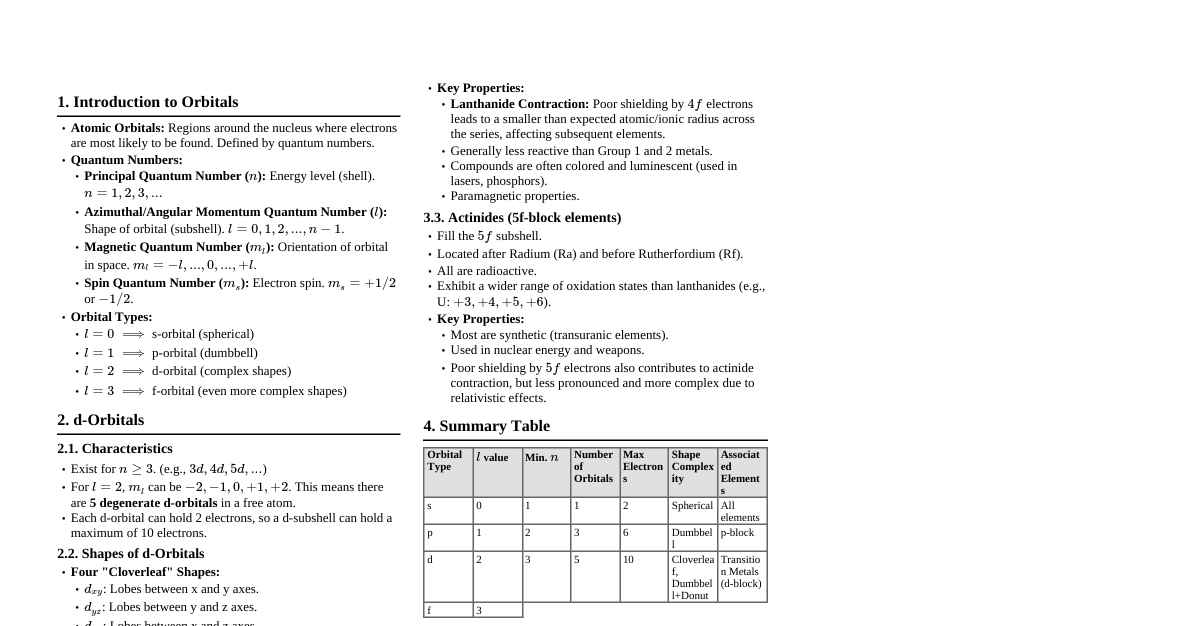
1. File Basics File Pointer: A pointer to a structure of type FILE , used to manage a file stream. FILE *fptr; Header: All file I/O functions are declared in <stdio.h> . 2. Opening a File: fopen() Syntax: FILE *fopen(const char *filename, const char *mode); Returns: A FILE pointer on success, NULL on failure. File Modes: Mode Description "r" Read. File must exist. "w" Write. Creates new file or truncates existing. "a" Append. Creates new file or appends to existing. "r+" Read/Write. File must exist. "w+" Read/Write. Creates new or truncates existing. "a+" Read/Append. Creates new or appends to existing. Binary Modes: Add "b" to any mode (e.g., "rb" , "wb+" ) for binary files. Example: FILE *file = fopen("data.txt", "w"); if (file == NULL) { // Handle error } 3. Closing a File: fclose() Syntax: int fclose(FILE *stream); Returns: $0$ on success, EOF on error. Important: Always close files to flush buffers and release resources. Example: if (fclose(file) == EOF) { // Handle error } 4. Character I/O fputc() : Writes a character to a file. Syntax: int fputc(int char_to_write, FILE *stream); Returns: Character written on success, EOF on error. fgetc() : Reads a character from a file. Syntax: int fgetc(FILE *stream); Returns: Character read on success, EOF on End-Of-File or error. Example: fputc('A', file); char c = fgetc(file); 5. String I/O fputs() : Writes a string to a file. Does not append newline. Syntax: int fputs(const char *str, FILE *stream); Returns: Non-negative on success, EOF on error. fgets() : Reads a string from a file. Reads up to n-1 characters or until newline/EOF. Syntax: char *fgets(char *str, int num, FILE *stream); Returns: str on success, NULL on EOF or error. Example: fputs("Hello C!", file); char buffer[100]; fgets(buffer, sizeof(buffer), file); 6. Formatted I/O fprintf() : Writes formatted output to a file. Syntax: int fprintf(FILE *stream, const char *format, ...); Works like printf but writes to a file. fscanf() : Reads formatted input from a file. Syntax: int fscanf(FILE *stream, const char *format, ...); Works like scanf but reads from a file. Example: int x = 10; float y = 3.14; fprintf(file, "Int: %d, Float: %.2f\n", x, y); fscanf(file, "Int: %d, Float: %f", &x, &y); 7. Block I/O (Binary Files) fwrite() : Writes blocks of data. Syntax: size_t fwrite(const void *ptr, size_t size, size_t nmemb, FILE *stream); ptr : Pointer to data. size : Size of each item in bytes. nmemb : Number of items to write. Returns: Number of items successfully written. fread() : Reads blocks of data. Syntax: size_t fread(void *ptr, size_t size, size_t nmemb, FILE *stream); ptr : Pointer to store data. Returns: Number of items successfully read. Example: struct Data { int id; float value; }; struct Data d = {1, 10.5}; fwrite(&d, sizeof(struct Data), 1, file); struct Data read_d; fread(&read_d, sizeof(struct Data), 1, file); 8. File Positioning fseek() : Sets the file position indicator. Syntax: int fseek(FILE *stream, long offset, int whence); offset : Number of bytes to move. whence : Position to seek from: SEEK_SET : Beginning of file. SEEK_CUR : Current position. SEEK_END : End of file. Returns: $0$ on success, non-zero on error. ftell() : Returns the current file position. Syntax: long ftell(FILE *stream); Returns: Current position on success, $-1L$ on error. rewind() : Sets the file position to the beginning. Syntax: void rewind(FILE *stream); Equivalent to (void)fseek(stream, 0L, SEEK_SET); Example: fseek(file, 0, SEEK_END); // Go to end long size = ftell(file); // Get file size rewind(file); // Go to beginning 9. Error Handling & EOF feof() : Checks for End-Of-File indicator. Syntax: int feof(FILE *stream); Returns: Non-zero if EOF indicator is set, $0$ otherwise. ferror() : Checks for error indicator. Syntax: int ferror(FILE *stream); Returns: Non-zero if error indicator is set, $0$ otherwise. clearerr() : Clears EOF and error indicators. Syntax: void clearerr(FILE *stream); Example: if (feof(file)) { /* EOF reached */ } if (ferror(file)) { /* Error occurred */ } 10. Other File Operations remove() : Deletes a file. Syntax: int remove(const char *filename); Returns: $0$ on success, non-zero on error. rename() : Renames a file. Syntax: int rename(const char *oldname, const char *newname); Returns: $0$ on success, non-zero on error. tmpfile() : Creates a temporary binary file that is automatically deleted when closed or program terminates. Syntax: FILE *tmpfile(void); Returns: FILE pointer on success, NULL on failure.