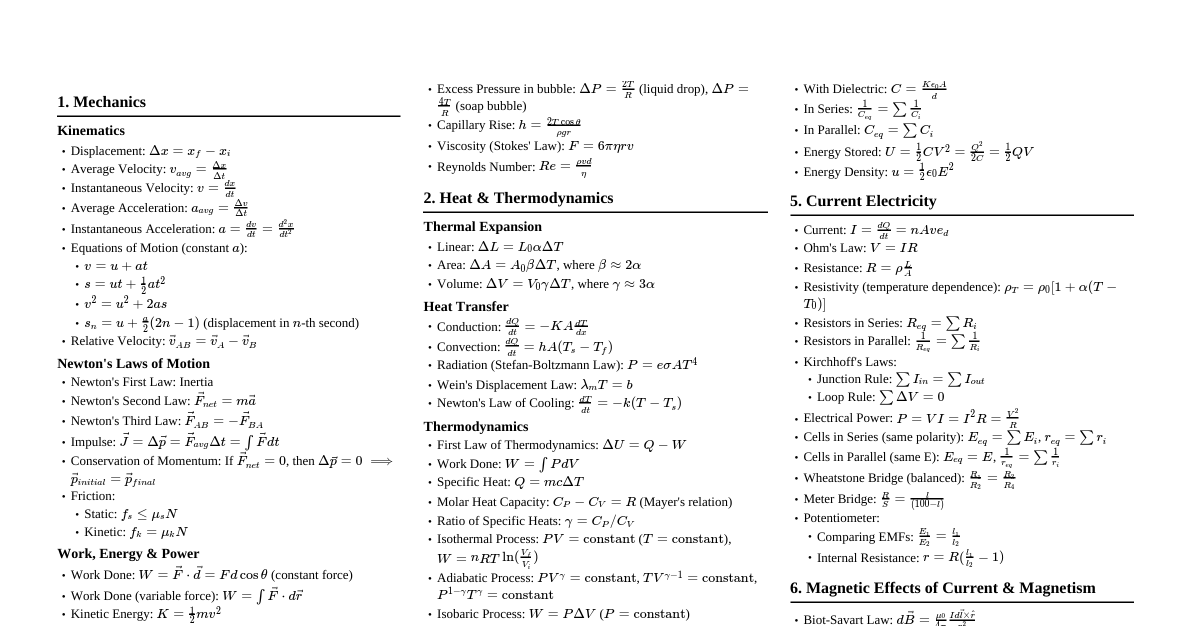
Physics: Mechanics Kinematics Displacement: $\Delta x = x_f - x_i$ Average Velocity: $v_{avg} = \frac{\Delta x}{\Delta t}$ Instantaneous Velocity: $v = \frac{dx}{dt}$ Average Acceleration: $a_{avg} = \frac{\Delta v}{\Delta t}$ Instantaneous Acceleration: $a = \frac{dv}{dt} = \frac{d^2x}{dt^2}$ Equations of Motion (constant $a$): $v = u + at$ $s = ut + \frac{1}{2}at^2$ $v^2 = u^2 + 2as$ $s_n = u + \frac{a}{2}(2n-1)$ Projectile Motion: Max Height: $H = \frac{u^2 \sin^2\theta}{2g}$ Time of Flight: $T = \frac{2u \sin\theta}{g}$ Range: $R = \frac{u^2 \sin(2\theta)}{g}$ Newton's Laws of Motion & Friction Newton's First Law: Inertia Newton's Second Law: $F = ma$ Newton's Third Law: Action-Reaction Friction: Static: $f_s \le \mu_s N$ Kinetic: $f_k = \mu_k N$ Banking of Road: $\tan\theta = \frac{v^2}{rg}$ (without friction) Work, Energy, Power Work Done: $W = \vec{F} \cdot \vec{d} = Fd \cos\theta$ Kinetic Energy: $K = \frac{1}{2}mv^2$ Potential Energy: Gravitational: $U_g = mgh$ Spring: $U_s = \frac{1}{2}kx^2$ Work-Energy Theorem: $W_{net} = \Delta K$ Power: $P = \frac{dW}{dt} = \vec{F} \cdot \vec{v}$ Conservation of Mechanical Energy: $K_i + U_i = K_f + U_f$ (for conservative forces) Rotational Motion Angular Displacement: $\Delta\theta$ Angular Velocity: $\omega = \frac{d\theta}{dt}$ Angular Acceleration: $\alpha = \frac{d\omega}{dt}$ Relation between linear and angular: $v = r\omega$, $a_t = r\alpha$, $a_c = \frac{v^2}{r} = r\omega^2$ Moment of Inertia: $I = \sum mr^2 = \int r^2 dm$ Torque: $\tau = \vec{r} \times \vec{F} = I\alpha$ Angular Momentum: $\vec{L} = \vec{r} \times \vec{p} = I\vec{\omega}$ Conservation of Angular Momentum: $I_1\omega_1 = I_2\omega_2$ (if $\tau_{ext} = 0$) Rotational Kinetic Energy: $K_R = \frac{1}{2}I\omega^2$ Gravitation Newton's Law of Gravitation: $F = G \frac{m_1 m_2}{r^2}$ Gravitational Potential Energy: $U = -\frac{G m_1 m_2}{r}$ Escape Velocity: $v_e = \sqrt{\frac{2GM}{R}}$ Orbital Velocity: $v_o = \sqrt{\frac{GM}{r}}$ Kepler's Laws Properties of Matter Young's Modulus: $Y = \frac{\text{Stress}}{\text{Strain}} = \frac{F/A}{\Delta L/L}$ Bulk Modulus: $B = -\frac{\Delta P}{\Delta V/V}$ Shear Modulus: $G = \frac{\text{Shear Stress}}{\text{Shear Strain}}$ Pressure in fluid: $P = h\rho g$ Archimedes' Principle Bernoulli's Equation: $P + \frac{1}{2}\rho v^2 + \rho gh = \text{constant}$ Surface Tension: $T = \frac{F}{L}$ Capillary Rise: $h = \frac{2T \cos\theta}{r\rho g}$ Heat & Thermodynamics Thermal Expansion: $\Delta L = L\alpha\Delta T$, $\Delta A = A\beta\Delta T$, $\Delta V = V\gamma\Delta T$ Heat Transfer: Conduction: $\frac{dQ}{dt} = -KA\frac{dT}{dx}$ Radiation (Stefan's Law): $P = e\sigma AT^4$ Specific Heat: $Q = mc\Delta T$ Latent Heat: $Q = mL$ First Law of