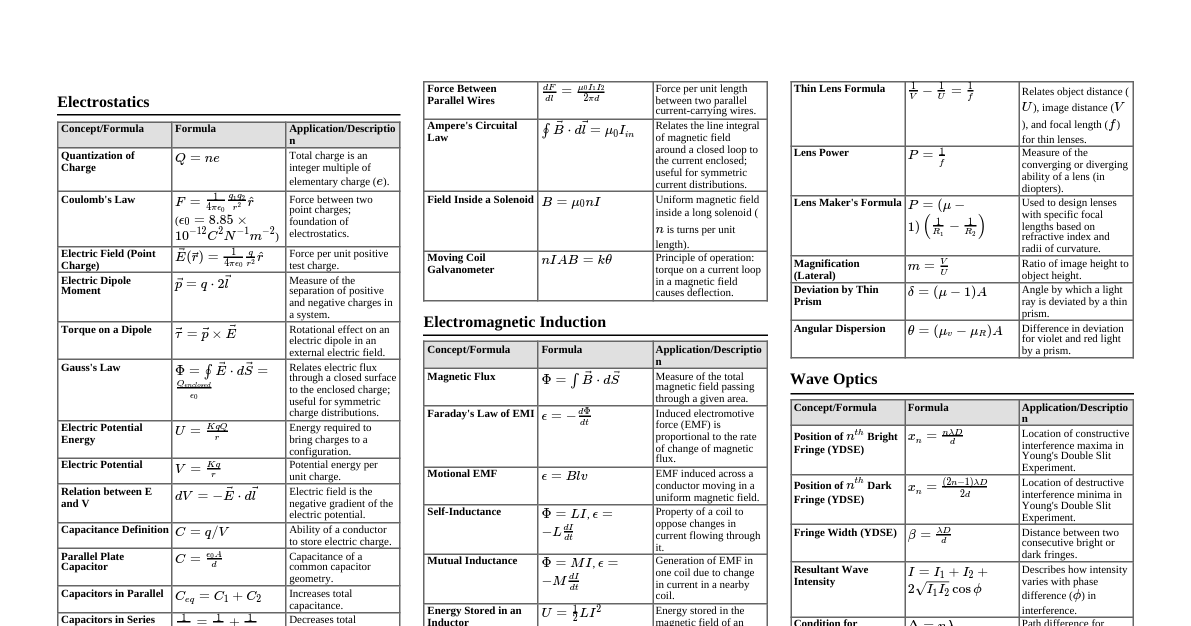
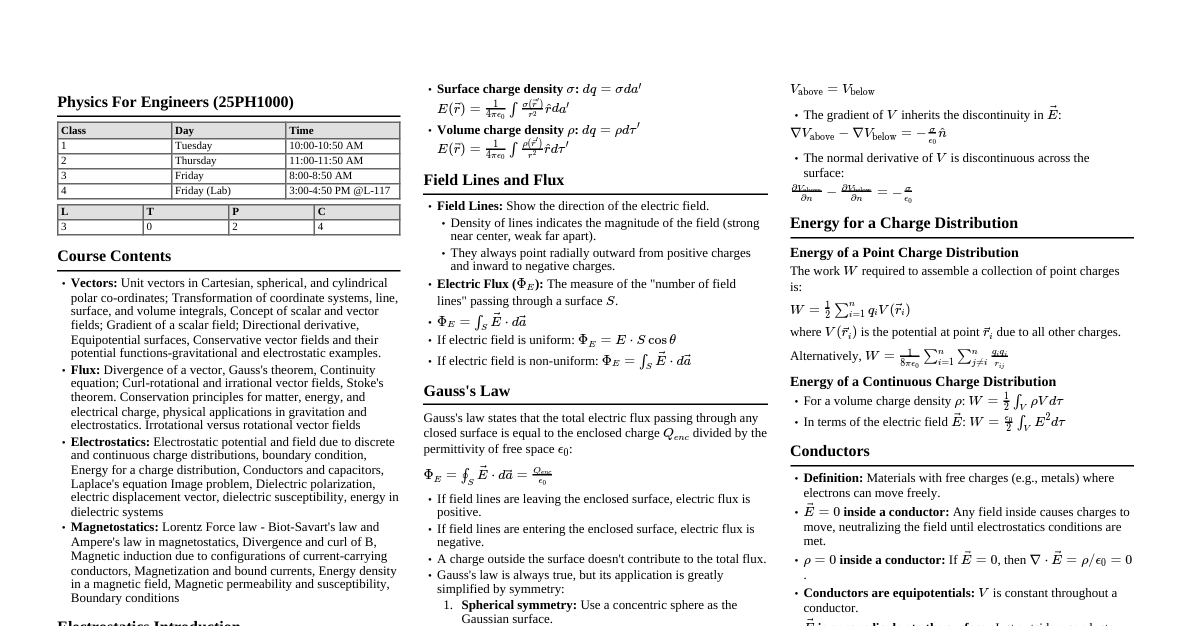
### Mathematical Methods #### Calculus - **Derivatives:** - $\frac{d}{dx}(x^n) = nx^{n-1}$ - $\frac{d}{dx}(e^x) = e^x$ - $\frac{d}{dx}(\ln x) = \frac{1}{x}$ - $\frac{d}{dx}(\sin x) = \cos x$ - $\frac{d}{dx}(\cos x) = -\sin x$ - Chain Rule: $\frac{dy}{dx} = \frac{dy}{du}\frac{du}{dx}$ - Product Rule: $\frac{d}{dx}(uv) = u\frac{dv}{dx} + v\frac{du}{dx}$ - Quotient Rule: $\frac{d}{dx}(\frac{u}{v}) = \frac{v\frac{du}{dx} - u\frac{dv}{dx}}{v^2}$ - **Integrals:** - $\int x^n dx = \frac{x^{n+1}}{n+1} + C$ (for $n \ne -1$) - $\int \frac{1}{x} dx = \ln|x| + C$ - $\int e^x dx = e^x + C$ - $\int \sin x dx = -\cos x + C$ - $\int \cos x dx = \sin x + C$ - Integration by Parts: $\int u dv = uv - \int v du$ - **Partial Derivatives:** $\frac{\partial f}{\partial x}$ - **Total Differential:** $df = \frac{\partial f}{\partial x}dx + \frac{\partial f}{\partial y}dy + \frac{\partial f}{\partial z}dz$ - **Jacobian:** $J = \det\left(\frac{\partial(u,v)}{\partial(x,y)}\right) = \begin{vmatrix} \frac{\partial u}{\partial x} & \frac{\partial u}{\partial y} \\ \frac{\partial v}{\partial x} & \frac{\partial v}{\partial y} \end{vmatrix}$ - **Taylor Expansion:** $f(x) = \sum_{n=0}^{\infty} \frac{f^{(n)}(a)}{n!}(x-a)^n = f(a) + f'(a)(x-a) + \frac{f''(a)}{2!}(x-a)^2 + \dots$ - **Maclaurin Series (Taylor at a=0):** - $e^x = 1 + x + \frac{x^2}{2!} + \frac{x^3}{3!} + \dots$ - $\sin x = x - \frac{x^3}{3!} + \frac{x^5}{5!} - \dots$ - $\cos x = 1 - \frac{x^2}{2!} + \frac{x^4}{4!} - \dots$ - $\ln(1+x) = x - \frac{x^2}{2} + \frac{x^3}{3} - \dots$ - $(1+x)^n = 1 + nx + \frac{n(n-1)}{2!}x^2 + \dots$ - **Fourier Series (for period $2L$):** $f(x) = a_0 + \sum_{n=1}^{\infty} (a_n \cos(\frac{n\pi x}{L}) + b_n \sin(\frac{n\pi x}{L}))$ - $a_0 = \frac{1}{2L}\int_{-L}^{L} f(x) dx$ - $a_n = \frac{1}{L}\int_{-L}^{L} f(x) \cos(\frac{n\pi x}{L}) dx$ - $b_n = \frac{1}{L}\int_{-L}^{L} f(x) \sin(\frac{n\pi x}{L}) dx$ - **Gamma Function:** $\Gamma(z) = \int_0^\infty t^{z-1}e^{-t}dt$, $\Gamma(n+1) = n!$ for integer $n$. #### Vector Algebra - **Magnitude:** $|\vec{A}| = \sqrt{A_x^2 + A_y^2 + A_z^2}$ - **Unit Vector:** $\hat{A} = \vec{A}/|\vec{A}|$ - **Dot Product:** $\vec{A} \cdot \vec{B} = |\vec{A}||\vec{B}|\cos\theta = A_x B_x + A_y B_y + A_z B_z$ - **Cross Product:** $\vec{A} \times \vec{B} = |\vec{A}||\vec{B}|\sin\theta \hat{n} = \begin{vmatrix} \hat{i} & \hat{j} & \hat{k} \\ A_x & A_y & A_z \\ B_x & B_y & B_z \end{vmatrix}$ - **Scalar Triple Product:** $\vec{A} \cdot (\vec{B} \times \vec{C})$ (Volume of parallelepiped) - **Vector Triple Product:** $\vec{A} \times (\vec{B} \times \vec{C}) = \vec{B}(\vec{A} \cdot \vec{C}) - \vec{C}(\vec{A} \cdot \vec{B})$ #### Vector Calculus - **Gradient:** $\nabla f = \frac{\partial f}{\partial x}\hat{i} + \frac{\partial f}{\partial y}\hat{j} + \frac{\partial f}{\partial z}\hat{k}$ - **Divergence:** $\nabla \cdot \vec{A} = \frac{\partial A_x}{\partial x} + \frac{\partial A_y}{\partial y} + \frac{\partial A_z}{\partial z}$ - **Curl:** $\nabla \times \vec{A} = \begin{vmatrix} \hat{i} & \hat{j} & \hat{k} \\ \frac{\partial}{\partial x} & \frac{\partial}{\partial y} & \frac{\partial}{\partial z} \\ A_x & A_y & A_z \end{vmatrix}$ - **Laplacian:** $\nabla^2 f = \nabla \cdot (\nabla f) = \frac{\partial^2 f}{\partial x^2} + \frac{\partial^2 f}{\partial y^2} + \frac{\partial^2 f}{\partial z^2}$ - **Product Rules:** - $\nabla(fg) = f\nabla g + g\nabla f$ - $\nabla \cdot (f\vec{A}) = (\nabla f) \cdot \vec{A} + f(\nabla \cdot \vec{A})$ - $\nabla \times (f\vec{A}) = (\nabla f) \times \vec{A} + f(\nabla \times \vec{A})$ - $\nabla \cdot (\vec{A} \times \vec{B}) = \vec{B} \cdot (\nabla \times \vec{A}) - \vec{A} \cdot (\nabla \times \vec{B})$ - $\nabla \times (\vec{A} \times \vec{B}) = (\vec{B} \cdot \nabla)\vec{A} - (\vec{A} \cdot \nabla)\vec{B} + \vec{A}(\nabla \cdot \vec{B}) - \vec{B}(\nabla \cdot \vec{A})$ - **Identities:** - $\nabla \times (\nabla f) = 0$ (Curl of a gradient is zero) - $\nabla \cdot (\nabla \times \vec{A}) = 0$ (Divergence of a curl is zero) - $\nabla \times (\nabla \times \vec{A}) = \nabla(\nabla \cdot \vec{A}) - \nabla^2 \vec{A}$ - **Line Integral:** $\int_C \vec{F} \cdot d\vec{l}$ - **Surface Integral:** $\int_S \vec{F} \cdot