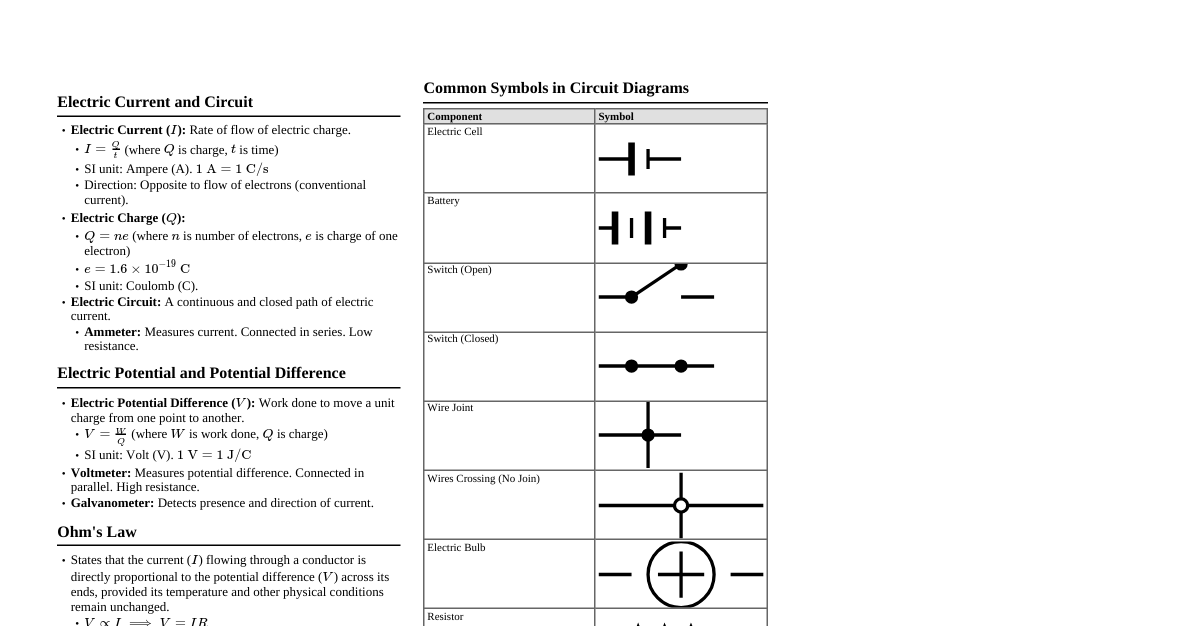
### Chemical Reactions and Equations - **Combination Reaction:** A + B $\rightarrow$ AB (e.g., C + O$_2$ $\rightarrow$ CO$_2$) - **Decomposition Reaction:** AB $\rightarrow$ A + B (e.g., CaCO$_3$ $\rightarrow$ CaO + CO$_2$) - **Displacement Reaction:** A + BC $\rightarrow$ AC + B (e.g., Fe + CuSO$_4$ $\rightarrow$ FeSO$_4$ + Cu) - **Double Displacement Reaction:** AB + CD $\rightarrow$ AD + CB (e.g., Na$_2$SO$_4$ + BaCl$_2$ $\rightarrow$ BaSO$_4$ + 2NaCl) - **Redox Reactions:** Oxidation (gain of O, loss of H, loss of e-) and Reduction (loss of O, gain of H, gain of e-). - **Corrosion:** Metals reacting with substances in the atmosphere (e.g., rusting of iron). - **Rancidity:** Oxidation of fats and oils in food, leading to bad smell and taste. ### Acids, Bases and Salts - **Acids:** Sour taste, turn blue litmus red, pH 7. Release OH$^-$ ions in water. (e.g., NaOH, KOH) - **Salts:** Formed by the reaction of acid and base (Neutralization). (e.g., NaCl, K$_2$SO$_4$) - **pH Scale:** Measures acidity/alkalinity. 0-6.9 (Acidic), 7 (Neutral), 7.1-14 (Basic). - **Indicators:** Litmus, Methyl Orange, Phenolphthalein. - **Important Compounds:** - **Bleaching Powder:** CaOCl$_2$ (for bleaching, disinfectant) - **Baking Soda:** NaHCO$_3$ (antacid, baking) - **Washing Soda:** Na$_2$CO$_3$.10H$_2$O (cleaning, softening water) - **Plaster of Paris:** CaSO$_4$.$\frac{1}{2}$H$_2$O (fracture support, decorative) ### Metals and Non-metals - **Metals:** Malleable, ductile, lustrous, good conductors of heat and electricity, usually solid (except Hg). React with oxygen to form basic oxides. (e.g., Fe, Cu, Al) - **Non-metals:** Brittle, non-lustrous, poor conductors (except graphite), can be solid, liquid, or gas. React with oxygen to form acidic or neutral oxides. (e.g., C, O, N, S) - **Reactivity Series:** K > Na > Ca > Mg > Al > Zn > Fe > Pb > H > Cu > Hg > Ag > Au. More reactive metal displaces less reactive metal. - **Ionic Bonds:** Formed by transfer of electrons (between metal and non-metal). - **Covalent Bonds:** Formed by sharing of electrons (between non-metals). - **Extraction of Metals:** - **High reactivity:** Electrolytic reduction (e.g., Na, Mg, Al) - **Medium reactivity:** Roasting (sulfide ores) or Calcination (carbonate ores) followed by reduction (e.g., Zn, Fe, Pb) - **Low reactivity:** Heating alone (e.g., Hg, Ag) ### Carbon and its Compounds - **Catenation:** Ability of carbon to form long chains, branches, and rings with other carbon atoms. - **Tetravalency:** Carbon has a valency of 4, forming 4 covalent bonds. - **Hydrocarbons:** Compounds of carbon and hydrogen. - **Saturated:** Alkanes (C$_n$H$_{2n+2}$) - single bonds only. - **Unsaturated:** Alkenes (C$_n$H$_{2n}$) - at least one double bond. Alkynes (C$_n$H$_{2n-2}$) - at least one triple bond. - **Functional Groups:** Atoms or groups of atoms that determine the chemical properties of organic compounds (e.g., -OH (alcohol), -COOH (carboxylic acid), -CHO (aldehyde), >C=O (ketone)). - **Homologous Series:** Series of organic compounds with the same functional group and similar chemical properties, differing by a -CH$_2$ group. - **Isomers:** Compounds with the same molecular formula but different structural formulas. - **Important Reactions:** - **Combustion:** Burning