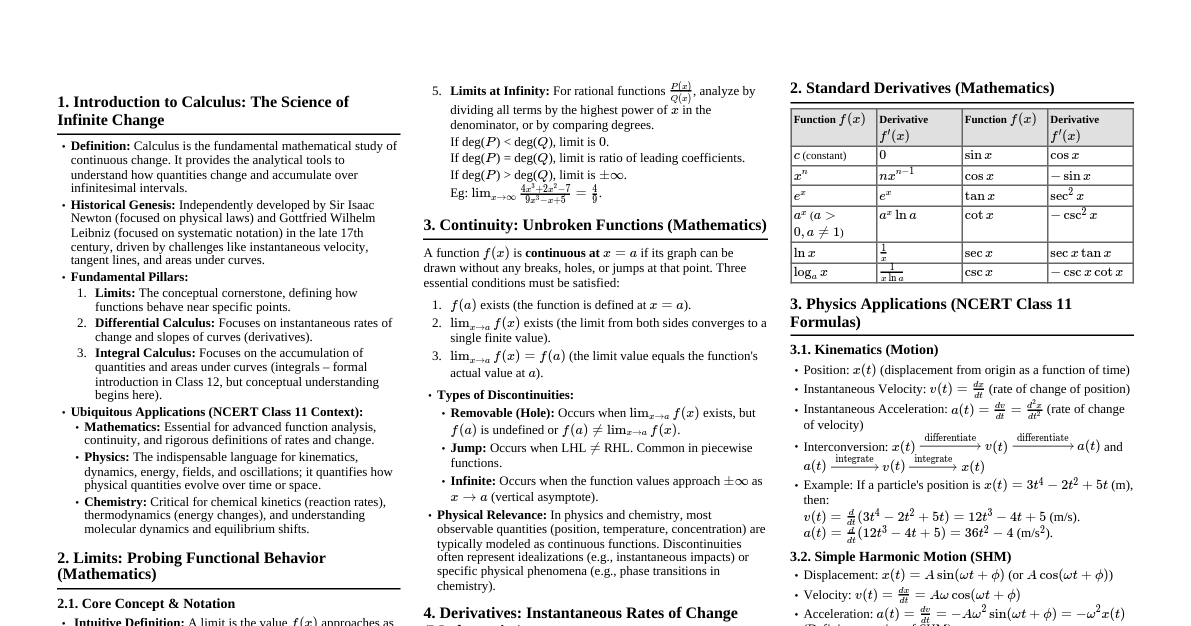
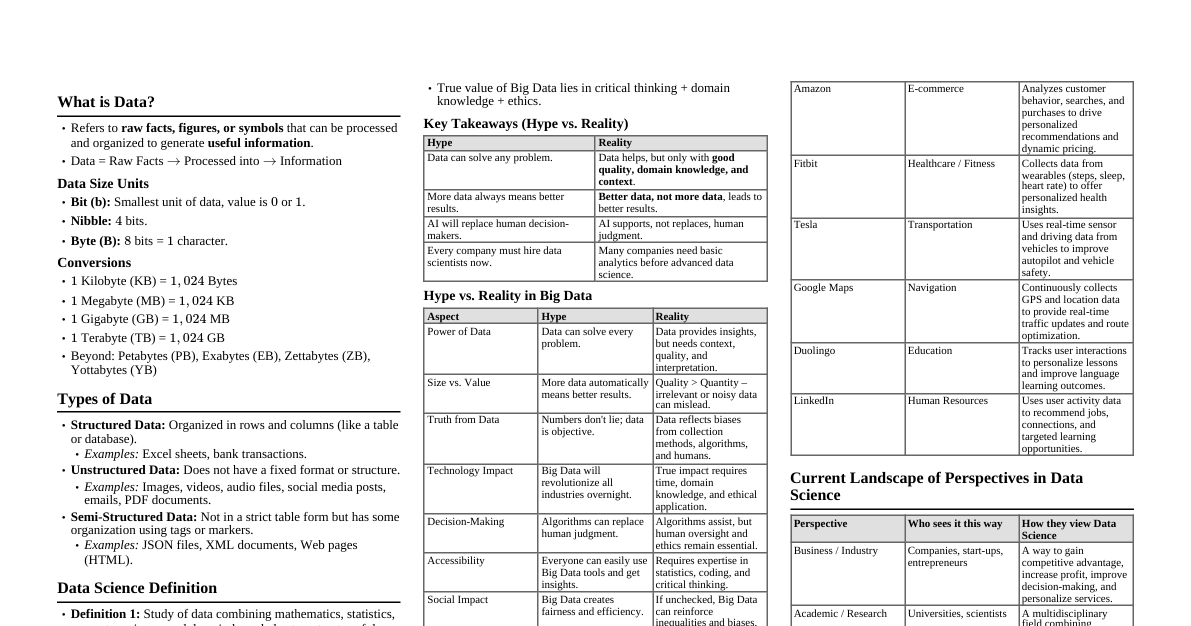
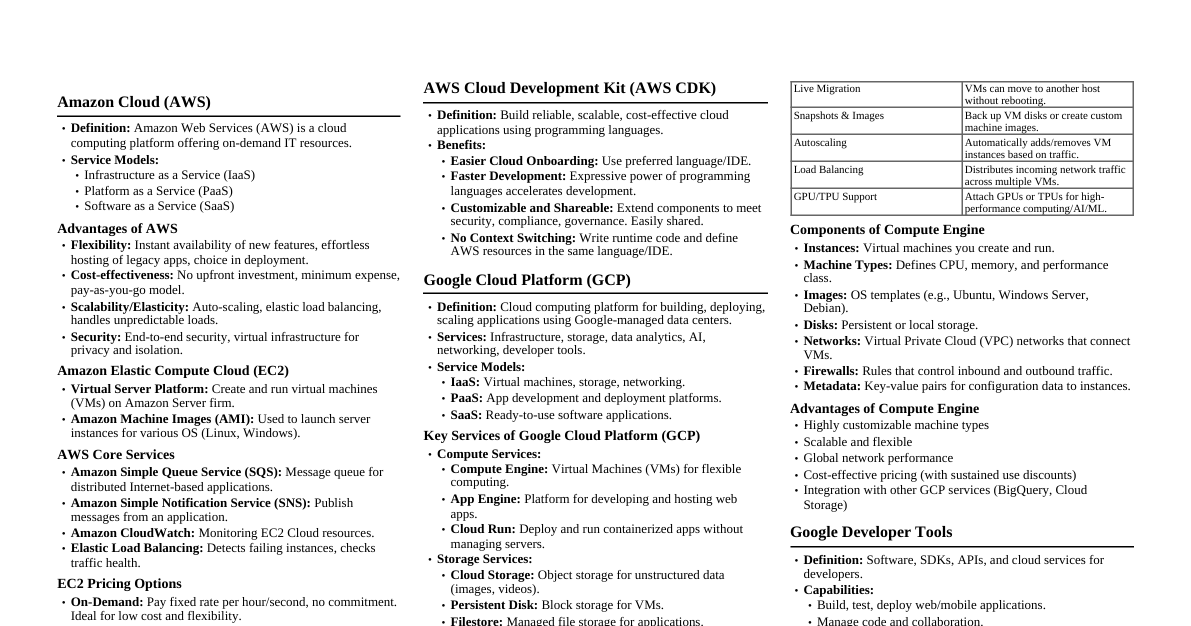
### Module 1: Computer Hardware Essentials This cheatsheet provides a quick overview of fundamental computer hardware components and their functions. #### Course Objectives: * **CO1:** Identify basic IT environment components. * **CO3:** Understand operating systems and network basics. ### Computer Hardware **Physical components** of a computer system. Works with software (instructions) to function. ### Von Neumann Architecture Modern computers store **programs and data in the same memory**. This allows for easier reprogramming. ### CPU - The Brain The CPU (Central Processing Unit) is the **brain of the computer**. It performs most processing, input/output, and storage functions. #### Main Components: 1. **Control Unit (CU):** Manages all CPU operations (fetch, decode, execute cycle). 2. **Arithmetic Logic Unit (ALU):** Performs calculations and logical operations. 3. **Registers:** Small, fast storage inside the CPU for temporary data. 4. **Cache Memory:** High-speed memory for frequently accessed data. #### How it Works: The Fetch-Decode-Execute Cycle 1. **Fetch:** Get instruction from memory. 2. **Decode:** Translate instruction. 3. **Execute:** Perform the instruction. 4. **Store:** Save result. ### CPU Types (by Cores) * **Single-Core:** One processing unit, handles one task at a time. * **Dual-Core:** Two processing units, better for basic multitasking. * **Multi-Core:** More than two cores (e.g., quad-core), excellent for heavy multitasking and demanding tasks. ### Memory Hardware components that store data for processing. #### Types of Memory: 1. **Primary Memory:** Fast, directly accessible by CPU (RAM, ROM, Cache). 