d\vec{S}$ - **Volume Integral:** $\int_V f dV$ - **Divergence Theorem (Gauss's Theorem):** $\oint_S \vec{F} \cdot d\vec{S} = \int_V (\nabla \cdot \vec{F}) dV$ - **Stokes' Theorem:** $\oint_C \vec{F} \cdot d\vec{l} = \int_S (\nabla \times \vec{F}) \cdot d\vec{S}$ #### Coordinate Systems - **Cylindrical Coordinates $(\rho, \phi, z)$:** - Position: $\vec{r} = \rho\hat{\rho} + z\hat{z}$ - Volume element: $dV = \rho d\rho d\phi dz$ - Gradient: $\nabla f = \frac{\partial f}{\partial \rho}\hat{\rho} + \frac{1}{\rho}\frac{\partial f}{\partial \phi}\hat{\phi} + \frac{\partial f}{\partial z}\hat{z}$ - Divergence: $\nabla \cdot \vec{A} = \frac{1}{\rho}\frac{\partial}{\partial \rho}(\rho A_\rho) + \frac{1}{\rho}\frac{\partial A_\phi}{\partial \phi} + \frac{\partial A_z}{\partial z}$ - Curl: $\nabla \times \vec{A} = \left(\frac{1}{\rho}\frac{\partial A_z}{\partial \phi} - \frac{\partial A_\phi}{\partial z}\right)\hat{\rho} + \left(\frac{\partial A_\rho}{\partial z} - \frac{\partial A_z}{\partial \rho}\right)\hat{\phi} + \frac{1}{\rho}\left(\frac{\partial}{\partial \rho}(\rho A_\phi) - \frac{\partial A_\rho}{\partial \phi}\right)\hat{z}$ - Laplacian: $\nabla^2 f = \frac{1}{\rho}\frac{\partial}{\partial \rho}(\rho\frac{\partial f}{\partial \rho}) + \frac{1}{\rho^2}\frac{\partial^2 f}{\partial \phi^2} + \frac{\partial^2 f}{\partial z^2}$ - **Spherical Coordinates $(r, \theta, \phi)$:** - Position: $\vec{r} = r\hat{r}$ - Volume element: $dV = r^2 \sin\theta dr d\theta d\phi$ - Gradient: $\nabla f = \frac{\partial f}{\partial r}\hat{r} + \frac{1}{r}\frac{\partial f}{\partial \theta}\hat{\theta} + \frac{1}{r\sin\theta}\frac{\partial f}{\partial \phi}\hat{\phi}$ - Divergence: $\nabla \cdot \vec{A} = \frac{1}{r^2}\frac{\partial}{\partial r}(r^2 A_r) + \frac{1}{r\sin\theta}\frac{\partial}{\partial \theta}(\sin\theta A_\theta) + \frac{1}{r\sin\theta}\frac{\partial A_\phi}{\partial \phi}$ - Laplacian: $\nabla^2 f = \frac{1}{r^2}\frac{\partial}{\partial r}(r^2\frac{\partial f}{\partial r}) + \frac{1}{r^2\sin\theta}\frac{\partial}{\partial \theta}(\sin\theta\frac{\partial f}{\partial \theta}) + \frac{1}{r^2\sin^2\theta}\frac{\partial^2 f}{\partial \phi^2}$ #### Differential Equations - **First Order Linear:** $\frac{dy}{dx} + P(x)y = Q(x)$, solution $y = e^{-\int P dx} \left( \int Q e^{\int P dx} dx + C \right)$ - **Homogeneous:** $\frac{dy}{dx} = f(y/x)$ - **Exact:** $M(x,y)dx + N(x,y)dy = 0$ if $\frac{\partial M}{\partial y} = \frac{\partial N}{\partial x}$ - **Second Order Linear (Constant Coefficients):** $ay'' + by' + cy = 0$, characteristic equation $ar^2 + br + c = 0$ - Roots $r_1, r_2$: $y(x) = C_1 e^{r_1 x} + C_2 e^{r_2 x}$ - Repeated root $r$: $y(x) = (C_1 + C_2 x) e^{rx}$ - Complex roots $\alpha \pm i\beta$: $y(x) = e^{\alpha x} (C_1 \cos(\beta x) + C_2 \sin(\beta x))$ - **Particular Solution (Method of Undetermined Coefficients, Variation of Parameters)** #### Matrices and Determinants - **Determinant:** $\det(A)$ - **Inverse:** $A^{-1} = \frac{1}{\det(A)} \text{adj}(A)$ - **Eigenvalues:** $\det(A - \lambda I) = 0$ - **Eigenvectors:** $(A - \lambda I)\vec{v} = 0$ - **Diagonalization:** $A = PDP^{-1}$ where $D$ is diagonal matrix of eigenvalues and $P$ is matrix of eigenvectors. - **Trace:** $\text{Tr}(A) = \sum A_{ii} = \sum \lambda_i$ - **Determinant:** $\det(A) = \prod \lambda_i$ #### Probability and Statistics - **Mean:** $\bar{x} = \frac{1}{N}\sum x_i$ - **Median:** Middle value when sorted. - **Mode:** Most frequent value. - **Variance:** $\sigma^2 = \frac{1}{N}\sum (x_i - \bar{x})^2$ - **Standard Deviation:** $\sigma = \sqrt{\sigma^2}$ - **Probability Density Function (PDF):** $P(x)dx$ for continuous variable - **Cumulative Distribution Function (CDF):** $F(x) = \int_{-\infty}^{x} P(t)dt$ - **Expectation Value:** $\langle X \rangle = \int x P(x)dx$ - **Standard Error of the Mean:** $\sigma_{\bar{x}} = \frac{\sigma}{\sqrt{N}}$ - **Binomial Distribution:** $P(k) = \binom{n}{k} p^k (1-p)^{n-k}$ - **Poisson Distribution:** $P(k) = \frac{\lambda^k e^{-\lambda}}{k!