in oxygen (e.g., CH$_4$ + 2O$_2$ $\rightarrow$ CO$_2$ + 2H$_2$O + Heat) - **Oxidation:** Adding oxygen (e.g., Ethanol to Ethanoic acid) - **Addition:** Unsaturated hydrocarbons adding H$_2$, Br$_2$, etc. - **Substitution:** Saturated hydrocarbons replacing H with other atoms. ### Periodic Classification of Elements - **Early Attempts:** - **Dobereiner's Triads:** Groups of three elements with similar properties, middle element's atomic mass is average of other two. - **Newlands' Law of Octaves:** Elements arranged by increasing atomic mass, properties repeat every 8th element. - **Mendeleev's Periodic Table:** Elements arranged by increasing atomic mass. Predicted properties of undiscovered elements. Left gaps. - **Modern Periodic Table:** Elements arranged by increasing atomic number (Moseley). - **Periods:** Horizontal rows (7 periods). Number of shells. - **Groups:** Vertical columns (18 groups). Number of valence electrons, similar chemical properties. - **Trends:** - **Atomic Size:** Decreases across a period, increases down a group. - **Metallic Character:** Decreases across a period, increases down a group. - **Non-metallic Character:** Increases across a period, decreases down a group. - **Electronegativity:** Increases across a period, decreases down a group. ### Life Processes - **Nutrition:** Process of taking in food and utilizing it. - **Autotrophic:** Organisms make their own food (e.g., plants - photosynthesis). - **Heterotrophic:** Organisms depend on others for food (e.g., animals - holozoic, saprophytic, parasitic). - **Respiration:** Process of releasing energy from food. - **Aerobic:** With oxygen (Glucose $\rightarrow$ CO$_2$ + H$_2$O + Energy). Occurs in mitochondria. - **Anaerobic:** Without oxygen (Glucose $\rightarrow$ Ethanol/Lactic Acid + Energy). Occurs in cytoplasm. - **Transportation:** - **Plants:** Xylem (water and minerals), Phloem (food). - **Animals (Humans):** Blood (RBC, WBC, platelets, plasma), Heart (pumps blood), Blood Vessels (arteries, veins, capillaries). - **Excretion:** Removal of metabolic waste products. - **Plants:** Stomata (CO$_2$, O$_2$, water vapor), falling leaves, resin, gum. - **Animals (Humans):** Kidneys (filter blood, form urine), Lungs (CO$_2$), Skin (sweat). ### Control and Coordination - **Nervous System (Humans):** - **Central Nervous System (CNS):** Brain and Spinal Cord. - **Peripheral Nervous System (PNS):** Nerves originating from CNS. - **Neuron:** Structural and functional unit of nervous system (Dendrite $\rightarrow$ Cell body $\rightarrow$ Axon $\rightarrow$ Nerve ending). - **Reflex Arc:** Quick, involuntary response (Receptor $\rightarrow$ Sensory neuron $\rightarrow$ Spinal cord $\rightarrow$ Motor neuron $\rightarrow$ Effector). - **Brain:** - **Forebrain:** Cerebrum (thought, memory, voluntary actions). - **Midbrain:** Relays sensory information. - **Hindbrain:** Cerebellum (balance, posture), Pons (respiration), Medulla (heartbeat, breathing, blood pressure). - **Endocrine System (Humans):** Glands that secrete hormones. - **Pituitary:** Master gland. - **Thyroid:** Thyroxine (metabolism). - **Pancreas:** Insulin (lowers blood sugar), Glucagon (raises blood sugar). - **Adrenal:** Adrenaline (fight or flight). - **Testes (males):** Testosterone. - **Ovaries (females):** Estrogen, Progesterone. - **Coordination in Plants:** - **Phytohormones:** Auxins (growth), Gibberellins (stem elongation), Cytokinins (cell division), Abscisic acid (growth inhibitor), Ethylene (fruit ripening). - **Tropism:** Directional growth response to stimuli (Phototropism, Geotropism, Hydrotropism, Chemotropism, Thigmotropism). ### How do Organisms Reproduce? - **Asexual Reproduction:** Single parent, offspring genetically identical. - **Fission:** Binary (Amoeba), Multiple (Plasmodium). - **Fragmentation:** Spirogyra. - **Regeneration:** Planaria, Hydra. - **Budding:** Hydra, Yeast. - **Vegetative Propagation:** Plants (stem, root, leaf). - **Spore Formation:** Fungi (Rhizopus). - **Sexual Reproduction:** Two parents, offspring genetically diverse. - **Flowering Plants:** - **Flower:** Reproductive organ (Sepals, Petals, Stamen (male), Pistil (female)). - **Pollination:** Transfer of pollen (self/cross). - **Fertilization:** Fusion of male and female gametes. Ovary becomes fruit, ovule becomes seed. - **Humans:** - **Male Reproductive System:** Testes (sperm, testosterone), Vas deferens, Urethra, Penis. - **Female Reproductive System:** Ovaries (eggs, estrogen, progesterone), Oviduct (fallopian tube), Uterus, Vagina. - **Menstrual Cycle:** Monthly cycle in females, prepares uterus for pregnancy. ### Heredity and Evolution - **Heredity:** Transmission of characters from parents to offspring. - **Variation:** Differences among individuals of a species. - **Mendel's Laws:** - **Law of Dominance:** In a cross between two pure parents, one character (dominant) expresses, the other (recessive) remains hidden. - **Law of Segregation:** Alleles for a character separate during gamete formation. - **Law of Independent Assortment:** Genes for different characters assort independently during gamete formation. - **Sex Determination:** - **Humans:** XX (female), XY (male). Father determines sex of child. - **Evolution:** Gradual change in living organisms over generations. - **Acquired Traits:** Developed during lifetime, not inherited (e.g., muscular body). - **Inherited Traits:** Passed from parents, genetic (e.g., eye color). - **Evidence of Evolution:** - **Fossils:** Remains of ancient life. - **Homologous Organs:** Same basic structure, different functions (e.g., forelimbs of human, bird, whale). - **Analogous Organs:** Different structure, similar function (e.g., wings of bird and insect). - **Embryology:** Similar embryonic development patterns. - **Natural Selection:** Mechanism of evolution (Darwin). Organisms better adapted to environment survive and reproduce more. - **Speciation:** Formation of new species. ### Light - Reflection and Refraction - **Reflection:** Bouncing back of light. - **Laws:** Angle of incidence = Angle of reflection. Incident ray, reflected ray, and normal lie in the same plane. - **Mirror Formula:** $\frac{1}{f} = \frac{1}{v} + \frac{1}{u}$ - **Magnification:** $m = -\frac{v}{u} = \frac{h'}{h}$ - **Sign Convention:** Distances measured from pole/optical center. Real is positive for v, virtual is negative. Upward positive, downward negative. - **Refraction:** Bending of light as it passes from one medium to another. - **Laws:** Snell's Law: $\frac{\sin i}{\sin r} = \text{constant}$ (refractive