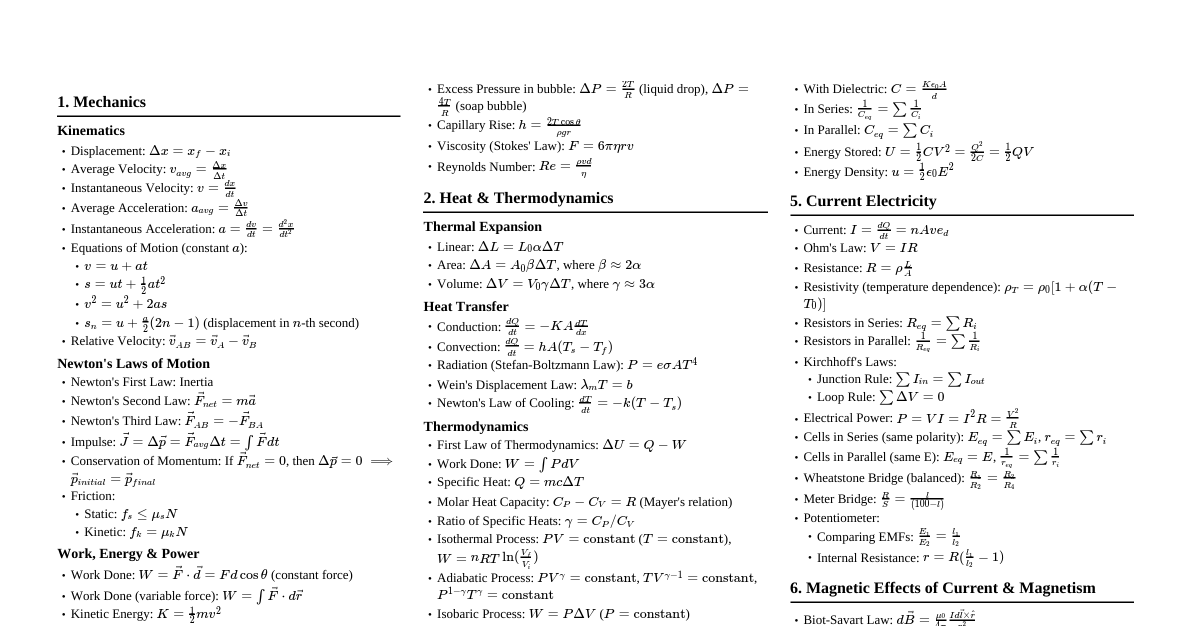
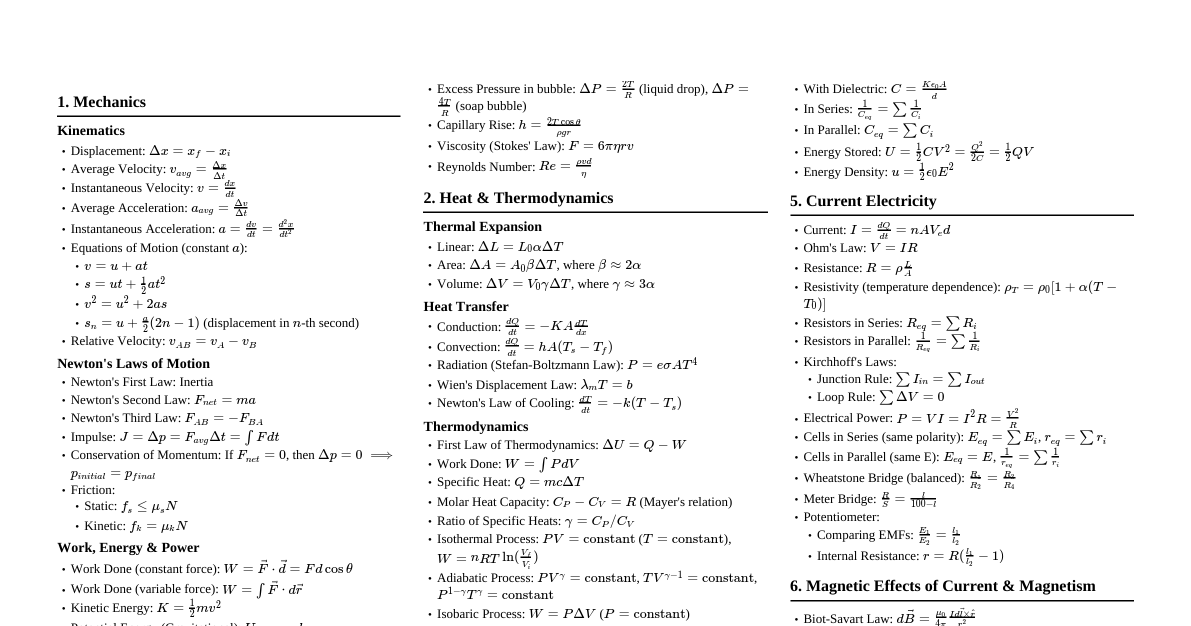
1. Measurement & Vectors SI Base Units: Length (m), Mass (kg), Time (s), Current (A), Temp (K), Amount (mol), Luminous Intensity (cd) Prefixes: G ($10^9$), M ($10^6$), k ($10^3$), c ($10^{-2}$), m ($10^{-3}$), $\mu$ ($10^{-6}$), n ($10^{-9}$), p ($10^{-12}$) Vector Components: $A_x = A \cos \theta$, $A_y = A \sin \theta$ Magnitude: $A = \sqrt{A_x^2 + A_y^2}$ Direction: $\theta = \tan^{-1}(A_y/A_x)$ Dot Product: $\vec{A} \cdot \vec{B} = AB \cos \phi = A_x B_x + A_y B_y + A_z B_z$ Cross Product: $|\vec{A} \times \vec{B}| = AB \sin \phi$. Direction by right-hand rule. $\vec{A} \times \vec{B} = (A_y B_z - A_z B_y)\hat{i} + (A_z B_x - A_x B_z)\hat{j} + (A_x B_y - A_y B_x)\hat{k}$ 2. Kinematics (1D & 2D) Average Velocity: $v_{avg} = \Delta x / \Delta t$ Average Acceleration: $a_{avg} = \Delta v / \Delta t$ Constant Acceleration Equations: $v = v_0 + at$ $x - x_0 = v_0 t + \frac{1}{2} a t^2$ $v^2 = v_0^2 + 2a(x - x_0)$ $x - x_0 = \frac{1}{2}(v_0 + v)t$ Projectile Motion: $x$-comp: $v_x = v_{0x}$, $x = x_0 + v_{0x} t$ $y$-comp: $v_y = v_{0y} - gt$, $y = y_0 + v_{0y} t - \frac{1}{2} gt^2$, $v_y^2 = v_{0y}^2 - 2g(y - y_0)$ Relative Velocity: $\vec{v}_{PA} = \vec{v}_{PB} + \vec{v}_{BA}$ 3. Newton's Laws of Motion Newton's First Law: An object at rest stays at rest and an object in motion stays in motion with the same speed and in the same direction unless acted upon by an unbalanced force. Newton's Second Law: $\vec{F}_{net} = m\vec{a}$ Newton's Third Law: If object A exerts a force on object B, then object B must exert a force of equal magnitude and opposite direction back on object A. ($\vec{F}_{AB} = -\vec{F}_{BA}$) Weight: $W = mg$ (gravitational force) Friction: Static: $f_s \le \mu_s F_N$ Kinetic: $f_k = \mu_k F_N$ Centripetal Force: $F_c = m a_c = m v^2 / r$ 4. Work, Energy & Power Work (Constant Force): $W = \vec{F} \cdot \vec{d} = Fd \cos \phi$ Work (Variable Force): $W = \int_{x_i}^{x_f} F(x) dx$ Kinetic Energy: $K = \frac{1}{2} m v^2$ Work-Kinetic Energy Theorem: $W_{net} = \Delta K = K_f - K_i$ Gravitational Potential Energy: $U_g = mgh$ Elastic Potential Energy (Spring): $U_s = \frac{1}{2} k x^2$ Conservation of Mechanical Energy: $E_{mech} = K + U = \text{constant}$ (if only conservative forces do