}$ - **Gaussian (Normal) Distribution:** $f(x) = \frac{1}{\sigma\sqrt{2\pi}} e^{-(x-\mu)^2/(2\sigma^2)}$ ### Mechanics and General Properties of Matter #### Kinematics - **Position:** $\vec{r}(t)$ - **Velocity:** $\vec{v} = \frac{d\vec{r}}{dt}$ - **Acceleration:** $\vec{a} = \frac{d\vec{v}}{dt}$ - **Constant Acceleration:** - $v = v_0 + at$ - $x = x_0 + v_0 t + \frac{1}{2}at^2$ - $v^2 = v_0^2 + 2a(x - x_0)$ - **Projectile Motion:** - Horizontal: $x = (v_0 \cos\theta)t$ - Vertical: $y = (v_0 \sin\theta)t - \frac{1}{2}gt^2$ - **Angular Velocity:** $\vec{\omega} = \frac{d\vec{\theta}}{dt}$ - **Angular Acceleration:** $\vec{\alpha} = \frac{d\vec{\omega}}{dt}$ - **Relation between linear and angular:** $\vec{v} = \vec{\omega} \times \vec{r}$, $a_t = r\alpha$, $a_c = r\omega^2 = v^2/r$ - **Polar Coordinates:** - $\vec{v} = \dot{r}\hat{r} + r\dot{\theta}\hat{\theta}$ - $\vec{a} = (\ddot{r} - r\dot{\theta}^2)\hat{r} + (r\ddot{\theta} + 2\dot{r}\dot{\theta})\hat{\theta}$ - **Cylindrical Coordinates:** - $\vec{v} = \dot{\rho}\hat{\rho} + \rho\dot{\phi}\hat{\phi} + \dot{z}\hat{z}$ - $\vec{a} = (\ddot{\rho} - \rho\dot{\phi}^2)\hat{\rho} + (\rho\ddot{\phi} + 2\dot{\rho}\dot{\phi})\hat{\phi} + \ddot{z}\hat{z}$ #### Newton's Laws - **First Law:** An object at rest stays at rest and an object in motion stays in motion with the same speed and in the same direction unless acted upon by an unbalanced force. - **Second Law:** $\vec{F}_{net} = m\vec{a} = \frac{d\vec{p}}{dt}$ - **Third Law:** $\vec{F}_{AB} = -\vec{F}_{BA}$ - **Friction Force:** $F_s \le \mu_s N$, $F_k = \mu_k N$ - **Drag Force (Stokes' Law for sphere):** $F_d = 6\pi\eta r v$ - **Centripetal Force:** $F_c = m\frac{v^2}{r} = m\omega^2 r$ (towards center) - **Centrifugal Force (non-inertial frame):** $F_c = m\frac{v^2}{r}$ or $m\omega^2 r$ (outward, pseudo force) - **Coriolis Force (non-inertial frame):** $\vec{F}_{cor} = -2m(\vec{\omega} \times \vec{v}')$ (pseudo force) #### Work, Energy, and Power - **Work Done by Constant Force:** $W = \vec{F} \cdot \vec{d} = Fd\cos\theta$ - **Work Done by Variable Force:** $W = \int \vec{F} \cdot d\vec{r}$ - **Kinetic Energy:** $K = \frac{1}{2}mv^2$ - **Work-Energy Theorem:** $W_{net} = \Delta K$ - **Potential Energy:** $U$, $\vec{F} = -\nabla U$ (for conservative forces) - Gravitational: $U_g = mgh$ (near Earth's surface) - Elastic: $U_s = \frac{1}{2}kx^2$ - **Conservation of Mechanical Energy:** $K_1 + U_1 = K_2 + U_2$ (if only conservative forces do work) - **Power:** $P = \frac{dW}{dt} = \vec{F} \cdot \vec{v}$ #### Linear Momentum - **Linear Momentum:** $\vec{p} = m\vec{v}$ - **Impulse:** $\vec{J} = \int \vec{F} dt = \Delta\vec{p}$ - **Conservation of Linear Momentum:** $\sum \vec{p}_{initial} = \sum \vec{p}_{final}$ (for an isolated system) - **Center of Mass:** $\vec{R}_{CM} = \frac{\sum m_i \vec{r}_i}{\sum m_i} = \frac{\int \vec{r} dm}{\int dm}$ - **Velocity of CM:** $\vec{V}_{CM} = \frac{\sum m_i \vec{v}_i}{\sum m_i}$ - **Equation of Motion of CM:** $\vec{F}_{ext} = M_{total}\vec{a}_{CM} = \frac{d\vec{P}_{total}}{dt}$ #### Collisions - **Elastic Collision:** Kinetic energy and momentum are conserved. - 1D: $v_1 - v_2 = -(v_1' - v_2')$ (relative velocity conserved) - **Inelastic Collision:** Momentum is conserved, but kinetic energy is not. - **Perfectly Inelastic Collision:** Objects stick together after collision. - **Coefficient of Restitution:** $e = -\frac{(v_1' - v_2')}{(v_1 - v_2)}$ ($e=1$ for elastic, $e=0$ for perfectly inelastic) #### Rotation and Angular Momentum - **Angular Velocity:** $\vec{\omega}$ - **Angular Acceleration:** $\vec{\alpha}$ - **Moment of Inertia:** $I = \sum m_i r_i^2 = \int r^2 dm$ - **Parallel Axis Theorem:** $I = I_{CM} + Md^2$ - **Perpendicular Axis Theorem (for planar objects):** $I_z = I_x + I_y$ - **Rotational Kinetic Energy:** $K_{rot} = \frac{1}{2}I\omega^2$ - **Torque:** $\vec{\tau} = \vec{r} \times \vec{F} = I\vec{\alpha} = \frac{d\vec{L}}{dt}$ - **Angular Momentum:** $\vec{L} = \vec{r} \times \vec{p} = I\vec{\omega}$ (for rigid body rotating about fixed axis) - **Conservation of Angular Momentum:** $\sum \vec{L}_{initial} = \sum \vec{L}_{final}$ (if net external torque is zero) #### Gravitation - **Newton's Law of Universal Gravitation:** $F = G\frac{m_1 m_2}{r^2}$ - **Gravitational Potential Energy:** $U_g = -G\frac{m_1 m_2}{r}$ - **Gravitational Field:** $\vec{g} = -\frac{GM}{r^2}\hat{r}$ - **Escape Velocity:** $v_{esc} = \sqrt{\frac{2GM}{R}}$ - **Orbital Velocity (Circular Orbit):** $v_{orb} = \sqrt{\frac{GM}{r}}$ - **Kepler's Laws:** 1. Planets move in elliptical orbits with the Sun at one focus. 