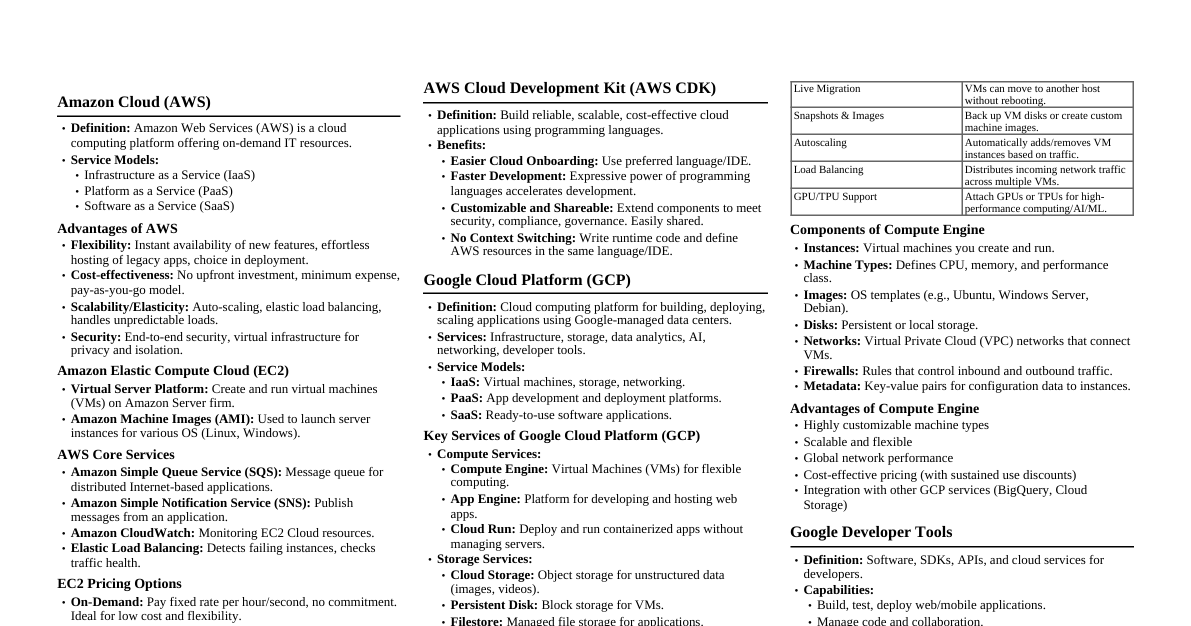
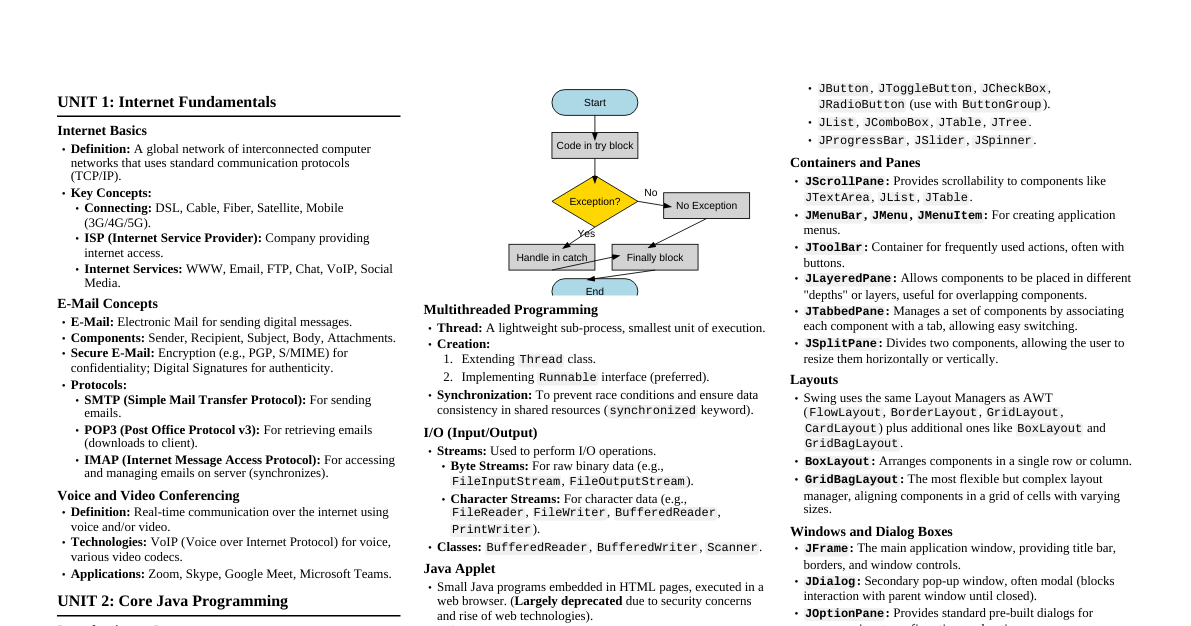
Cloud Computing Definition Cloud refers to a network or the internet. Technology uses remote servers to store, manage, and access data online. Data includes files, images, documents, audio, and video. Cloud Operations Developing new applications and services. Storage, backup, and data recovery. Hosting blogs and websites. Software delivery on demand. Data analysis. Streaming videos and audios. Why Cloud Computing? Overcomes traditional IT infrastructure complexities. Reduces IT infrastructure costs by eliminating need for server rooms, databases, mail servers, networking equipment, etc. Avoids large capital expenditure on IT setup. Essential Characteristics of Cloud Computing On-demand Self-service Users manage allotted storage, server uptime, etc. Users monitor consumption and use tools/resources directly from the cloud portal. Broad Network Access Services and resources accessed via various devices and platforms (internet). Access anytime, anywhere using smartphones, tablets, laptops, desktops. Resource Pooling Group of resources assigned to users. Computation, network, storage can be pooled. Resources dynamically provided based on need, not permanently allocated. Rapid Elasticity Ability to dynamically scale resources up or down based on demand. Measured Service Cloud services charge based on resource usage (e.g., per hour, number of transactions). Usage (storage, data transfer) is measured. Roots of Cloud Computing Internet Technologies: Publicly accessible, central storage, networks, bandwidth. Distributed Computing: Grid, utility, and cluster computing. Data stored on hard disks or internet, accessible from anywhere. Hardware: Virtual cloud computing, less need for physical hardware. Virtualization allows access to resources from virtual machines, making services cheaper. System Management: Autonomous cloud and data center automation. Improves productivity, ensures easy data access, allows configuration changes, and self-managing administration. Reduces human involvement. Service Models Software as a Service (SaaS) "On-demand software" hosted by a cloud service provider. Users access applications via internet and web browser. No need to install/run applications on local computers; eliminates hardware/software maintenance. Pay-as-you-go complete software solution. Many apps run directly in browser; no downloads/installations. Examples: Email, calendaring, office tools, CRM, ERP, marketing software, accounting software, HR software. Characteristics of SaaS Managed from a central location. Hosted on a remote server. Accessible over the internet. Users not responsible for hardware/software updates. Updates applied automatically. Purchased on a pay-as-per-use basis. Advantages of SaaS Easy to Buy: Monthly/annual subscriptions, low cost access to business functionality. One to Many: Single application instance shared by multiple users. Less Hardware Required: Software hosted remotely, no need for additional hardware investment. Low Maintenance: No installation, setup, or daily maintenance. Usage-based Pricing: Vendors price based on usage parameters. Easy Monitoring: Provides automatic updates. No Special Software/Hardware: All users have same version, accessed via web browser. Reduced IT Support Costs: Outsourced hardware/software maintenance. Multi-device Support: Accessible from desktops, laptops, tablets, phones. API Integration: Easily integrates with other software/services via standard APIs. No Client-side Installation: Accessed directly via internet connection. Disadvantages of SaaS Security: Data stored in cloud presents security concerns (breaches, unauthorized access). Not inherently more secure than in-house. Latency: Data/applications stored remotely can lead to greater latency than local deployment. Not suitable for applications needing millisecond response times. Total Dependency on Internet: Most SaaS apps unusable without internet. Difficult Vendor Switching: Transferring large data files and converting/importing to