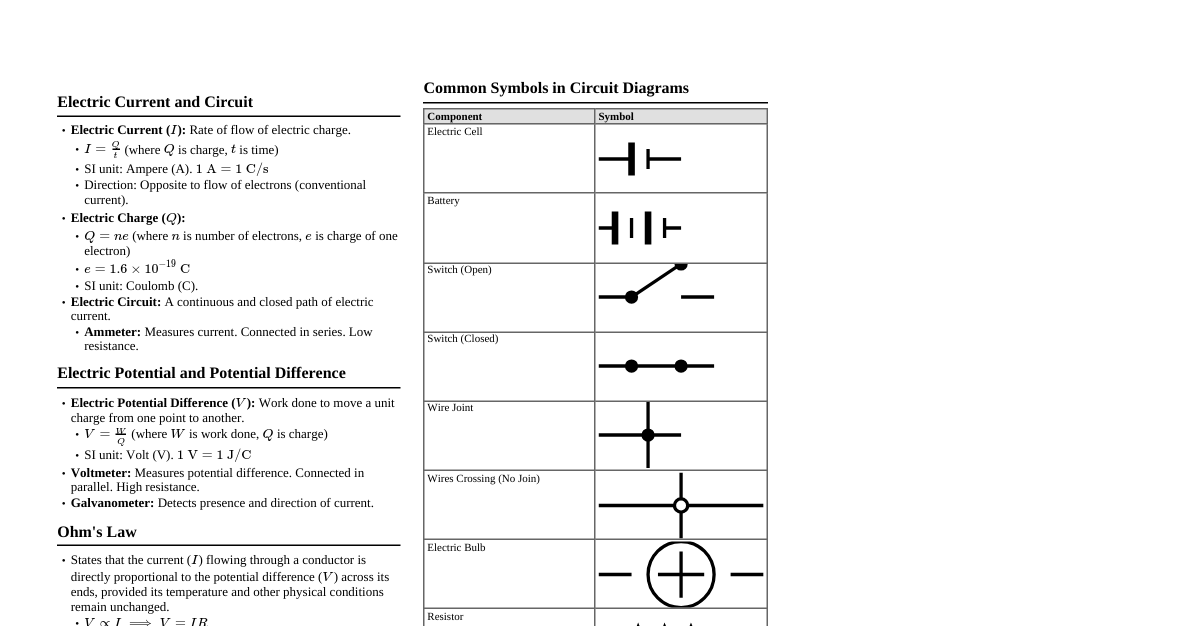
1. Food: Where Does It Come From? Ingredients: Materials needed to prepare food items. Sources of Food: Plants: Grains, cereals, vegetables, fruits. Animals: Milk, eggs, meat, honey. Edible Parts of Plants: Roots (carrot), stems (potato), leaves (spinach), flowers (cauliflower), fruits (apple), seeds (wheat). Animal Products: Milk: From cow, buffalo, goat, camel. Used to make butter, cheese, curd. Eggs: From hen, duck. Meat: From chicken, goat, fish. Honey: Made by honeybees from nectar. Food Habits of Animals: Herbivores: Eat only plants (cow, deer, goat). Carnivores: Eat only other animals (lion, tiger, snake). Omnivores: Eat both plants and animals (human, bear, crow). 2. Components of Food Nutrients: Substances that provide nourishment essential for the maintenance of life and for growth. Main Nutrients: Carbohydrates: Energy-giving food (rice, wheat, potato, sugar). Fats: Also provide energy and warmth (butter, oil, nuts). Proteins: Body-building food, help in growth and repair (milk, eggs, meat, pulses). Vitamins: Protect body against diseases, maintain good health (fruits, vegetables). Minerals: Essential for proper body function, growth, and health (milk, fruits, vegetables, salt). Roughage (Dietary Fibre): Helps in bowel movement, adds bulk to food, prevents constipation (whole grains, fresh fruits, vegetables). Water: Helps absorb nutrients, regulate body temperature, remove waste. Deficiency Diseases: Diseases caused by lack of nutrients over a long period. Carbohydrates/Fats: Weakness, lack of energy. Proteins: Stunted growth, swelling of face, skin diseases. Vitamin A: Loss of vision (night blindness). Vitamin B1: Beriberi (weak muscles, very little energy to work). Vitamin C: Scurvy (bleeding gums). Vitamin D: Rickets (bones become soft and bent). Calcium: Bone and tooth decay. Iodine: Goitre (swollen neck gland). Iron: Anaemia (weakness). Balanced Diet: A diet that provides all the essential nutrients, roughage, and water in the right amounts. 3. Fibre to Fabric Fibre: Thin strands from which fabrics are made. Fabric: Cloth made by weaving or knitting fibres. Types of Fibres: Natural Fibres: Obtained from plants and animals. Plant Fibres: Cotton, Jute. Animal Fibres: Wool, Silk. Synthetic Fibres: Man-made fibres (polyester, nylon, acrylic). Cotton: Grows in black soil and warm climate. Fruiting bodies called cotton bolls. Ginning: Process of separating cotton fibres from seeds. Jute: Obtained from the stem of the jute plant. Cultivated during rainy season. Used for making sacks, mats, ropes, yarn. Spinning: Process of making yarn from fibres (e.g., using charkha, takli). Yarn: Spun fibres twisted together. Fabric Production: Weaving: Process of arranging two sets of yarn together to make a fabric (done on looms). Knitting: A single yarn is used to make a piece of fabric (e.g., sweaters). History of Clothing: Early people used leaves, animal skins, furs. Later, they learned to weave. 4. Sorting Materials into Groups Objects around us: Made of one or more materials. Materials: Wood, paper, plastic, steel, glass, cotton. Properties of Materials: Lustre: Shininess (metals like gold, silver). Hardness: How easily a material can be compressed or scratched (diamond is hard, sponge is soft). Soluble/Insoluble: Dissolves in water (salt, sugar) or does not dissolve (sand, oil). Float/Sink: Objects that are lighter than water float (wood, plastic), heavier objects sink (iron, stone). Transparency: Transparent: Can see through clearly (glass, clear water). Translucent: Can see through, but not clearly (oiled paper, frosted glass). Opaque: Cannot see through at all (wood, cardboard, metal). Why Group Materials? Convenience in storing. To study their properties and use them for suitable purposes. 5. Separation of Substances Why separate? To remove undesirable substances or obtain useful components. Methods of Separation: Handpicking: Separating slightly larger impurities like stones, husk from rice, pulses. Threshing: Separating grain from stalks. Winnowing: Separating heavier and lighter components of a mixture by wind or blowing air (husk from grain). Sieving: Separating components of different sizes using a sieve (flour from bran, sand from pebbles). Sedimentation: Heavier insoluble particles settle down at the bottom of a liquid. Decantation: Pouring out the liquid without disturbing the settled sediment. Filtration: Separating insoluble solids from a liquid using a filter (tea leaves from tea, muddy water). Evaporation: Converting a liquid into vapour to separate dissolved solids (salt from saltwater). Condensation: Converting water vapour into its liquid form. Saturated Solution: A solution in which no more solute can be dissolved at a given temperature. 