2. A line segment joining a planet and the Sun sweeps out equal areas during equal intervals of time. 3. The square of the orbital period $T$ is proportional to the cube of the semi-major axis $a$: $T^2 = \left(\frac{4\pi^2}{GM}\right)a^3$. #### Fluid Mechanics - **Density:** $\rho = m/V$ - **Pressure:** $P = F/A$ - **Pressure in a Fluid at Depth h:** $P = P_0 + \rho gh$ - **Buoyant Force (Archimedes' Principle):** $F_B = \rho_{fluid} V_{displaced} g$ - **Equation of Continuity (steady, incompressible flow):** $A_1 v_1 = A_2 v_2$ - **Bernoulli's Equation (steady, incompressible, non-viscous flow):** $P + \frac{1}{2}\rho v^2 + \rho gh = \text{constant}$ - **Viscosity (Newton's Law of Viscosity):** $\tau = \eta \frac{dv_x}{dy}$ - **Poiseuille's Law (laminar flow in pipe):** $Q = \frac{\pi R^4 \Delta P}{8\eta L}$ - **Reynolds Number:** $Re = \frac{\rho v L}{\eta}$ (Laminar if $Re 3000$) - **Surface Tension:** $\gamma = F/L$ - **Capillary Rise:** $h = \frac{2\gamma \cos\theta}{\rho g r}$ #### Elasticity - **Stress:** $\sigma = F/A$ - **Strain:** $\epsilon = \Delta L/L_0$ (linear), $\epsilon_V = \Delta V/V_0$ (volume), $\epsilon_S = \Delta x/h$ (shear) - **Young's Modulus:** $Y = \sigma/\epsilon$ (for linear stress/strain) - **Bulk Modulus:** $B = -P/(\Delta V/V_0)$ - **Shear Modulus (Rigidity Modulus):** $G = \text{shear stress / shear strain}$ - **Poisson's Ratio:** $\nu = -\frac{\text{lateral strain}}{\text{longitudinal strain}}$ ### Oscillations, Waves and Optics #### Simple Harmonic Motion (SHM) - **Differential Equation:** $\frac{d^2x}{dt^2} + \omega^2 x = 0$ - **General Solution:** $x(t) = A\cos(\omega t + \phi)$ or $x(t) = A\sin(\omega t + \phi')$ - **Velocity:** $v(t) = -A\omega\sin(\omega t + \phi)$ - **Acceleration:** $a(t) = -A\omega^2\cos(\omega t + \phi) = -\omega^2 x(t)$ - **Angular Frequency:** $\omega = \sqrt{k/m}$ (mass-spring), $\omega = \sqrt{g/L}$ (simple pendulum) - **Period:** $T = 2\pi/\omega$ - **Frequency:** $f = 1/T = \omega/(2\pi)$ - **Energy:** $E = \frac{1}{2}kA^2 = \frac{1}{2}m\omega^2 A^2$ - **Superposition of SHMs:** - Same frequency, same direction: $x(t) = A_1\cos(\omega t + \phi_1) + A_2\cos(\omega t + \phi_2) = R\cos(\omega t + \delta)$ where $R^2 = A_1^2 + A_2^2 + 2A_1A_2\cos(\phi_1-\phi_2)$ - Lissajous figures (perpendicular SHMs) #### Damped and Forced Oscillations - **Damped SHM:** $m\frac{d^2x}{dt^2} + b\frac{dx}{dt} + kx = 0$ - Damping constant: $\beta = b/(2m)$ - Natural frequency: $\omega_0 = \sqrt{k/m}$ - Damped frequency: $\omega' = \sqrt{\omega_0^2 - \beta^2}$ (underdamped) - Solution (underdamped): $x(t) = Ae^{-\beta t}\cos(\omega' t + \phi)$ - Quality Factor: $Q = \frac{\omega_0}{2\beta} = \frac{m\omega_0}{b}$ - **Forced SHM:** $m\frac{d^2x}{dt^2} + b\frac{dx}{dt} + kx = F_0\cos(\omega_d t)$ - Steady-state amplitude: $A(\omega_d) = \frac{F_0}{\sqrt{m^2(\omega_d^2 - \omega_0^2)^2 + b^2\omega_d^2}}$ - Resonance frequency: $\omega_{res} = \sqrt{\omega_0^2 - 2\beta^2}$ (for amplitude) - Amplitude at resonance: $A_{res} \approx \frac{F_0}{b\omega_0}$ (for small damping) #### Waves - **Wave Equation (1D):** $\frac{\partial^2 y}{\partial x^2} = \frac{1}{v^2}\frac{\partial^2 y}{\partial t^2}$ - **General Wave Function:** $y(x,t) = A\sin(kx - \omega t + \phi)$ or $y(x,t) = f(x \pm vt)$ - **Wave Speed:** $v = f\lambda = \omega/k$ - **Wave Number:** $k = 2\pi/\lambda$ - **Angular Frequency:** $\omega = 2\pi f$ - **Speed of Wave on String:** $v = \sqrt{T/\mu}$ (T: tension, $\mu$: linear mass density) - **Energy Density:** $u = \frac{1}{2}\rho\omega^2 A^2$ - **Intensity:** $I = \frac{1}{2}\rho\omega^2 A^2 v$ - **Power:** $P = \frac{1}{2}\mu\omega^2 A^2 v$ - **Group Velocity:** $v_g = \frac{d\omega}{dk}$ - **Phase Velocity:** $v_p = \frac{\omega}{k}$ - **Standing Waves (on string fixed at both ends):** $\lambda_n = 2L/n$, $f_n = n(v/2L)$ - **Beat Frequency:** $f_{beat} = |f_1 - f_2|$ #### Sound Waves - **Speed of Sound in Fluid:** $v = \sqrt{B/\rho}$ (B: Bulk modulus) - **Speed of Sound in Solid Rod:** $v = \sqrt{Y/\rho}$ (Y: Young's modulus) - **Speed of Sound in Ideal Gas:** $v = \sqrt{\gamma RT/M}$ - **Intensity Level (Decibels):** $\beta = 10 \log_{10}(I/I_0)$ - **Doppler