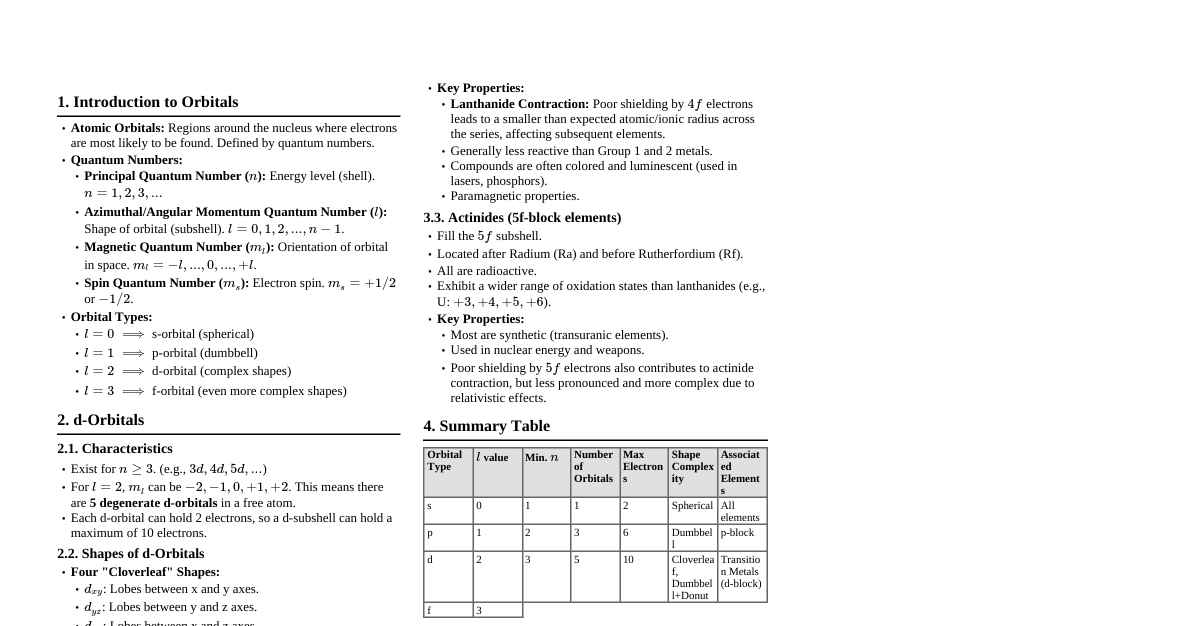
Course Objectives To understand numerical methods to find roots of functions and first order unconstrained minimization of functions. To introduce concept of interpolation methods and numerical integration. To understand numerical methods to solve systems of algebraic equations and curve fitting by splines. To understand numerical methods for the solution of Ordinary and partial differential equations. Course Outcomes (CO) CO 1: Ability to develop mathematical models of low level engineering problems. CO 2: Ability to apply interpolation methods and numerical integration. CO 3: Ability to solve simultaneous linear equations and curve fitting by splines. CO 4: Ability to numerically solve ordinary differential equations that are initial value or boundary value problems. UNIT - I: Roots & Optimization Numerical Computations Basics Taylor Series: $f(x) = f(a) + f'(a)(x-a) + \frac{f''(a)}{2!}(x-a)^2 + \dots$ Rolle's Theorem: If $f(a)=f(b)$ and $f$ is continuous on $[a,b]$ and differentiable on $(a,b)$, then there exists $c \in (a,b)$ such that $f'(c)=0$. Mean Value Theorem: If $f$ is continuous on $[a,b]$ and differentiable on $(a,b)$, then there exists $c \in (a,b)$ such that $f'(c) = \frac{f(b)-f(a)}{b-a}$. Approximations and Errors in numerical computations. Data representation and computer arithmetic, Loss of significance. Location of Roots of Equation Bisection Method: Requires $f(a)f(b) New midpoint $c = \frac{a+b}{2}$. Convergence: Linear. Newton-Raphson Method: $x_{n+1} = x_n - \frac{f(x_n)}{f'(x_n)}$ Convergence: Quadratic. Secant Method: $x_{n+1} = x_n - f(x_n)\frac{x_n - x_{n-1}}{f(x_n) - f(x_{n-1})}$ Convergence: Superlinear ($\approx 1.618$). Unconstrained One Variable Function Minimization Fibonacci Search Golden Section Search Newton's Method for optimization: $x_{k+1} = x_k - \frac{f'(x_k)}{f''(x_k)}$ (for minimum, $f'(x)=0$) Multivariate Function Minimization Method of Steepest Descent Nelder-Mead Algorithm (Simplex Method) UNIT - II: Interpolation & Numerical Integration Interpolation Assumptions for interpolation, errors in polynomial interpolation. Finite differences: Forward, Backward, Central. Gregory-Newton's Forward Interpolation Formula: $P_n(x) = y_0 + s\Delta y_0 + \frac{s(s-1)}{2!}\Delta^2 y_0 + \dots + \frac{s(s-1)\dots(s-n+1)}{n!}\Delta^n y_0$, where $s = \frac{x-x_0}{h}$. Gregory-Newton's Backward Interpolation Formula: $P_n(x) = y_n + s\nabla y_n + \frac{s(s+1)}{2!}\nabla^2 y_n + \dots + \frac{s(s+1)\dots(s+n-1)}{n!