index). Incident ray, refracted ray, and normal lie in the same plane. - **Refractive Index (n):** $n = \frac{\text{speed of light in vacuum}}{\text{speed of light in medium}}$ - **Lens Formula:** $\frac{1}{f} = \frac{1}{v} - \frac{1}{u}$ - **Power of Lens (P):** $P = \frac{1}{f}$ (in dioptres, f in meters). Convex lens (positive power), Concave lens (negative power). ### The Human Eye and the Colorful World - **Human Eye:** - **Cornea:** Transparent front part, refracts light. - **Iris:** Controls pupil size. - **Pupil:** Regulates amount of light entering. - **Lens:** Focuses light on retina. - **Retina:** Light-sensitive screen (rods for dim light, cones for color). - **Optic Nerve:** Transmits signals to brain. - **Defects of Vision:** - **Myopia (Nearsightedness):** Distant objects blurred. Corrected by concave lens. - **Hypermetropia (Farsightedness):** Near objects blurred. Corrected by convex lens. - **Presbyopia:** Age-related, difficulty focusing on near objects. Corrected by bifocal lenses. - **Cataract:** Lens becomes cloudy. - **Dispersion of Light:** Splitting of white light into its constituent colors (VIBGYOR) by a prism. - **Atmospheric Refraction:** - Twinkling of stars. - Advanced sunrise and delayed sunset. - **Scattering of Light:** - Tyndall effect (path of light visible in colloid). - Blue color of sky (short wavelengths scattered more). - Reddish appearance of sun at sunrise/sunset (blue light scattered away). ### Electricity - **Electric Current (I):** Flow of charge. $I = \frac{Q}{t}$ (Amperes, A). - **Electric Potential Difference (V):** Work done per unit charge. $V = \frac{W}{Q}$ (Volts, V). - **Ohm's Law:** $V = IR$ (Resistance, R in Ohms, $\Omega$). - **Resistance:** $R = \rho \frac{L}{A}$ ($\rho$ = resistivity, L = length, A = area). - **Resistors in Series:** $R_{eq} = R_1 + R_2 + ...$ (Current same, Voltage divides). - **Resistors in Parallel:** $\frac{1}{R_{eq}} = \frac{1}{R_1} + \frac{1}{R_2} + ...$ (Voltage same, Current divides). - **Joule's Law of Heating:** $H = I^2Rt = VIt = \frac{V^2}{R}t$ (Heat energy). - **Electric Power (P):** Rate at which energy is consumed. $P = VI = I^2R = \frac{V^2}{R}$ (Watts, W). - **Commercial Unit of Energy:** Kilowatt-hour (kWh). 1 kWh = 3.6 x 10$^6$ J. ### Magnetic Effects of Electric Current - **Magnetic Field:** Region around a magnet or current-carrying conductor where its magnetic effect can be felt. - **Magnetic Field Lines:** - Emerge from North pole, enter South pole (outside magnet). - Form closed loops. - Never intersect. - Closer lines indicate stronger field. - **Right-Hand Thumb Rule:** Direction of magnetic field around a straight current-carrying conductor. - **Solenoid:** Coil of many circular turns of insulated copper wire. Acts like a bar magnet. - **Electromagnet:** Temporary magnet created by passing current through a solenoid. - **Fleming's Left-Hand Rule:** Direction of force on a current-carrying conductor in a magnetic field. (Thumb = Force, Forefinger = Field, Middle finger = Current). - **Electric Motor:** Converts electrical energy to mechanical energy. - **Electromagnetic Induction:** Producing induced current in a coil by changing magnetic field. - **Fleming's Right-Hand Rule:** Direction of induced current. (Thumb = Motion, Forefinger = Field, Middle