Effect:** $f' = f \left(\frac{v \pm v_o}{v \mp v_s}\right)$ (observer/source moving towards/away) #### Optics - **Fermat's Principle:** Light travels the path of least time. - **Snell's Law:** $n_1\sin\theta_1 = n_2\sin\theta_2$ - **Critical Angle for Total Internal Reflection:** $\sin\theta_c = n_2/n_1$ (for $n_1 > n_2$) - **Lensmaker's Formula:** $\frac{1}{f} = (n-1)\left(\frac{1}{R_1} - \frac{1}{R_2}\right)$ - **Lens/Mirror Formula:** $\frac{1}{f} = \frac{1}{u} + \frac{1}{v}$ (u: object distance, v: image distance) - **Magnification:** $m = -v/u = h_i/h_o$ - **Power of a Lens:** $P = 1/f$ (in diopters if f in meters) - **Optical Path Difference (OPD):** $\Delta x = n_2 d_2 - n_1 d_1$ - **Dispersion:** $n(\lambda)$ #### Interference - **Constructive Interference:** $\Delta x = m\lambda$ or $\Delta\phi = 2m\pi$ - **Destructive Interference:** $\Delta x = (m + 1/2)\lambda$ or $\Delta\phi = (2m+1)\pi$ - **Young's Double Slit:** - Bright fringes: $d\sin\theta = m\lambda$, $y_m = \frac{m\lambda L}{d}$ - Dark fringes: $d\sin\theta = (m+1/2)\lambda$, $y_m = \frac{(m+1/2)\lambda L}{d}$ - **Thin Films:** Conditions for constructive/destructive interference depend on phase shifts at boundaries. - For normal incidence, if refractive index increases at both boundaries or decreases at both: - Constructive: $2nt = m\lambda$ - Destructive: $2nt = (m+1/2)\lambda$ - If refractive index increases at one boundary and decreases at other: - Constructive: $2nt = (m+1/2)\lambda$ - Destructive: $2nt = m\lambda$ - **Michelson Interferometer:** $\Delta d = m\lambda/2$ (for m fringes shift) #### Diffraction - **Single Slit Diffraction:** - Minima: $a\sin\theta = m\lambda$ ($m = \pm 1, \pm 2, \dots$) - Intensity: $I(\theta) = I_0 \left(\frac{\sin(\beta/2)}{\beta/2}\right)^2$ where $\beta = k a \sin\theta$ - **Diffraction Grating:** - Maxima: $d\sin\theta = m\lambda$ ($m = 0, \pm 1, \pm 2, \dots$) - **Rayleigh Criterion:** $\theta_{min} = 1.22\frac{\lambda}{D}$ (for circular aperture) - **Resolving Power of Grating:** $R = \frac{\lambda}{\Delta\lambda} = Nm$ (N: number of slits, m: order) #### Polarization - **Malus's Law:** $I = I_0 \cos^2\theta$ (transmitted intensity through analyzer) - **Brewster's Angle:** $\tan\theta_B = n_2/n_1$ (angle where reflected light is completely polarized) - **Birefringence:** Double refraction in anisotropic materials. - **Optical Activity:** Rotation of plane of polarization. ### Electricity and Magnetism #### Electrostatics - **Coulomb's Law:** $\vec{F} = k\frac{q_1 q_2}{r^2}\hat{r} = \frac{1}{4\pi\epsilon_0}\frac{q_1 q_2}{r^2}\hat{r}$ - **Electric Field:** $\vec{E} = \vec{F}/q = k\frac{q}{r^2}\hat{r}$ - **Electric Field from Continuous Charge Distribution:** $\vec{E} = k\int \frac{dq}{r^2}\hat{r}$ - **Electric Potential:** $V = k\frac{q}{r}$, $\vec{E} = -\nabla V$ - **Potential Energy of Charge in Field:** $U = qV$ - **Potential Energy of System of Charges:** $U = \sum_{i ### Kinetic Theory, Thermodynamics #### Kinetic Theory of Gases - **Average Kinetic Energy (per molecule, 1D):** $\langle E_k \rangle = \frac{1}{2}kT$ - **Average Kinetic Energy (per molecule, 3D):** $\langle E_k \rangle = \frac{3}{2}kT$ - **RMS Speed:** $v_{rms} = \sqrt{\frac{3kT}{m}} = \sqrt{\frac{3RT}{M}}$ (M is molar mass) - **Average Speed:** $\langle v \rangle = \sqrt{\frac{8kT}{\pi m}}$ - **Most Probable Speed:** $v_p = \sqrt{\frac{2kT}{m}}$ - **Ideal Gas Law:** $PV = nRT = NkT$ ($R = N_A k$) - **Internal Energy of Ideal Gas:** $U = \frac{f}{2}nRT$ (f = degrees of freedom) - **Equipartition Theorem:** Each quadratic degree of freedom contributes $\frac{1}{2}kT$ to the average energy. - **Specific Heat Capacity (Molar):** - $C_V = \frac{f}{2}R$ (constant volume) - $C_P = C_V + R$ (constant pressure) - Ratio of specific heats: $\gamma = C_P/C_V = 1 + 2/f$ - **Adiabatic Process for Ideal Gas:** $PV^\gamma = \text{constant}$, $TV^{\gamma-1} = \text{constant}$, $P^{1-\gamma}T^\gamma = \text{constant}$ - **Mean Free Path:** $\lambda = \frac{1}{\sqrt{2} n \pi d^2}$ (n: number density, d: molecular diameter) - **Collision Frequency:** $Z = \frac{v_{avg}}{\lambda}$ - **Viscosity:** $\eta \approx \frac{1}{3}\rho \langle v \rangle \lambda$ - **Thermal Conductivity:** $K \approx \frac{1}{3}C_V \langle v \rangle \lambda n$ - **Diffusion