work) Non-Conservative Forces: $W_{nc} = \Delta E_{mech} = \Delta K + \Delta U$ Power: $P_{avg} = W / \Delta t$, $P = dW/dt = \vec{F} \cdot \vec{v}$ 5. Momentum & Collisions Linear Momentum: $\vec{p} = m\vec{v}$ Impulse: $\vec{J} = \int \vec{F} dt = \Delta \vec{p}$ Impulse-Momentum Theorem: $\vec{J} = \vec{p}_f - \vec{p}_i$ Conservation of Linear Momentum: $\vec{P}_{net} = \text{constant}$ (if $\vec{F}_{net, ext} = 0$) Collisions: Elastic: Momentum & Kinetic Energy conserved Inelastic: Momentum conserved, Kinetic Energy NOT conserved Perfectly Inelastic: Objects stick together, Momentum conserved, max KE loss Center of Mass: $x_{CM} = \frac{1}{M} \sum m_i x_i$, $\vec{v}_{CM} = \frac{1}{M} \sum m_i \vec{v}_i$ 6. Rotation Angular Position: $\theta$ (radians) Angular Velocity: $\omega = d\theta/dt$ Angular Acceleration: $\alpha = d\omega/dt$ Rotational Kinematics (Constant $\alpha$): $\omega = \omega_0 + \alpha t$ $\theta = \theta_0 + \omega_0 t + \frac{1}{2} \alpha t^2$ $\omega^2 = \omega_0^2 + 2\alpha(\theta - \theta_0)$ Tangential Relations: $s = r\theta$, $v_t = r\omega$, $a_t = r\alpha$ Centripetal Acceleration: $a_c = v_t^2 / r = \omega^2 r$ Moment of Inertia: $I = \sum m_i r_i^2 = \int r^2 dm$ Rotational Kinetic Energy: $K_{rot} = \frac{1}{2} I \omega^2$ Torque: $\vec{\tau} = \vec{r} \times \vec{F}$, $\tau = rF \sin \phi$ Newton's Second Law for Rotation: $\tau_{net} = I\alpha$ Angular Momentum: $\vec{L} = \vec{r} \times \vec{p} = I\vec{\omega}$ Conservation of Angular Momentum: $\vec{L}_{net} = \text{constant}$ (if $\vec{\tau}_{net, ext} = 0$) 7. Oscillations & Waves Simple Harmonic Motion (SHM): $x(t) = A \cos(\omega t + \phi)$ $v(t) = -A\omega \sin(\omega t + \phi)$ $a(t) = -A\omega^2 \cos(\omega t + \phi) = -\omega^2 x(t)$ Angular Frequency: $\omega = \sqrt{k/m}$ (spring), $\omega = \sqrt{g/L}$ (pendulum) Period: $T = 2\pi / \omega = 1/f$ Wave Speed: $v = \lambda f$ Wave on String: $v = \sqrt{\tau / \mu}$ ($\tau$ = tension, $\mu$ = linear density) Intensity: $I = P/A$ Sound Level (dB): $\beta = 10 \log(I/I_0)$, $I_0 = 10^{-12} \text{ W/m}^2$ Doppler Effect: $f' = f \frac{v \pm v_D}{v \mp v_S}$ (top signs for approaching, bottom for receding) Standing Waves: String fixed at both ends: $\lambda_n = 2L/n$, $f_n = n v / (2L)$ ($n=1,2,3...$) Open-open pipe: $\lambda_n = 2L/n$, $f_n = n v / (2L)$ ($n=1,2,3...