}\nabla^n y_n$, where $s = \frac{x-x_n}{h}$. Lagrange's Interpolation Formula: $P_n(x) = \sum_{j=0}^{n} y_j L_j(x)$, where $L_j(x) = \prod_{k=0, k \neq j}^{n} \frac{x-x_k}{x_j-x_k}$. Newton's Divided Difference Interpolation: $P_n(x) = f[x_0] + (x-x_0)f[x_0,x_1] + \dots + (x-x_0)\dots(x-x_{n-1})f[x_0,\dots,x_n]$. Numerical Integration (Definite Integral) Newton-Cotes Quadrature Formulae. Trapezoidal Rule: $\int_a^b f(x) dx \approx \frac{h}{2} [f(x_0) + 2\sum_{i=1}^{n-1} f(x_i) + f(x_n)]$. Simpson's One-Third Rule: $\int_a^b f(x) dx \approx \frac{h}{3} [f(x_0) + 4\sum_{i=1,3,\dots}^{n-1} f(x_i) + 2\sum_{i=2,4,\dots}^{n-2} f(x_i) + f(x_n)]$ (for even $n$). Simpson's Three-Eight Rule: $\int_a^b f(x) dx \approx \frac{3h}{8} [f(x_0) + 3\sum_{i=1,4,\dots}^{n-2} f(x_i) + 3\sum_{i=2,5,\dots}^{n-1} f(x_i) + 2\sum_{i=3,6,\dots}^{n-3} f(x_i) + f(x_n)]$ (for $n$ as a multiple of 3). Errors in quadrature formulae. Romberg's Algorithm. Gaussian Quadrature Formula. UNIT - III: Systems of Linear Equations & Splines System of Linear Algebraic Equations Existence of solution. Gauss Elimination Method: Transforms matrix to upper triangular form. Concept of Pivoting (Partial and Complete). Gauss-Jordan Method: Transforms matrix to reduced row echelon form (identity matrix). Computational effort analysis for these methods. Triangular Matrix Factorization Methods Dolittle Algorithm: $A = LU$ (unit diagonal for $L$). Crout's Algorithm: $A = LU$ (unit diagonal for $U$). Cholesky Method: For symmetric positive-definite matrices, $A = LL^T$. Eigenvalue Problem Power Method: Iterative method to find the dominant eigenvalue and its corresponding eigenvector. $Ax = \lambda x$. Approximation by Spline Function First-Degree Splines (Linear Splines). Second-Degree Splines (Quadratic Splines). Natural Cubic Splines. B-Splines. Interpolation and Approximation using splines. UNIT - IV: Numerical Solution of Differential Equations Numerical Solution of Ordinary Differential Equations (ODEs) Picard's Method: Iterative method for solving initial value problems. Taylor Series Method: $y(x+h) = y(x) + h y'(x) + \frac{h^2}{2!} y''(x) + \dots$. Euler's Method: $y_{n+1} = y_n + h f(x_n, y_n)$. Runge-Kutta Methods (RK2, RK4): RK2 (Heun's Method): $y_{n+1} = y_n + \frac{h}{2} (k_1 + k_2)$, where $k_1 = f(x_n, y_n)$, $k_2 = f(x_n+h, y_n+hk_1)$. RK4: $y_{n+1} = y_n + \frac{h}{6} (k_1 + 2k_2 + 2k_3 + k_4)$. Predictor-Corrector Methods: Euler's Predictor-Corrector: Predictor: $y_{n+1}^* = y_n + h f(x_n, y_n)$ Corrector: $y_{n+1} = y_n + \frac{h}{2} [f(x_n, y_n) + f(x_{n+1}, y_{n+1}^*)]$ Adams-Bashforth Method. Milne's Method. Numerical Solution of Partial Differential Equations (PDEs) Parabolic Equations (e.g., Heat Equation). Hyperbolic Equations (e.g., Wave Equation). Elliptic Equations (e.g., Laplace Equation). Implementation of these methods is typically done in C/C++.