another SaaS is complex and slow. Platform as a Service (PaaS) Provides a platform and environment for developers to develop, test, run, and manage applications using the internet. Services hosted in the cloud, accessed via web browser. PaaS provider hosts hardware/software, freeing users from in-house installation. Consumer does not manage underlying cloud infrastructure (network, servers, OS, storage). Consumer controls deployed applications and configuration settings for hosting environment. Examples: Google App Engine (GAE), Salesforce.com, Windows Azure. Characteristics of PaaS Accessible to various users via the same development application. Integrates with web services and databases. Builds on virtualization technology, allowing scalable resources. Supports multiple languages and frameworks. Provides "Auto-scale" ability. Advantages of PaaS Simplified Development: Developers focus on innovation, not infrastructure management. Lower Risk: No upfront hardware/software investment; only PC and internet needed to build apps. Prebuilt Business Functionality: Some vendors offer defined functionality, allowing projects to start directly. Instant Community: Online communities for sharing experiences and advice. Scalability: Applications scale from one to thousands of users without changes. Disadvantages of PaaS Vendor Lock-in: Applications written for a specific PaaS vendor make migration difficult. Data Privacy: Corporate data not within company walls poses privacy risks. Integration Issues: Mixing local and cloud applications can increase complexity. Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS) / Hardware as a Service (HaaS) Allows customers to outsource IT infrastructures: servers, networking, processing, storage, virtual machines, and other resources. Customers access resources over the internet on a pay-as-per-use model. Clients dynamically scale configuration to meet changing requirements, billed only for services used. Examples: Amazon Web Services, Reliance Communications, Sify Technologies, Tata Communications. Characteristics of IaaS Resources available as a service. Highly scalable services. Dynamic and flexible. GUI and API-based access. Automated administrative tasks. Advantages of IaaS Shared Infrastructure: Multiple users share same physical infrastructure. Web Access: IT users access resources over the internet. Pay-as-per-use Model: Pay only for what's used. Focus on Core Business: Providers handle infrastructure, allowing organizations to focus on their core business. On-demand Scalability: Users don't worry about hardware upgrades or troubleshooting. Disadvantages of IaaS Security: Not always 100% secure. Maintenance & Upgrade: Providers maintain software but may not upgrade for all organizations. Interoperability Issues: Difficult to migrate virtual machines (VMs) between IaaS providers, leading to vendor lock-in. Cloud Deployment Models Public Cloud Private Cloud Hybrid Cloud Community Cloud Public Cloud Open to all for storage and access via internet, pay-per-usage. Computing resources managed and operated by a Cloud Service Provider (CSP). Examples: Amazon EC2, IBM SmartCloud Enterprise, Microsoft Azure, Google App Engine. Advantages of Public Cloud Lower cost than private/hybrid clouds. Maintained by CSP, no maintenance worries. Easier to integrate, better flexibility. Location independent, services delivered via internet. Highly scalable. Accessible by general public, no user limits. Disadvantages of Public Cloud Less secure due to shared public resources. Performance depends on internet link to cloud provider. Client has no control of data. Private Cloud Internal or corporate cloud. Used by organizations to build and manage data centers internally or by third party. Deployed using Open-source tools like Openstack and Eucalyptus. Divided into: On-premise private cloud and Outsourced private cloud. Advantages of Private Cloud High level of security and privacy. Better performance, improved speed and space capacity. IT team quickly allocates and delivers on-demand IT resources. Organization