6. Changes Around Us Changes: Events that lead to alteration in state, shape, size, or position. Types of Changes: Reversible Changes: Can be reversed to their original state (melting ice, stretching rubber band). Irreversible Changes: Cannot be reversed to their original state (burning paper, cooking food, growth of a plant). Ways to bring about a change: By heating (melting wax, cooking food). By mixing with another substance (mixing cement with water). By applying force (shaping clay). Expansion: Increase in size on heating (e.g., metals expand). Contraction: Decrease in size on cooling. 7. Getting to Know Plants Parts of a Plant: Root System: Underground part. Tap Root: Main single root with smaller lateral roots (carrot, radish). Fibrous Root: Cluster of roots originating from the base of the stem (grass, wheat). Functions: Anchor plant, absorb water and minerals. Shoot System: Part above the ground. Stem: Supports branches, leaves, flowers, transports water and food. Leaves: Site of photosynthesis, transpiration. Venation: Pattern of veins on the leaf. Reticulate: Net-like. Parallel: Parallel veins. Transpiration: Loss of water from leaves in the form of vapour. Flowers: Reproductive part of the plant. Sepals: Protect the bud. Petals: Often brightly coloured. Stamens: Male part. Pistil: Female part. Types of Plants: Herbs: Small, non-woody stems (mint, spinach). Shrubs: Medium-sized, woody stems branching near the ground (rose). Trees: Tall, strong woody stems (mango, neem). Creepers: Plants with weak stems that spread on the ground (pumpkin). Climbers: Plants with weak stems that take support and climb up (money plant). 8. Body Movements Movement: Change in position of a part of the body. Locomotion: Movement of the entire body from one place to another. Skeletons: Framework of bones that provides shape, support, and protection. Human Skeleton: Made of bones and cartilage. Bones: Hard, rigid structures. Cartilage: Softer, elastic tissue (e.g., ear). Joints: Place where two or more bones meet. Ball and Socket Joint: Allows movement in all directions (shoulder, hip). Pivotal Joint: Rotational movement (neck). Hinge Joint: Back and forth movement (knee, elbow). Fixed Joint: No movement (skull bones). Muscles: Attached to bones, contract and relax to cause movement. Muscles work in pairs. Movement in Animals: Earthworm: Body segments expand and contract. Snail: Muscular foot produces wave-like movements. Cockroach: Three pairs of legs for walking, two pairs of wings for flying. Birds: Hollow bones, strong muscles, adapted wings for flight. Fish: Streamlined body, strong muscles, fins for swimming. Snake: Long backbone, many muscles, body loops to push against the ground. 9. The Living Organisms - Characteristics and Habitats Habitat: The surroundings where organisms live (e.g., desert, mountain, ocean). Adaptation: Specific features or habits that enable an organism to live in its habitat. Biotic Components: Living things (plants, animals). Abiotic Components: Non-living things (rocks, soil, air, water, sunlight). Adaptations in different habitats: Desert: Plants (Cactus): Thick waxy stem, leaves reduced to spines, deep roots. Animals (Camel): Long legs, humps for fat storage. Mountains: Trees: Cone-shaped, sloping branches. Animals (Yak): Thick fur. Ocean: Fish: Streamlined body, gills for breathing. Dolphins/Whales: Breathe through blowholes. Characteristics of Living Organisms: Need Food: For energy and growth. Respiration: Breathing. Response to Stimuli: React to changes in surroundings. Excretion: Removal of waste products. Reproduction: Produce more of their own kind. Movement: Internal or external. Growth: Increase in size. 10. Motion and Measurement of Distances Motion: Change in position of an object with time. Rest: Object does not change its position with time. Types of Motion: Rectilinear Motion: Along a straight line (car on a straight road). Circular Motion: Along a circular path (fan blades). Periodic Motion: Repeats itself after a fixed interval of time (pendulum, swing). Standard Units of Measurement: Length: Metre (m) Mass: Kilogram (kg) Time: Second (s) Measuring Length: Using a ruler, measuring tape. $1 \text{ km} = 1000 \text{ m}$ $1 \text{ m} = 100 \text{ cm}$ $1 \text{ cm} = 10 \text{ mm}$ Correct way to measure: Place ruler along the object. Eye position perpendicular to the mark being read. Start measurement from zero mark. 11. Light, Shadows and Reflections Light: A form of energy that enables us to see objects. Luminous Objects: Objects that emit their own light (sun, torch). Non-luminous Objects: Objects that reflect light from other sources (moon, chair). Transparent Objects: Allow light to pass through them completely (glass, clear water). Translucent Objects: Allow some light to pass through, but scatter it (oiled paper, frosted glass). Opaque Objects: Do not allow any light to pass through them (wood, metal). Shadows: Formed when an opaque object blocks the path of light. Require a source of light, an opaque object, and a screen. Always formed on the opposite side of the light source. Colour of shadow is always black. Pinhole Camera: A simple camera that forms an inverted image. Reflection: The bouncing back of light when it strikes a surface. Mirror: A smooth, polished surface that reflects light. Image formed by a plane mirror: Erect. Same size as the object. Laterally inverted. 12. Electricity and Circuits Electricity: A form of energy. Electric Cell: A source of electricity. Has a positive terminal (+) and a negative terminal (-). Electric Bulb: Consists of a filament that glows when electricity passes through it. Electric Circuit: A complete path for electricity to flow. Switch: A device that either breaks the circuit (OFF) or completes it (ON). Conductors: Materials that allow electric current to pass through them (metals like copper, iron). Insulators: Materials that do not allow electric current to pass through them (plastic, wood, rubber). Safety with Electricity: Never touch live wires. 13. Fun with Magnets Magnet: A material that attracts ferromagnetic materials (iron, nickel). Magnetic Materials: Substances attracted by a magnet (iron, nickel). Non-magnetic Materials: Substances not attracted by a magnet (plastic, wood). Poles of a Magnet: Every magnet has two poles: North (N) and South (S). Magnetic strength is strongest at the poles. Properties of Magnets: Attraction: Attracts magnetic materials. Directional Property: A freely suspended magnet always points in the North-South direction. Like poles repel, unlike poles attract. Magnetic Compass: A device used to find directions. Making a Magnet: By rubbing an iron piece repeatedly with one pole of a magnet. Loss of Magnetic Properties: Magnets lose their properties if heated, hammered, or dropped. 14. Water Water Cycle: Continuous movement of water. Evaporation: Water changes into vapour. Transpiration: Water vapour released by plants. Condensation: Water vapour cools down and forms droplets (clouds). Precipitation: Water droplets fall as rain, snow. Forms of Water: Solid (ice), Liquid (water), Gas (water vapour). Uses of Water: Drinking, cooking, washing, irrigation. Scarcity of Water: Lack of sufficient fresh water. Conservation of Water: Reduce, Reuse, Recycle. Rainwater Harvesting: Collecting and storing rainwater. Droughts: Long periods of insufficient rainfall. Floods: Excess rainfall. 15. Air Around Us Air: Mixture of several gases. Composition of Air: Nitrogen (approx. 78%) Oxygen (approx. 21%) Carbon Dioxide (approx. 0.03-0.04%) Water Vapour, Dust Particles, other gases (remaining 1%) Properties of Air: Occupies space. Has weight. Exerts pressure. Is present everywhere. Importance of Air: Oxygen: Essential for respiration and burning. Carbon Dioxide: Used by plants for photosynthesis. Water Vapour: Important for the water cycle. Wind: Moving air. Air Pollution: Contamination of air by harmful substances. 16. Garbage In, Garbage Out Garbage (Waste): Unwanted or discarded materials. Types of Waste: Biodegradable Waste: Decomposes naturally (food scraps, paper). Non-biodegradable Waste: Does not decompose naturally (plastics, metals, glass). Waste Management: Methods to handle waste. Segregation: Separating waste. Composting: Converting organic waste into manure. Recycling: Processing used materials into new products. Landfills: Areas where garbage is collected and buried. Reduce, Reuse, Recycle (3 R's): Principles of waste management. Plastic: A major non-biodegradable pollutant.