Thermodynamics: $\Delta U = Q - W$ Work Done (Thermodynamics): $W = \int P dV$ Efficiency of Heat Engine: $\eta = 1 - \frac{T_2}{T_1}$ Carnot Cycle Oscillations & Waves Simple Harmonic Motion (SHM): $x(t) = A \sin(\omega t + \phi)$ Angular Frequency: $\omega = \sqrt{\frac{k}{m}}$ (spring), $\omega = \sqrt{\frac{g}{L}}$ (pendulum) Time Period: $T = \frac{2\pi}{\omega}$ Wave Equation: $y(x,t) = A \sin(kx - \omega t + \phi)$ Wave Speed: $v = f\lambda = \frac{\omega}{k}$ Speed of sound in fluid: $v = \sqrt{\frac{B}{\rho}}$ Speed of sound in string: $v = \sqrt{\frac{T}{\mu}}$ Doppler Effect: $f' = f \left( \frac{v \pm v_o}{v \mp v_s} \right)$ Standing Waves: nodes, antinodes Beats: $f_{beat} = |f_1 - f_2|$ Physics: Electromagnetism & Modern Physics Electrostatics Coulomb's Law: $F = k \frac{q_1 q_2}{r^2}$ Electric Field: $\vec{E} = \frac{\vec{F}}{q} = k \frac{q}{r^2} \hat{r}$ Electric Potential: $V = k \frac{q}{r}$ Relation $E$ and $V$: $\vec{E} = -\nabla V$ Electric Dipole Moment: $\vec{p} = q \vec{d}$ Electric Flux: $\Phi_E = \oint \vec{E} \cdot d\vec{A} = \frac{Q_{enc}}{\epsilon_0}$ (Gauss's Law) Capacitance: $C = \frac{Q}{V}$ Capacitors in series: $\frac{1}{C_{eq}} = \sum \frac{1}{C_i}$ Capacitors in parallel: $C_{eq} = \sum C_i$ Energy stored in capacitor: $U = \frac{1}{2}CV^2 = \frac{Q^2}{2C} = \frac{1}{2}QV$ Current Electricity Ohm's Law: $V = IR$ Resistance: $R = \frac{\rho L}{A}$ Resistors in series: $R_{eq} = \sum R_i$ Resistors in parallel: $\frac{1}{R_{eq}} = \sum \frac{1}{R_i}$ Kirchhoff's Laws Joule's Heating: $H = I^2Rt = VIt = \frac{V^2}{R}t$ Electric Power: $P = VI = I^2R = \frac{V^2}{R}$ Wheatstone Bridge, Meter Bridge, Potentiometer Magnetic Effects of Current & Magnetism Biot-Savart Law: $d\vec{B} = \frac{\mu_0}{4\pi} \frac{I d\vec{l} \times \vec{r}}{r^3}$ Magnetic Field due to long straight wire: $B = \frac{\mu_0 I}{2\pi r}$ Magnetic Field at center of loop: $B = \frac{\mu_0 I}{2R}$ Ampere's Circuital Law: $\oint \vec{B} \cdot d\vec{l} = \mu_0 I_{enc}$ Lorentz Force: $\vec{F} = q(\vec{E} + \vec{v} \times \vec{B})$ Force on current carrying wire: $\vec{F} = I(\vec{L} \times \vec{B})$ Magnetic Dipole Moment: $\vec{M} = NIA\hat{n}$ Torque on current loop: $\vec{\tau} = \vec{M} \times \vec{B}$ Electromagnetic Induction (EMI) & AC Magnetic Flux: $\Phi_B = \int \vec{B} \cdot d\vec{A}$ Faraday's Law of EMI: $\mathcal{E} = -\frac{d\Phi_B}{dt}$ Lenz's Law Self-Inductance: $\Phi = LI$, $\mathcal{E} = -L\frac{dI}{dt}$ Mutual Inductance: $\Phi_2 = MI_1$, $\mathcal{E}_2 = -M\frac{dI_1}{dt}$ Energy stored in inductor: $U = \frac{1}{2}LI^2$ AC Circuits: Reactance: $X_L = \omega L$, $X_C = \frac{1}{\omega C}$ Impedance: $Z = \sqrt{R^2 + (X_L - X_C)^2}$ Phase angle: $\tan\phi = \frac{X_L - X_C}{R}$ Resonance: $X_L = X_C \Rightarrow \omega_0 = \frac{1}{\sqrt{LC}}$ Power Factor: $\cos\phi = \frac{R}{Z}$ Electromagnetic Waves Speed of EM wave: $c = \frac{1}{\sqrt{\mu_0\epsilon_0}}$ Properties of EM waves: transverse, $\vec{E} \perp \vec{B}$ Maxwell's Equations EM Spectrum Optics Reflection: Angle of incidence = Angle of reflection Mirror Formula: $\frac{1}{f} = \frac{1}{v} + \frac{1}{u}$ (for spherical mirrors) Magnification: $m = -\frac{v}{u}$ Refraction (Snell's Law): $n_1 \sin\theta_1 = n_2 \sin\theta_2$ Lens Maker's Formula: $\frac{1}{f} = (n-1)\left(\frac{1}{R_1} - \frac{1}{R_2}\right)$ Lens Formula: $\frac{1}{f} = \frac{1}{v} - \frac{1}{u}$ Total Internal Reflection: $\sin C = \frac{n_2}{n_1}$ Dispersion: Different $n$ for different colors Interference (Young's Double Slit): Path difference: $\Delta x = d \sin\theta$ Bright fringes: $\Delta x = n\lambda$ Dark fringes: $\Delta x = (n+\frac{1}{2})\lambda$ Fringe width: $\beta = \frac{\lambda D}{d}$ Diffraction (Single Slit): Minima: $a \sin\theta = n\lambda$ Polarization: Brewster's Law, Malus's Law Modern Physics Photoelectric Effect: $K_{max} = h\nu - \phi_0$ De Broglie Wavelength: $\lambda = \frac{h}{p} = \frac{h}{mv}$ Bohr's Model of Hydrogen Atom: Radius: $r_n = 0.529 n^2 \text{ Å}$ Energy: $E_n = -\frac{13.6}{n^2} \text{ eV}$ X-rays: Mosley's Law, continuous and characteristic spectrum Radioactivity: Decay Law: $N = N_0 e^{-\lambda t}$ Half-life: $T_{1/2} = \frac{\ln 2}{\lambda}$ Binding Energy: $E_b = (\Delta m) c^2$ Nuclear Fission, Fusion Semiconductors: Intrinsic, Extrinsic, P-N Junction Diode, Transistors Logic Gates: AND, OR, NOT, NAND, NOR, XOR, XNOR Chemistry: Physical Chemistry Basic Concepts of Chemistry Mole Concept: $n = \frac{\text{mass}}{\text{molar mass}} = \frac{\text{number of particles}}{N_A}$ Molarity: $M = \frac{\text{moles of solute}}{\text{volume of solution (L)}}$ Molality: $m = \frac{\text{moles of solute}}{\text{mass of solvent (kg)}}$ Equivalent Weight: $\text{Eq. Wt.} = \frac{\text{Molar Mass}}{n\text{-factor}}$ Stoichiometry, Limiting Reagent Atomic Structure Bohr's Model (energy levels, radii, velocity) Hydrogen Spectrum (Lyman, Balmer, Paschen, etc.) Quantum Numbers: $n, l, m_l, m_s$ Heisenberg's Uncertainty Principle: $\Delta x \cdot \Delta p \ge \frac{h}{4\pi}$ De Broglie Wavelength: $\lambda = \frac{h}{mv}$ States of Matter Ideal Gas Equation: $PV = nRT$ Dalton's Law of Partial Pressures: $P_{total} = P_1 + P_2 + ...