$) Open-closed pipe: $\lambda_n = 4L/n$, $f_n = n v / (4L)$ ($n=1,3,5...$) 8. Thermodynamics Temperature Conversion: $T_F = \frac{9}{5} T_C + 32$, $T_K = T_C + 273.15$ Thermal Expansion: $\Delta L = L \alpha \Delta T$, $\Delta A = A \beta \Delta T$, $\Delta V = V \gamma \Delta T$ ($\beta \approx 2\alpha$, $\gamma \approx 3\alpha$) Heat Capacity: $Q = C \Delta T$ Specific Heat: $Q = mc \Delta T$ Latent Heat: $Q = mL$ ($L_f$ for fusion, $L_v$ for vaporization) First Law of Thermodynamics: $\Delta E_{int} = Q - W$ ($W$ is work done BY system) Work Done by Gas: $W = \int P dV$ Ideal Gas Law: $PV = nRT = NkT$ ($R = 8.314 \text{ J/(mol K)}$, $k = 1.38 \times 10^{-23} \text{ J/K}$) Kinetic Theory: $K_{avg} = \frac{3}{2} kT$, $v_{rms} = \sqrt{3RT/M}$ Heat Transfer: Conduction: $P_{cond} = k A \frac{T_H - T_C}{L}$ Radiation: $P_{rad} = \sigma \epsilon A T^4$ ($\sigma = 5.67 \times 10^{-8} \text{ W/(m}^2 \text{K}^4)$) Entropy: $\Delta S = \int dQ/T$ (reversible process) Carnot Engine Efficiency: $\epsilon = 1 - T_C/T_H$ 9. Electricity Coulomb's Law: $F = k \frac{|q_1 q_2|}{r^2}$, $k = 1/(4\pi\epsilon_0) = 8.99 \times 10^9 \text{ N m}^2/\text{C}^2$ Electric Field: $\vec{E} = \vec{F}/q_0 = k \frac{q}{r^2} \hat{r}$ Electric Flux: $\Phi_E = \oint \vec{E} \cdot d\vec{A}$ Gauss' Law: $\epsilon_0 \Phi_E = q_{enc}$ Electric Potential Energy: $U = qV$ Electric Potential: $V = k \frac{q}{r}$, $\vec{E} = -\nabla V$ Capacitance: $C = q/V$ Parallel Plate Capacitor: $C = \epsilon_0 A/d$ Energy Stored in Capacitor: $U = \frac{1}{2} CV^2 = \frac{1}{2} qV = \frac{q^2}{2C}$ Current: $I = dq/dt = n A v_d q$ Resistance: $R = \rho L/A$ Ohm's Law: $V = IR$ Power (Electric): $P = IV = I^2 R = V^2 / R$ Resistors: Series $R_{eq} = \sum R_i$, Parallel $1/R_{eq} = \sum 1/R_i$ Capacitors: Series $1/C_{eq} = \sum 1/C_i$, Parallel $C_{eq} = \sum C_i$ RC Circuits: Charging $q(t) = C\mathcal{E}(1 - e^{-t/RC})$, Discharging $q(t) = Q_0 e^{-t/RC}$ 10. Magnetism Magnetic Force on Charge: $\vec{F}_B = q \vec{v} \times \vec{B}$ Magnetic Force on Current: $\vec{F}_B = I \vec{L} \times \vec{B}$ Magnetic Field (Biot-Savart): $d\vec{B} = \frac{\mu_0}{4\pi} \frac{I d\vec{s} \times \hat{r}}{r^2}$ Magnetic Field (Long Straight Wire): $B = \frac{\mu_0 I}{2\pi r}$ Magnetic Field (Solenoid): $B = \mu_0 n I$ Ampere's Law: $\oint \vec{B} \cdot d\vec{s} = \mu_0 I_{enc}$ Magnetic Flux: $\Phi_B = \int \vec{B} \cdot d\vec{A}$ Faraday's Law of Induction: $\mathcal{E} = -N \frac{d\Phi_B}{dt}$ Motional EMF: $\mathcal{E} = BLv$ Inductance: $L = N \Phi_B / I$ Energy Stored in Inductor: $U = \frac{1}{2} L I^2$ RL Circuits: Current growth $I(t) = (\mathcal{E}/R)(1 - e^{-tL/R})$, Current decay $I(t) = (I_0) e^{-tL/R}$ LC Oscillations: $\omega = 1/\sqrt{LC}$ Transformers: $V_S/V_P = N_S/N_P = I_P/I_S$ 11. Electromagnetic Waves Speed of Light in Vacuum: $c = 1/\sqrt{\mu_0 \epsilon_0} = 3 \times 10^8 \text{ m/s}$ Wave Speed: $c = \lambda f$ Energy Density: $u = u_E + u_B = \frac{1}{2}\epsilon_0 E^2 + \frac{1}{2\mu_0} B^2$ Poynting Vector: $\vec{S} = \frac{1}{\mu_0} (\vec{E} \times \vec{B})$. Magnitude $S = EB/\mu_0$ Intensity (Average Poynting Vector): $I = S_{avg} = \frac{1}{2\mu_0} E_{max} B_{max} = \frac{E_{max}^2}{2\mu_0 c}$ Radiation Pressure: $P_r = I/c$ (absorbed), $P_r = 2I/c$ (reflected) 12. Light & Optics Index of Refraction: $n = c/v$ Snell's Law: $n_1 \sin \theta_1 = n_2 \sin \theta_2$ Critical Angle: $\sin \theta_c = n_2/n_1$ ($n_1 > n_2$) Mirror/Lens Equation: $1/f = 1/p + 1/i$ Magnification: $m = -i/p$ Spherical Mirrors: $f = R/2$ (concave +f, convex -f) Thin Lenses: $f$ (converging +f, diverging -f) Young's Double Slit: Constructive: $d \sin \theta = m\lambda$ ($m=0, \pm 1, \pm 2, ...$) Destructive: $d \sin \theta = (m + 1/2)\lambda$ ($m=0, \pm 1, \pm 2, ...$) Single Slit Diffraction: Minima: $a \sin \theta = m\lambda$ ($m=\pm 1, \pm 2, ...$) Diffraction Grating: Maxima: $d \sin \theta = m\lambda$ ($m=0, \pm 1, \pm 2, ...$) Thin Film Interference: Consider phase changes upon reflection. Brewster's Angle: $\tan \theta_B = n_2/n_1$ 13. Modern Physics Planck's Quantum Hypothesis: $E = hf$ ($h = 6.626 \times 10^{-34} \text{ J s}$) Photoelectric Effect: $K_{max} = hf - \Phi$ ($\Phi$ = work function) Photon Momentum: $p = h/\lambda$ Compton Effect: $\Delta \lambda = \lambda' - \lambda = \frac{h}{mc}(1 - \cos \phi)$ De Broglie Wavelength: $\lambda = h/p = h/(mv)$ Heisenberg Uncertainty Principle: $\Delta x \Delta p_x \ge \hbar/2$ $\Delta E \Delta t \ge \hbar/2$ Hydrogen Atom Energy Levels: $E_n = -13.6 \text{ eV} / n^2$ Radioactive Decay: $N(t) = N_0 e^{-\lambda t}$, $T_{1/2} = \ln(2)/\lambda$ Mass-Energy Equivalence: $E = mc^2$