2. **Secondary Memory:** Slower, non-volatile (permanent) storage (HDDs, SSDs, USB drives). ### Primary Memory Details #### RAM (Random Access Memory) * **Volatile:** Data is lost when power is off. * Stores programs and data *currently in use*. * **Types:** DRAM (main memory, needs refreshing), SRAM (cache, faster, no refreshing). #### ROM (Read Only Memory) * **Non-volatile:** Data remains when power is off. * Stores permanent instructions (e.g., firmware, BIOS). * **Types:** PROM (write once), EPROM (erasable with UV), EEPROM (electrically erasable). ### Secondary Memory Details Permanent storage, slower but larger capacity. #### Hard Disk Drives (HDDs) * **Magnetic Storage:** Data stored on spinning platters using magnetism. * **Components:** Platters, read/write heads, actuator arm. * **Characteristics:** High capacity, affordable, but slower and has moving parts (prone to mechanical failure). #### Solid State Drives (SSDs) * **Flash Memory:** No moving parts, uses NAND flash memory chips. * **Characteristics:** Much faster, durable, energy-efficient, silent. More expensive, limited write endurance. #### Optical Drives (CDs, DVDs, Blu-rays) * **Laser Technology:** Data stored as pits and lands, read by a laser. * **Uses:** Media distribution, backups. * **Characteristics:** Portable, affordable, but lower capacity and slower than HDDs/SSDs. ### I/O Communication How the computer exchanges data with external devices (keyboard, monitor, storage). #### Methods: 1. **Programmed I/O (PIO):** CPU directly manages data transfer, waits for device. (Inefficient) 2. **Interrupt-Driven I/O:** Device tells