$ Graham's Law of Diffusion: $\frac{r_1}{r_2} = \sqrt{\frac{M_2}{M_1}}$ Van der Waals Equation (Real Gases): $\left(P + \frac{an^2}{V^2}\right)(V-nb) = nRT$ Kinetic Theory of Gases (postulates, average/RMS/most probable speeds) Chemical Bonding & Molecular Structure Lewis Structures, Formal Charge VSEPR Theory (shapes of molecules) Hybridization ($sp, sp^2, sp^3, sp^3d, sp^3d^2$) Molecular Orbital Theory (Bond order, magnetic properties) Hydrogen Bonding, Dipole Moment Chemical Thermodynamics First Law: $\Delta U = Q + W$ Work done: $W = -P\Delta V$ (expansion) Enthalpy: $H = U + PV$ Hess's Law of Constant Heat Summation Second Law: $\Delta S_{total} \ge 0$ Gibbs Free Energy: $\Delta G = \Delta H - T\Delta S$ $\Delta G = -RT \ln K_{eq}$ Solutions Raoult's Law: $P_A = P_A^0 x_A$ Colligative Properties: Relative lowering of vapor pressure: $\frac{P^0 - P_s}{P^0} = x_{solute}$ Elevation in boiling point: $\Delta T_b = K_b m$ Depression in freezing point: $\Delta T_f = K_f m$ Osmotic Pressure: $\pi = iCRT$ Van't Hoff factor ($i$) Equilibrium Law of Mass Action: $K_c, K_p$ Relation: $K_p = K_c(RT)^{\Delta n_g}$ Le Chatelier's Principle Ionic Equilibrium: pH scale: $pH = -\log[H^+]$ $K_w = [H^+][OH^-] = 10^{-14}$ at $25^\circ C$ Henderson-Hasselbalch Equation: $pH = pK_a + \log\frac{[\text{salt}]}{[\text{acid}]}$ (for buffers) Solubility Product: $K_{sp}$ Redox Reactions & Electrochemistry Oxidation Numbers Balancing Redox Reactions Electrochemical Cell (Galvanic/Voltaic cell) Standard Electrode Potential ($E^0$) Nernst Equation: $E = E^0 - \frac{0.0591}{n} \log Q$ (at $25^\circ C$) $\Delta G^0 = -nFE^0$ Faraday's Laws of Electrolysis Chemical Kinetics Rate of Reaction: Rate $= k[A]^x[B]^y$ Integrated Rate Laws: Zero Order: $[A]_t = [A]_0 - kt$ First Order: $\ln[A]_t = \ln[A]_0 - kt$, $t_{1/2} = \frac{0.693}{k}$ Arrhenius Equation: $k = Ae^{-E_a/RT}$ Collision Theory Surface Chemistry Adsorption (Physisorption, Chemisorption) Freundlich and Langmuir Adsorption Isotherms Catalysis (Homogeneous, Heterogeneous) Colloids (Types, Preparation, Properties, Tyndall Effect, Brownian Movement) Emulsions Chemistry: Inorganic Chemistry Classification of Elements & Periodicity Modern Periodic Law Periodic Trends: Atomic Radius, Ionization Enthalpy, Electron Gain Enthalpy, Electronegativity Diagonal Relationship General Principles & Processes of Isolation of Metals (Metallurgy) Concentration (Gravity separation, Froth Floatation, Leaching) Calcination, Roasting Reduction (Smelting, Electrolytic reduction) Refining (Distillation, Liquation, Electrolytic, Zone refining, Vapor phase refining) Ellingham Diagram Hydrogen Isotopes of Hydrogen Preparation, Properties, Uses of $H_2O_2$ and $D_2O$ Hard and Soft water s-Block Elements (Alkali & Alkaline Earth Metals) General characteristics, trends Preparation and properties of important compounds (e.g., NaOH, NaHCO$_3$, Na$_2CO_3$, CaO, CaSO$_4 \cdot \frac{1}{2}H_2O$) p-Block Elements Group 13 (Boron family): Borax, Diborane, Boric acid Group 14 (Carbon family): Allotropes of Carbon, Silicones, Silicates, Zeolites Group 15 (Nitrogen family): Ammonia, Nitric