Coefficient:** $D \approx \frac{1}{3}\langle v \rangle \lambda$ - **Van der Waals Equation of State:** $(P + \frac{an^2}{V^2})(V - nb) = nRT$ - **Maxwell-Boltzmann Distribution (Speed):** $f(v) = 4\pi \left(\frac{m}{2\pi kT}\right)^{3/2} v^2 e^{-mv^2/(2kT)}$ - **Boltzmann Distribution (Energy):** $P(E) = C e^{-E/kT}$ (C: normalization constant) #### Thermodynamics Laws - **Zeroth Law:** If two systems are in thermal equilibrium with a third system, they are in thermal equilibrium with each other. - **First Law:** $\Delta U = Q - W$ or $dU = dQ - dW$ - $Q$: heat added to the system - $W$: work done BY the system - Work done by gas: $W = \int P dV$ - **Second Law:** - Clausius Statement: Heat cannot spontaneously flow from a colder body to a hotter body. - Kelvin-Planck Statement: It is impossible to construct a heat engine that operates in a cycle and produces no other effect than the extraction of heat from a reservoir and the performance of an equivalent amount of work. - **Entropy Change:** $dS \ge \frac{dQ}{T}$ (equality for reversible processes) - For reversible process: $\Delta S = \int \frac{dQ_{rev}}{T}$ - For irreversible process: $\Delta S_{total} = \Delta S_{system} + \Delta S_{surroundings} > 0$ - **Third Law:** The entropy of a perfect crystal at absolute zero is zero. #### Thermodynamic Processes - **Isothermal (T = constant):** $Q = W = nRT \ln(V_f/V_i)$ - **Adiabatic (Q = 0):** $W = -\Delta U = -\frac{f}{2}nR\Delta T$ - **Isobaric (P = constant):** $W = P\Delta V$, $Q = nC_P\Delta T$ - **Isochoric (V = constant):** $W = 0$, $Q = \Delta U = nC_V\Delta T$ #### Heat Engines, Refrigerators, Heat Pumps - **Efficiency of Heat Engine:** $\eta = \frac{W}{Q_H} = 1 - \frac{Q_C}{Q_H}$ - **Carnot Efficiency (Maximum):** $\eta_{Carnot} = 1 - \frac{T_C}{T_H}$ - **Coefficient of Performance (Refrigerator):** $COP_{ref} = \frac{Q_C}{W} = \frac{Q_C}{Q_H - Q_C}$ - **Coefficient of Performance (Heat Pump):** $COP_{hp} = \frac{Q_H}{W} = \frac{Q_H}{Q_H - Q_C}$ - **Carnot COP:** $COP_{ref, Carnot} = \frac{T_C}{T_H - T_C}$, $COP_{hp, Carnot} = \frac{T_H}{T_H - T_C}$ #### Thermodynamic Potentials - **Internal Energy:** $U$ ($dU = TdS - PdV$) - **Enthalpy:** $H = U + PV$ ($dH = TdS + VdP$) - **Helmholtz Free Energy:** $F = U - TS$ ($dF = -SdT - PdV$) - **Gibbs Free Energy:** $G = H - TS$ ($dG = -SdT + VdP$) #### Maxwell Relations - $(\frac{\partial T}{\partial V})_S = -(\frac{\partial P}{\partial S})_V$ - $(\frac{\partial T}{\partial P})_S = (\frac{\partial V}{\partial S})_P$ - $(\frac{\partial S}{\partial V})_T = (\frac{\partial P}{\partial T})_V$ - $(\frac{\partial S}{\partial P})_T = -(\frac{\partial V}{\partial T})_P$ #### Phase Transitions - **Clausius-Clapeyron Equation:** $\frac{dP}{dT} = \frac{L}{T\Delta V}$ (L: latent heat, $\Delta V$: change in volume) #### Statistical Mechanics - **Microstates and Macrostates:** $\Omega$ (number of microstates) - **Boltzmann Entropy:** $S = k \ln\Omega$ - **Partition Function (Canonical Ensemble):** $Z = \sum_i e^{-E_i/kT}$ - **Average Energy:** $\langle E \rangle = -\frac{\partial \ln Z}{\partial \beta}$ where $\beta = 1/kT$ - **Helmholtz Free Energy:** $F = -kT \ln Z$ - **Grand Canonical Partition Function:** $\mathcal{Z} = \sum_i e^{-(E_i - \mu N_i)/kT}$ ### Modern Physics #### Special Relativity - **Lorentz Factor:** $\gamma = \frac{1}{\sqrt{1 - v^2/c^2}}$ - **Lorentz Transformation:** - $x' = \gamma (x - vt)$ - $y' = y$ - $z' = z$ - $t' = \gamma (t - vx/c^2)$ - **Inverse Lorentz Transformation:** - $x = \gamma (x' + vt')$ - $t = \gamma (t' + vx'/c^2)$ - **Length Contraction:** $L = L_0/\gamma$ (length parallel to motion) - **Time Dilation:** $\Delta t = \gamma \Delta t_0$ (moving clock runs slower) - **Relativistic Velocity Addition:** $u' = \frac{u - v}{1 - uv/c^2}$ (u' is velocity in S', u in S, v is S' relative to S) - **Relativistic Momentum:** $\vec{p} = \gamma m\vec{v}$ - **Relativistic Energy:** $E = \gamma mc^2$ - **Total Energy:** $E^2 = (pc)^2 + (mc^2)^2$ - **Rest Energy:** $E_0 = mc^2$ - **Kinetic Energy:** $K = E - E_0 = (\gamma - 1)mc^2$ #### Quantum Mechanics - **Planck's Law (Blackbody Radiation):** $B(\lambda, T) = \frac{2hc^2}{\lambda^5} \frac{1}{e^{hc/(\lambda kT)} - 1}$ - **Wien's Displacement Law:** $\lambda_{max} T = b$ (b is Wien's