CPU when ready, CPU handles it, then returns to other tasks. (More efficient) 3. **Direct Memory Access (DMA):** Device transfers data directly to/from memory without CPU involvement. (Most efficient for bulk data) ### Device Management The OS manages and coordinates hardware devices. * **Device Drivers:** Software that lets the OS communicate with hardware. * **Device Controllers:** Hardware that manages a specific I/O device. * **Functions:** Allocates/deallocates devices, schedules access, monitors status. ### Interface Cards Hardware components that expand a computer's functionality. * **Network Interface Cards (NICs):** Connects computer to a network (wired/wireless). * **Graphics Cards (GPUs):** Enhances graphics processing (for gaming, video editing). * **Sound Cards:** Produces and records sound. ### Buses in Computer Communication pathways within the computer for data transfer. * **Data Bus:** Transfers actual data (bidirectional). * **Address Bus:** Specifies memory locations (unidirectional). * **Control Bus:** Carries control signals (e.g., read/write commands). ### Firmware Software embedded into hardware devices (e.g., BIOS, router firmware). * Acts as a bridge between hardware and software. * Provides basic instructions for hardware startup and operation. * **Non-volatile:** Stored permanently, but often updatable. ### Boot Process The sequence a computer follows to start up and load the OS. 1. **Power On + POST:** Hardware checks. 2. **Firmware (BIOS/UEFI):** Initializes hardware, finds boot device. 3. **Bootloader:** Loads OS kernel into memory. 4. **OS Kernel Init:** OS starts core functions and services. 5. **Login Screen:** Ready for user interaction.