Acid, Phosphorus Allotropes, Phosphine, Halides Group 16 (Oxygen family): Ozone, Sulphuric Acid, Sulphur Allotropes Group 17 (Halogen family): Halides, Interhalogen compounds, Oxoacids of Halogens Group 18 (Noble Gases): Xenon compounds ($XeF_2, XeF_4, XeF_6$) d- and f-Block Elements (Transition & Inner Transition) General characteristics, electronic configuration Oxidation states, magnetic properties, catalytic properties Preparation and properties of $K_2Cr_2O_7$ and $KMnO_4$ Lanthanides and Actinides (general characteristics) Coordination Compounds Nomenclature (IUPAC) Werner's Theory Valence Bond Theory (VBT) (hybridization, magnetic properties) Crystal Field Theory (CFT) (splitting of d-orbitals, color, magnetic properties) Isomerism (Structural, Stereoisomerism) Environmental Chemistry Air Pollution (Smog, Acid Rain, Greenhouse Effect, Ozone Depletion) Water Pollution (BOD, COD) Soil Pollution Chemistry: Organic Chemistry General Organic Chemistry (GOC) IUPAC Nomenclature of Organic Compounds Isomerism (Structural, Stereoisomerism - Geometrical, Optical) Electronic effects: Inductive, Resonance, Hyperconjugation, Electromeric effect Reaction Intermediates: Carbocations, Carbanions, Free Radicals Types of Organic Reactions: Substitution, Addition, Elimination, Rearrangement Acidity and Basicity of Organic Compounds Hydrocarbons Alkanes: Preparation (Wurtz, Decarboxylation), Reactions (Halogenation, Combustion) Alkenes: Preparation (Dehydration of alcohol, Dehydrohalogenation), Reactions (Hydrogenation, Halogenation, Hydrohalogenation - Markovnikov's rule, Anti-Markovnikov's rule, Ozonolysis, Polymerization) Alkynes: Preparation, Reactions (Acidity of terminal alkynes, Addition reactions) Aromatic Compounds: Benzene (Aromaticity - Hückel's Rule), Electrophilic Substitution Reactions (Nitration, Halogenation, Sulphonation, Friedel-Crafts Alkylation/Acylation) Haloalkanes & Haloarenes Nomenclature, Nature of C-X bond Preparation (from alcohol, hydrocarbons) Reactions: Nucleophilic Substitution ($S_N1, S_N2$), Elimination (Saytzeff rule), Reaction with metals (Wurtz, Wurtz-Fittig, Fittig) Haloarenes: Nucleophilic Aromatic Substitution (less reactive), Electrophilic Substitution Alcohols, Phenols & Ethers Alcohols: Preparation (from Grignard, Carbonyl compounds), Reactions (Oxidation, Dehydration, Esterification) Phenols: Preparation (from Cumene, Haloarenes), Acidity, Electrophilic Substitution (Kolbe's, Reimer-Tiemann) Ethers: Preparation (Williamson Synthesis), Reactions (Cleavage with HI/HBr) Aldehydes, Ketones & Carboxylic Acids Aldehydes & Ketones: Preparation (Oxidation of alcohol, Ozonolysis) Reactions: Nucleophilic Addition (HCN, Grignard), Reduction (Clemmensen, Wolff-Kishner), Oxidation (Tollens', Fehling's), Aldol