constant) - **Stefan-Boltzmann Law:** $P = \sigma AT^4$ - **Rayleigh-Jeans Law (classical limit):** $B(\lambda, T) = \frac{2ckT}{\lambda^4}$ - **Photoelectric Effect:** $K_{max} = hf - \phi$ (hf: photon energy, $\phi$: work function) - **Photon Momentum:** $p = h/\lambda = E/c$ - **Compton Effect:** $\Delta\lambda = \lambda' - \lambda = \frac{h}{m_e c}(1 - \cos\theta)$ - **Bohr's Model (Hydrogen Atom):** - **Energy Levels:** $E_n = -\frac{13.6}{n^2} \text{ eV}$ - **Radius:** $r_n = a_0 n^2$ ($a_0 = 0.0529 \text{ nm}$: Bohr radius) - **Angular Momentum:** $L = n\hbar$ - **Rydberg Formula:** $\frac{1}{\lambda} = R_H \left(\frac{1}{n_f^2} - \frac{1}{n_i^2}\right)$ - **De Broglie Wavelength:** $\lambda = h/p$ - **Heisenberg Uncertainty Principle:** - Position-Momentum: $\Delta x \Delta p_x \ge \hbar/2$ - Energy-Time: $\Delta E \Delta t \ge \hbar/2$ - **Wave Function:** $\Psi(\vec{r}, t)$, $|\Psi|^2$ is probability density - **Normalization Condition:** $\int |\Psi|^2 dV = 1$ - **Expectation Value:** $\langle A \rangle = \int \Psi^* \hat{A} \Psi dV$ ($\hat{A}$ is operator for observable A) - **Operators:** - Position: $\hat{x} = x$ - Momentum: $\hat{p}_x = -i\hbar\frac{\partial}{\partial x}$ - Kinetic Energy: $\hat{T} = -\frac{\hbar^2}{2m}\nabla^2$ - Potential Energy: $\hat{V} = V(\vec{r}, t)$ - Hamiltonian: $\hat{H} = \hat{T} + \hat{V}$ - **Schrödinger Equation:** - **Time-Dependent:** $i\hbar\frac{\partial\Psi}{\partial t} = \hat{H}\Psi$ - **Time-Independent:** $\hat{H}\psi = E\psi$ - **Particle in a Box (1D, length L):** - Energy Levels: $E_n = \frac{n^2\pi^2\hbar^2}{2mL^2}$ ($n=1,2,3,\dots$) - Wave functions: $\psi_n(x) = \sqrt{\frac{2}{L}}\sin(\frac{n\pi x}{L})$ - **Harmonic Oscillator (1D):** - Energy Levels: $E_n = (n + 1/2)\hbar\omega$ ($n=0,1,2,\dots$) - $\omega = \sqrt{k/m}$ - **Hydrogen Atom:** - Energy Levels: $E_n = -\frac{Z^2 R_y}{n^2}$ ($R_y = 13.6 \text{ eV}$: Rydberg energy) - Quantum Numbers: $n$ (principal), $l$ (orbital angular momentum), $m_l$ (magnetic), $m_s$ (spin) - Allowed values: $n=1,2,3,\dots$; $l=0,1,\dots,n-1$; $m_l=-l,\dots,l$; $m_s=\pm 1/2$ - **Angular Momentum:** - Total angular momentum: $L^2 = l(l+1)\hbar^2$ - Z-component: $L_z = m_l\hbar$ - **Spin Angular Momentum:** $S^2 = s(s+1)\hbar^2$, $S_z = m_s\hbar$ (for electron $s=1/2$) - **Total Angular Momentum:** $\vec{J} = \vec{L} + \vec{S}$ - **Pauli Exclusion Principle:** No two identical fermions (half-integer spin) can occupy the same quantum state simultaneously. #### Nuclear Physics - **Atomic Number (Z):** Number of protons - **Mass Number (A):** Number of protons + neutrons - **Neutron Number (N):** $N = A - Z$ - **Nuclear Radius:** $R = R_0 A^{1/3}$ ($R_0 \approx 1.2 \text{ fm}$) - **Mass-Energy Equivalence:** $E = mc^2$ - **Binding Energy:** $\text{BE} = (Zm_p + Nm_n - M_{nucleus})c^2$ - **Binding Energy per Nucleon:** $\text{BE}/A$ - **Radioactive Decay Law:** $N(t) = N_0 e^{-\lambda t}$ - **Activity:** $A = |\frac{dN}{dt}| = \lambda N$ - **Half-Life:** $T_{1/2} = \frac{\ln 2}{\lambda}$ - **Mean Lifetime:** $\tau = 1/\lambda = T_{1/2}/\ln 2$ - **Alpha Decay:** $^A_Z X \to ^{A-4}_{Z-2} Y + ^4_2 He$ - **Beta Decay:** - $\beta^-$ decay: $^A_Z X \to ^A_{Z+1} Y + e^- + \bar{\nu}_e$ - $\beta^+$ decay: $^A_Z X \to ^A_{Z-1} Y + e^+ + \nu_e$ - **Gamma Decay:** $^A_Z X^* \to ^A_Z X + \gamma$ - **Q-value of Reaction:** $Q = (M_{reactants} - M_{products})c^2$ - **Nuclear Fission/Fusion:** Energy released due to change in binding energy. #### Particle Physics - **Fundamental Forces:** Strong, Weak, Electromagnetic, Gravitational - **Standard Model:** Quarks, Leptons, Gauge Bosons (photon, W/Z, gluon) - **Conservation Laws:** Charge, Lepton Number, Baryon Number, Strangeness (for strong/EM interactions) - **Hadrons:** Baryons (3 quarks, e.g., proton, neutron), Mesons (quark-antiquark, e.g., pion, kaon) - **Leptons:** Electron, muon, tau, and their neutrinos. ### Solid State Physics, Devices and Electronics #### Solid State Physics - **Crystal Structures:** - **Bravais Lattices:** 14 unique lattices - **Unit Cell:** Smallest repeating unit - **Basis:** Atoms associated with each lattice point - **Coordination Number:** Number of nearest neighbors - **Atomic Packing Factor (APF):** Volume of atoms in unit cell / Volume of unit