finger = Induced Current). - **Electric Generator:** Converts mechanical energy to electrical energy. - **AC (Alternating Current):** Reverses direction periodically. - **DC (Direct Current):** Flows in one direction only. - **Domestic Electric Circuits:** Live wire (red), Neutral wire (black), Earth wire (green). Short circuit, overloading. ### Sources of Energy - **Conventional Sources:** - **Fossil Fuels:** Coal, petroleum, natural gas (non-renewable, cause pollution). - **Thermal Power Plants:** Use fossil fuels to produce electricity. - **Hydro Power Plants:** Use flowing water to generate electricity (renewable, but environmental impact). - **Biomass Energy:** From organic matter (e.g., biogas from cow dung). - **Wind Energy:** From wind turbines (renewable, clean). - **Non-Conventional/Renewable Sources:** - **Solar Energy:** From sun. Solar cells (photovoltaic), solar heaters. - **Ocean Thermal Energy Conversion (OTEC):** Uses temperature difference between surface and deep ocean water. - **Geothermal Energy:** From Earth's interior. - **Nuclear Energy:** From nuclear fission (e.g., Uranium). High energy yield, but radioactive waste. - **Environmental Consequences:** Pollution, global warming, acid rain. - **Sustainable Energy:** Meeting present needs without compromising future generations. ### Our Environment - **Ecosystem:** Biotic (living) and Abiotic (non-living) components interacting together. - **Components:** - **Producers:** Autotrophs (plants). - **Consumers:** Heterotrophs (herbivores, carnivores, omnivores). - **Decomposers:** Bacteria, fungi (break down dead organic matter). - **Food Chain:** Flow of energy from one organism to another (e.g., Grass $\rightarrow$ Deer $\rightarrow$ Tiger). - **Food Web:** Interconnected food chains. - **Ten Percent Law:** Only 10% of energy is transferred to the next trophic level. - **Biomagnification:** Increase in concentration of harmful chemical substances at successive trophic levels. - **Ozone Layer:** O$_3$ layer in stratosphere, protects from harmful UV radiation. Depleted by CFCs. - **Waste Management:** - **Biodegradable:** Decomposed by microorganisms (e.g., paper, food waste). - **Non-biodegradable:** Not decomposed (e.g., plastics, glass). - **Methods:** Reduce, Reuse, Recycle. ### Management of Natural Resources - **Natural Resources:** Air, water, soil, forests, wildlife, minerals, fossil fuels. - **Conservation:** Wise and judicious use of resources to ensure availability for future generations. - **Forests and Wildlife:** - **Importance:** Biodiversity, timber, medicines, ecological balance, prevent soil erosion. - **Threats:** Deforestation, poaching. - **Conservation Efforts:** Reforestation, protected areas (national parks, wildlife sanctuaries). - **Water Resources:** - **Importance:** Drinking, agriculture, industry. - **Conservation:** Rainwater harvesting, dams, efficient irrigation. - **Water Pollution:** Industrial waste, sewage, agricultural runoff. - **Coal and Petroleum:** - **Importance:** Energy sources. - **Conservation:** Use renewable alternatives, efficient use. - **Alternatives:** Solar, wind, hydro. - **Sustainable Development:** Development that meets the needs of the present without compromising the ability of future generations to meet their own needs.