Condensation, Cannizzaro Reaction, Haloform Reaction Carboxylic Acids: Preparation (Oxidation of alcohol/aldehyde, Grignard), Acidity, Reactions (Esterification, Decarboxylation) Derivatives of Carboxylic Acids: Acid Halides, Anhydrides, Esters, Amides (preparation and reactions) Nitrogen Containing Compounds Amines: Classification, Preparation (Reduction of nitro compounds/nitriles, Gabriel Phthalimide Synthesis, Hoffmann Bromamide Degradation), Basicity, Reactions (Acylation, Carbylamine, Diazotization) Diazonium Salts: Preparation, Reactions (Sandmeyer, Gattermann, Coupling) Cyanides and Isocyanides Biomolecules Carbohydrates: Classification (Monosaccharides, Disaccharides, Polysaccharides), Glucose (structure, reactions), Sucrose, Starch, Cellulose Proteins: Amino acids (Zwitter ion), Peptides, Structure of proteins (Primary, Secondary, Tertiary, Quaternary), Denaturation Vitamins: Classification (Fat/Water soluble), Deficiency diseases Nucleic Acids: DNA, RNA (structure, functions) Polymers Classification (Addition, Condensation, Natural, Synthetic) Types of Polymerization (Addition, Condensation) Examples and uses: Polyethylene, PVC, Teflon, Nylon-6,6, Buna-S, Buna-N, Dacron, Bakelite, Melamine Biodegradable Polymers Chemistry in Everyday Life Drugs: Analgesics, Antiseptics, Disinfectants, Antacids, Antihistamines, Tranquilizers, Antibiotics Food Additives: Artificial Sweeteners, Food Preservatives, Antioxidants Cleansing Agents: Soaps, Detergents Mathematics: Algebra Complex Numbers & Quadratic Equations Complex Number: $z = x+iy = r(\cos\theta + i\sin\theta)$ Modulus: $|z| = \sqrt{x^2+y^2}$ Argument: $\arg(z) = \theta$ De Moivre's Theorem: $(\cos\theta + i\sin\theta)^n = \cos(n\theta) + i\sin(n\theta)$ Cube roots of unity: $1, \omega, \omega^2$ where $1+\omega+\omega^2=0$ and $\omega^3=1$ Quadratic Equation: $ax^2+bx+c=0$ Roots: $x = \frac{-b \pm \sqrt{b^2-4ac}}{2a}$ Discriminant: $D = b^2-4ac$ Relation between roots and coefficients: $\alpha+\beta = -b/a$, $\alpha\beta = c/a$ Permutations & Combinations Permutation: $^nP_r = \frac{n!}{(n-r)!}$ (arrangement) Combination: $^nC_r = \frac{n!}{r!(n-r)!}$ (selection) Properties of $^nC_r$: $^nC_r = ^nC_{n-r}$, $^nC_r + ^nC_{r-1} = ^{n+1}C_r$ Binomial Theorem $(x+y)^n = \sum_{r=0}^n \ ^nC_r x^{n-r} y^r$ General Term: $T_{r+1} = ^nC_r x^{n-r} y^r$ Middle Term(s) Properties of Binomial Coefficients Sequences & Series Arithmetic Progression (AP): $a_n = a + (n-1)d$, $S_n = \frac{n}{2}(2a + (n-1)d) = \frac{n}{2}(a+l)$ Geometric Progression (GP): $a_n = ar^{n-1}$, $S_n = \frac{a(r^n-1)}{r-1}$ ($r \ne 1$), $S_\infty = \frac{a}{1-r}$ ($|r| Harmonic Progression (HP): Reciprocals are in AP Arithmetic-Geometric Progression (AGP) Sum of special series: $\sum n, \sum n^2, \sum n^3$ Matrices & Determinants