has full control, no dependency on others. Suitable for organizations needing separate cloud for personal use and data security. Disadvantages of Private Cloud Requires skilled people to manage and operate. Accessible only within the organization, limited operations. Not suitable for organizations with high user base or lacking prebuilt infrastructure/manpower. Hybrid Cloud Combination of public and private clouds. Partially secure: public cloud services accessible by anyone, private cloud services only by organization users. Examples: Google Application Suite (Gmail, Google Apps, Google Drive), Office 365, Amazon Web Services. Advantages of Hybrid Cloud Suitable for organizations needing more security than public cloud. Helps deliver new products and services quickly. Excellent way to reduce risk. Offers flexible and secure resources due to public and private cloud components. Disadvantages of Hybrid Cloud Security not as good as private cloud. Complex to manage due to multiple deployment models. Reliability of services depends on cloud service providers. Community Cloud Allows a group of organizations to share systems and services. Owned, managed, and operated by one or more organizations in the community, a third party, or a combination. Example: Health Care community cloud. Advantages of Community Cloud Cost-effective as shared by several organizations/communities. Flexible and scalable, compatible with every user, allows document modification. Better security than public cloud. Provides collaborative and distributive environment. Allows sharing of cloud resources, infrastructure, and capabilities among organizations. Disadvantages of Community Cloud Not a good choice for every organization. Security features not as good as private cloud. Sharing responsibilities among organizations is difficult. Fixed amount of data storage and bandwidth shared among members. Costly compared to public cloud. Cloud Computing Architecture Front End Used by the client. Contains client-side interfaces and applications for accessing cloud computing platforms. Includes web browsers (Chrome, Firefox, Internet Explorer, etc.). Back End Used by the service provider. Manages all resources required to provide cloud computing services. Includes data storage, security mechanisms, virtual machines, deployment models, servers, traffic control mechanisms. Components of Cloud Computing Architecture Client Infrastructure: Front end component, provides GUI to interact with the cloud. Application: Software or platform client wants to access. Service: Manages type of service accessed based on client's requirement. Runtime Cloud: Provides execution and runtime environment for virtual machines. Storage: Important component for storing and managing data. Infrastructure: Provides services at host, application, and network levels. Includes hardware, software, network devices, virtualization software. Management: Manages components (application, service, runtime cloud, storage, infrastructure, security) and establishes coordination. Security: In-built back end component, implements security mechanisms. Internet: Medium for front end and back end interaction. Applications of Cloud Art Applications: Quickly design cards, booklets, images. Business Applications: Based on cloud service providers, available 24/7. Data Storage and Backup: Store and access data (files, images, audio, video) via internet. Cloud provider responsible for security and backup recovery. Education Applications: Online distance learning platforms, student information portals. Virtual classrooms, accessibility, secure storage, scalability, minimal hardware requirements. Entertainment Applications: Multi-cloud strategy to interact with target audience. Online games, video conferencing. Management Applications: Cloud management tools for admins to manage cloud activities (resource deployment, data integration, disaster recovery). Provide administrative control over platforms, apps, infrastructure. Social Applications: Social networking apps (Facebook, Twitter, LinkedIn) to connect users.