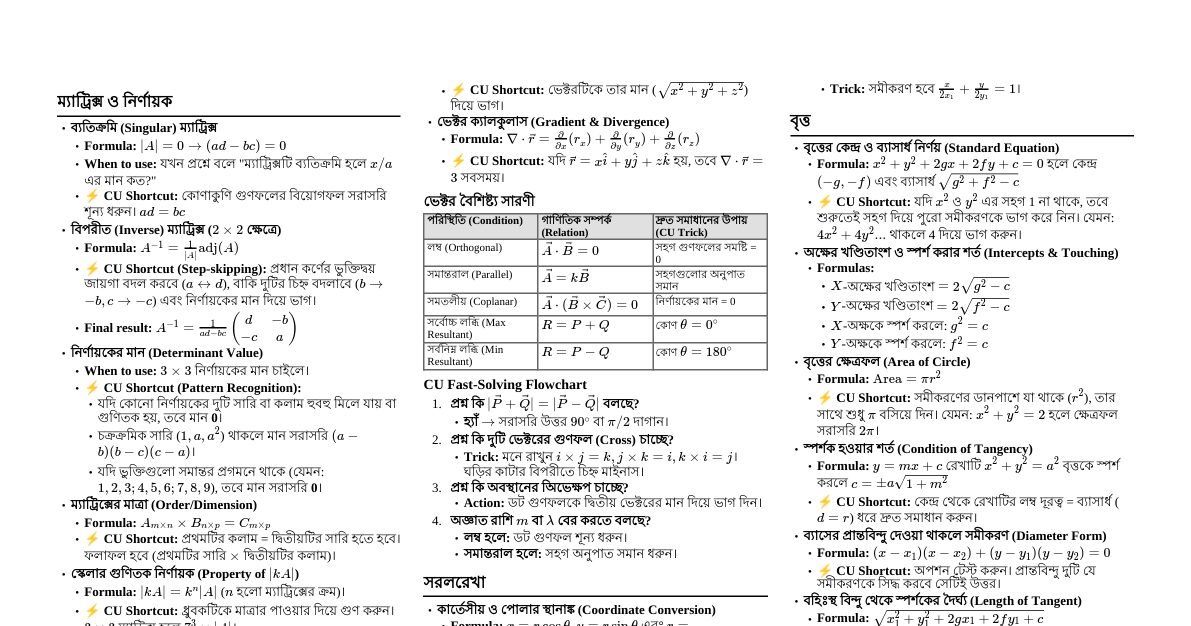
1. Multiplication Tricks Multiply by 5 To multiply any number by 5, first multiply by 10, then divide by 2. Example: $36 \times 5 = (36 \times 10) / 2 = 360 / 2 = 180$ Example: $123 \times 5 = (123 \times 10) / 2 = 1230 / 2 = 615$ Multiply by 9 To multiply by 9, multiply by 10 and subtract the original number. Example: $45 \times 9 = (45 \times 10) - 45 = 450 - 45 = 405$ Example: $78 \times 9 = (78 \times 10) - 78 = 780 - 78 = 702$ Multiply by 11 For a two-digit number $AB$: $A(A+B)B$. If $A+B > 9$, carry over the tens digit. Example: $34 \times 11$: $3(3+4)4 = 374$ Example: $58 \times 11$: $5(5+8)8 = 5(13)8 = (5+1)38 = 638$ For larger numbers: Sum adjacent digits from right to left. Example: $123 \times 11$: Last digit: $3$ $2+3 = 5$ $1+2 = 3$ First digit: $1$ Result: $1353$ Multiplying Numbers Ending in 0 Multiply the non-zero parts and add the total number of zeros at the end. Example: $30 \times 400 = (3 \times 4) \text{ followed by } (1+2) \text{ zeros} = 12000$ 2. Division Tricks Divisibility Rules Number Rule Example 2 Ends in $0, 2, 4, 6, 8$ (even) $246$ (yes), $135$ (no) 3 Sum of digits is divisible by 3 $123 \implies 1+2+3=6$ (yes) 4 Last two digits are divisible by 4 $1324 \implies 24$ (yes) 5 Ends in $0$ or $5$ $75$ (yes), $92$ (no) 6 Divisible by both 2 and 3 $126$ (even, $1+2+6=9$) (yes) 9 Sum of digits is divisible by 9 $819 \implies 8+1+9=18$ (yes) 10 Ends in $0$ $230$ (yes) 3. Squaring Numbers Squaring Numbers Ending in 5 For a number $N5$, where $N$ is the tens digit: The last two digits are always $25$. The preceding digits are $N \times (N+1)$. Example: $35^2$: $N=3$. $3 \times (3+1) = 3 \times 4 = 12$. So, $1225$. Example: $85^2$: $N=8$. $8 \times (8+1) = 8 \times 9 = 72$. So, $7225$. Squaring Numbers Near 50 Base is $25$. For $50+x$: $(25+x)$ followed by $x^2$. For $50-x$: $(25-x)$ followed by $x^2$. If $x^2$ is a single digit, prepend a $0$. Example: $53^2$: $x=3$. $25+3 = 28$. $3^2 = 09$. So, $2809$. Example: $48^2$: $x=2$. $25-2 = 23$. $2^2 = 04$. So, $2304$. General Squaring (A+B)^2 or (A-B)^2 $(a+b)^2 = a^2 + 2ab + b^2$ $(a-b)^2 = a^2 - 