Types of Matrices (Square, Diagonal, Identity, Scalar, Symmetric, Skew-Symmetric) Matrix Operations (Addition, Multiplication) Determinant: $|A|$ Properties of Determinants Adjoint of a matrix: $adj(A)$ Inverse of a matrix: $A^{-1} = \frac{1}{|A|} adj(A)$ Solving system of linear equations (Cramer's Rule, Matrix Method) Mathematical Induction Principle of Mathematical Induction Mathematical Reasoning Statements, Logical Connectives (AND, OR, NOT, IMPLIES, IFF) Truth Tables Tautology, Contradiction, Contingency Converse, Inverse, Contrapositive Statistics & Probability Measures of Central Tendency: Mean, Median, Mode Measures of Dispersion: Variance ($\sigma^2 = \frac{\sum (x_i - \bar{x})^2}{n}$), Standard Deviation ($\sigma$) Probability: $P(A) = \frac{\text{Number of favorable outcomes}}{\text{Total number of outcomes}}$ Conditional Probability: $P(A|B) = \frac{P(A \cap B)}{P(B)}$ Bayes' Theorem: $P(B_k|A) = \frac{P(A|B_k)P(B_k)}{\sum P(A|B_i)P(B_i)}$ Bernoulli Trials & Binomial Distribution: $P(X=k) = ^nC_k p^k q^{n-k}$ Mathematics: Calculus Functions Domain, Range, Codomain Types of Functions: One-one (Injective), Onto (Surjective), Bijective Even and Odd Functions Composition of Functions: $(f \circ g)(x) = f(g(x))$ Inverse of a Function: $f^{-1}(x)$ Graphs of basic functions Limits, Continuity & Differentiability Limit: $\lim_{x \to a} f(x)$ Standard Limits: $\lim_{x \to 0} \frac{\sin x}{x} = 1$, $\lim_{x \to 0} \frac{\tan x}{x} = 1$, $\lim_{x \to 0} \frac{e^x-1}{x} = 1$, $\lim_{x \to 0} \frac{\ln(1+x)}{x} = 1$ L'Hopital's Rule Continuity: $\lim_{x \to a^-} f(x) = \lim_{x \to a^+} f(x) = f(a)$ Differentiability Differentiation Derivatives of standard functions Chain Rule: $\frac{dy}{dx} = \frac{dy}{du} \frac{du}{dx}$ Product Rule: $(uv)' = u'v + uv'$ Quotient Rule: $(\frac{u}{v})' = \frac{u'v - uv'}{v^2}$ Implicit Differentiation Logarithmic Differentiation Higher Order Derivatives Applications of Derivatives Rate of Change Tangents and Normals: Slope of tangent $m = \frac{dy}{dx}$ Increasing and Decreasing Functions Maxima and Minima (First and Second Derivative Test) Rolle's Theorem, Mean Value Theorem (Lagrange's, Cauchy's) Integral Calculus Indefinite Integrals of standard functions Methods of Integration: Substitution, By Parts ($\int u dv = uv - \int v du$), Partial Fractions Definite Integrals: $\int_a^b f(x) dx = F(b) - F(a)$ (Fundamental Theorem of Calculus) Properties of Definite Integrals Area under the curve: $A = \int_a^b y dx$ Differential Equations Order and Degree Formation of Differential Equations Solution of Differential Equations: Variable Separable Method Homogeneous Differential Equations Linear Differential Equations: $\frac{dy}{dx} + Py = Q$, Integrating Factor $IF = e^{\int P dx}$ Mathematics: Coordinate Geometry Straight Lines Distance Formula: $\sqrt{(x_2-x_1)^2 + (y_2-y_1)^2}$ Section Formula (Internal & External division) Area of a Triangle Slope of a Line: $m = \tan\theta = \frac{y_2-y_1}{x_2-x_1}$ Equation of a Line: Slope-intercept form: $y = mx+c$ Point-slope form: $y-y_1 = m(x-x_1)$ Two-point form: $y-y_1 = \frac{y_2-y_1}{x_2-x_1}(x-x_1)$ Intercept form: $\frac{x}{a} + \frac{y}{b} = 1$ Normal form: $x \cos\alpha + y \sin\alpha = p$ Angle between two lines: $\tan\theta = \left|\frac{m_1-m_2}{1+m_1m_2}\right|$ Distance of a point from a line: $d = \frac{|Ax_1+By_1+C|}{\sqrt{A^2+B^2}}$ Distance between parallel lines Family of Lines Conic Sections General Equation of Second Degree: $Ax^2+Bxy+Cy^2+Dx+Ey+F=0$ Circle: $(x-h)^2 + (y-k)^2 = r^2$ Parabola: $y^2 = 4ax$, $x^2 = 4ay$ (and shifted forms) Ellipse: $\frac{x^2}{a^2} + \frac{y^2}{b^2} = 1$ Hyperbola: $\frac{x^2}{a^2} - \frac{y^2}{b^2} = 1$ Eccentricity ($e$), Focus, Directrix, Latus Rectum for each conic Tangents and Normals to conics Mathematics: Vector Algebra & 3D Geometry Vector Algebra Types of Vectors (Zero, Unit, Co-initial, Collinear) Vector Addition and Subtraction (Triangle, Parallelogram Law) Scalar (Dot) Product: $\vec{a} \cdot \vec{b} = |\vec{a}||\vec{b}|\cos\theta$ Vector (Cross) Product: $\vec{a} \times \vec{b} = |\vec{a}||\vec{b}|\sin\theta \hat{n}$ Scalar Triple Product: $[\vec{a} \ \vec{b} \ \vec{c}] = \vec{a} \cdot (\vec{b} \times \vec{c})$ Vector Triple Product: $\vec{a} \times (\vec{b} \times \vec{c}) = (\vec{a} \cdot \vec{c})\vec{b} - (\vec{a} \cdot \vec{b})\vec{c}$ Three Dimensional Geometry Direction Cosines and Direction Ratios Equation of a Line: Cartesian: $\frac{x-x_1}{l} = \frac{y-y_1}{m} = \frac{z-z_1}{n}$ Vector: $\vec{r} = \vec{a} + \lambda \vec{b}$ Shortest Distance between two skew lines Equation of a Plane: Normal form: $\vec{r} \cdot \hat{n} = d$ Cartesian: $Ax+By+Cz+D=0$ Intercept form: $\frac{x}{a} + \frac{y}{b} + \frac{z}{c} = 1$ Angle between two lines, two planes, a line and a plane Distance of a point from a plane Mathematics: Trigonometry Trigonometric Ratios & Identities Basic Identities: $\sin^2\theta + \cos^2\theta = 1$, $\sec^2\theta - \tan^2\theta = 1$, $\csc^2\theta - \cot^2\theta = 1$ Compound Angles: $\sin(A\pm B)$, $\cos(A\pm B)$, $\tan(A\pm B)$ Multiple and Submultiple Angles: $\sin 2A, \cos 2A, \tan 2A, \sin 3A, \cos 3A, \tan 3A$ Transformation Formulae (Sum/Difference to Product, Product to Sum/Difference) Trigonometric Equations General solutions for $\sin x = \sin\alpha$, $\cos x = \cos\alpha$, $\tan x = \tan\alpha$ Inverse Trigonometric Functions Domain and Range Properties of inverse trigonometric functions Heights and Distances Applications of trigonometry in solving problems related to heights and distances