cell - **Common Structures:** Simple Cubic (SC), Body-Centered Cubic (BCC), Face-Centered Cubic (FCC), Hexagonal Close-Packed (HCP) - **Miller Indices $(hkl)$:** Notation for crystal planes - **Bragg's Law:** $2d\sin\theta = n\lambda$ (d: interplanar spacing) - **Reciprocal Lattice:** Used for diffraction analysis - **Band Theory:** - **Conductors:** Overlapping valence and conduction bands. - **Insulators:** Large band gap ($E_g > 3 \text{ eV}$). - **Semiconductors:** Small band gap ($E_g \approx 1 \text{ eV}$). - **Free Electron Model (Drude-Lorentz):** - **Electrical Conductivity:** $\sigma = \frac{ne^2\tau}{m_e}$ ($\tau$: scattering time) - **Hall Coefficient:** $R_H = \frac{1}{ne}$ - **Semiconductors:** - **Intrinsic Carrier Concentration:** $n_i^2 = N_c N_v e^{-E_g/kT}$ ($N_c, N_v$: effective density of states) - **Conductivity:** $\sigma = nq\mu_e + pq\mu_h$ (n,p: electron/hole conc., $\mu_e, \mu_h$: electron/hole mobility) - **Fermi Level (Intrinsic):** $E_F = \frac{E_c + E_v}{2} + \frac{3}{4}kT \ln(\frac{m_h^*}{m_e^*})$ - **Mass Action Law:** $np = n_i^2$ - **Doping:** - n-type: $n \approx N_D$, $p = n_i^2/N_D$ - p-type: $p \approx N_A$, $n = n_i^2/N_A$ - **Diffusion Current:** $J_e = eD_e \frac{dn}{dx}$, $J_h = -eD_h \frac{dp}{dx}$ - **Drift Current:** $J_e = ne\mu_e E$, $J_h = pe\mu_h E$ - **Einstein Relation:** $D/\mu = kT/e$ - **Superconductivity (Type I, Type II):** - **Meissner Effect:** Expulsion of magnetic field. - **Critical Temperature ($T_c$), Critical Field ($H_c$).** - **BCS Theory:** Cooper pairs. #### Devices - **p-n Junction Diode:** - **I-V Characteristics (Ideal):** $I = I_0 (e^{eV/(nkT)} - 1)$ ($I_0$: reverse saturation current, n: ideality factor) - **Depletion Region Width:** $W \propto \sqrt{(V_0 - V_R)/N}$ - **Built-in Potential:** $V_{bi} = \frac{kT}{e} \ln(\frac{N_A N_D}{n_i^2})$ - **Zener Diode:** Operation in reverse breakdown, used for voltage regulation. - **LED (Light Emitting Diode):** Forward biased p-n junction, recombination emits light. - **Photodiode:** Reverse biased p-n junction, converts light to current. - **Bipolar Junction Transistor (BJT):** - **Operating Modes:** Cutoff, Active, Saturation. - **Characteristics (Common Emitter):** - $I_E = I_B + I_C$ - $I_C = \beta I_B$ (Active region, $\beta$: current gain) - $\alpha = \frac{\beta}{1+\beta}$ - **Field-Effect Transistor (FET) / MOSFET:** - **JFET, MOSFET (enhancement/depletion mode)** - **Drain Current (MOSFET Saturation):** $I_D = \frac{1}{2}\mu_n C_{ox} \frac{W}{L} (V_{GS} - V_T)^2$ #### Analog Electronics - **Operational Amplifier (OPAMP):** - **Ideal OPAMP characteristics:** Infinite input impedance, zero output impedance, infinite open-loop gain, zero common-mode gain. - **Inverting Amplifier:** $V_{out} = -\frac{R_f}{R_{in}}V_{in}$ - **Non-Inverting Amplifier:** $V_{out} = (1 + \frac{R_f}{R_{in}})V_{in}$ - **Voltage Follower:** $V_{out} = V_{in}$ (gain = 1) - **Summing Amplifier, Integrator, Differentiator.** - **Filters:** - **RC Low-Pass Filter:** $V_{out}/V_{in} = \frac{1}{1 + j\omega RC}$ - **RC High-Pass Filter:** $V_{out}/V_{in} = \frac{j\omega RC}{1 + j\omega RC}$ - **Cut-off Frequency:** $f_c = \frac{1}{2\pi RC}$ - **Oscillators:** - **Barkhausen Criterion:** Loop gain ($A\beta$) must be 1 and phase shift around loop must be $0^\circ$ or $360^\circ$. - **Wien Bridge Oscillator, Phase-Shift Oscillator.** #### Digital Electronics - **Number Systems:** Binary, Octal, Decimal, Hexadecimal. - **Binary Arithmetic:** Addition, Subtraction (2's complement). - **Logic Gates:** AND, OR, NOT, NAND, NOR, XOR, XNOR. - **Boolean Algebra:** - **Identities:** $A+0=A, A\cdot 1=A, A+1=1, A\cdot 0=0, A+A=A, A\cdot A=A, A+\bar{A}=1, A\cdot \bar{A}=0$ - **Commutative:** $A+B = B+A, A\cdot B = B\cdot A$ - **Associative:** $(A+B)+C = A+(B+C), (A\cdot B)\cdot C = A\cdot (B\cdot C)$ - **Distributive:** $A\cdot(B+C) = A\cdot B + A\cdot C, A+(B\cdot C) = (A+B)\cdot(A+C)$ - **De Morgan's Theorems:** $\overline{A+B} = \bar{A}\bar{B}$, $\overline{A\cdot B} = \bar{A}+\bar{B}$ - **Karnaugh Maps:** For logic simplification. - **Combinational Logic:** Adders, Decoders, Encoders, Multiplexers, Demultiplexers. - **Sequential Logic:** Flip-Flops (SR, JK, D, T), Registers, Counters. - **Memory:** RAM (SRAM, DRAM), ROM.