2ab + b^2$ Example: $32^2 = (30+2)^2 = 30^2 + 2(30)(2) + 2^2 = 900 + 120 + 4 = 1024$ Example: $47^2 = (50-3)^2 = 50^2 - 2(50)(3) + 3^2 = 2500 - 300 + 9 = 2209$ 4. Percentage Tricks Finding Percentages $10\%$ of a number: Move decimal one place to the left. Example: $10\%$ of $230 = 23.0$ $1\%$ of a number: Move decimal two places to the left. Example: $1\%$ of $230 = 2.30$ Calculating Complex Percentages Break down percentages into easier components. Example: Find $30\%$ of $150$: $10\%$ of $150 = 15$ $30\% = 3 \times 10\% = 3 \times 15 = 45$ Example: Find $15\%$ of $80$: $10\%$ of $80 = 8$ $5\%$ of $80 = (10\% / 2) = 8 / 2 = 4$ $15\% = 10\% + 5\% = 8 + 4 = 12$ 5. Addition & Subtraction Adding Large Numbers Round to the nearest convenient number, then adjust. Example: $38 + 57$: $(40 - 2) + (60 - 3) = 100 - 5 = 95$ Or $(38+2) + (57-2) = 40 + 55 = 95$ Subtracting Large Numbers Adjust both numbers by the same amount to make subtraction easier. Example: $73 - 29$: Add 1 to both: $(73+1) - (29+1) = 74 - 30 = 44$ 6. Fractions Adding/Subtracting Fractions with Different Denominators Find a common denominator (LCM). $\frac{a}{b} + \frac{c}{d} = \frac{ad + bc}{bd}$ Example: $\frac{1}{3} + \frac{1}{4} = \frac{1 \times 4 + 1 \times 3}{3 \times 4} = \frac{4+3}{12} = \frac{7}{12}$ Multiplying Fractions Multiply numerators and multiply denominators. $\frac{a}{b} \times \frac{c}{d} = \frac{ac}{bd}$ Example: $\frac{2}{3} \times \frac{4}{5} = \frac{2 \times 4}{3 \times 5} = \frac{8}{15}$ Dividing Fractions Invert the second fraction and multiply. $\frac{a}{b} \div \frac{c}{d} = \frac{a}{b} \times \frac{d}{c} = \frac{ad}{bc}$ Example: $\frac{1}{2} \div \frac{3}{4} = \frac{1}{2} \times \frac{4}{3} = \frac{4}{6} = \frac{2}{3}$ 7. Unit Conversions Common Conversions Unit Conversion Length $1 \text{ km} = 1000 \text{ m}$ $1 \text{ m} = 100 \text{ cm}$ $1 \text{ cm} = 10 \text{ mm}$ Mass $1 \text{ kg} = 1000 \text{ g}$ $1 \text{ tonne} = 1000 \text{ kg}$ Time $1 \text{ min} = 60 \text{ sec}$ $1 \text{ hour} = 60 \text{ min}$ $1 \text{ day} = 24 \text{ hours}$ Volume $1 \text{ L} = 1000 \text{ mL}$ $1 \text{ m}^3 = 1000 \text{ L}$