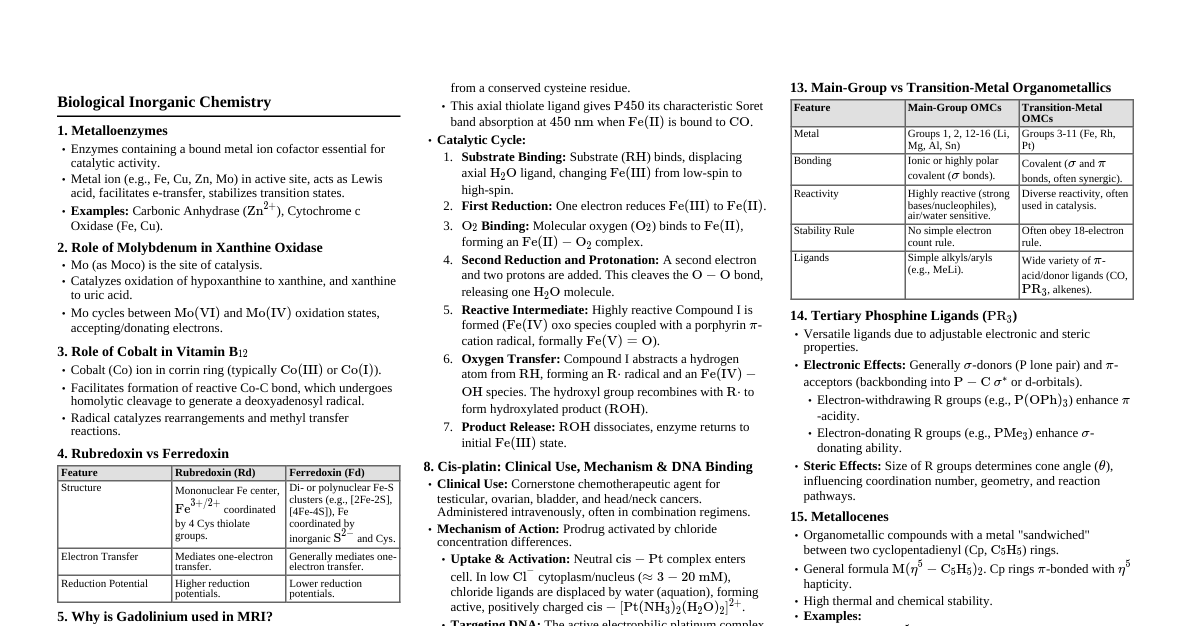
1. Algebra & Functions Quadratic Equation: $ax^2 + bx + c = 0 \implies x = \frac{-b \pm \sqrt{b^2 - 4ac}}{2a}$ Logarithms: $\log(xy) = \log x + \log y$ $\log(x/y) = \log x - \log y$ $\log(x^n) = n \log x$ $\ln x = 2.303 \log_{10} x$ $\log_b a = \frac{\log_c a}{\log_c b}$ Exponentials: $e^{a+b} = e^a e^b$, $e^{a-b} = e^a / e^b$, $(e^a)^b = e^{ab}$ Linear Equation: $y = mx + c$ (slope $m$, y-intercept $c$) Polynomials: $(a+b)^2 = a^2+2ab+b^2$, $(a-b)^2 = a^2-2ab+b^2$, $(a+b)(a-b) = a^2-b^2$ 2. Differentiation Definition: $\frac{dy}{dx} = \lim_{\Delta x \to 0} \frac{f(x+\Delta x) - f(x)}{\Delta x}$ Basic Rules: $\frac{d}{dx}(c) = 0$ $\frac{d}{dx}(x^n) = nx^{n-1}$ $\frac{d}{dx}(e^{ax}) = ae^{ax}$ $\frac{d}{dx}(\ln x) = \frac{1}{x}$ $\frac{d}{dx}(\sin x) = \cos x$ $\frac{d}{dx}(\cos x) = -\sin x$ Product Rule: $\frac{d}{dx}(uv) = u\frac{dv}{dx} + v\frac{du}{dx}$ Quotient Rule: $\frac{d}{dx}\left(\frac{u}{v}\right) = \frac{v\frac{du}{dx} - u\frac{dv}{dx}}{v^2}$ Chain Rule: $\frac{dy}{dx} = \frac{dy}{du} \cdot \frac{du}{dx}$ Partial Derivatives: For $f(x,y)$, $\left(\frac{\partial f}{\partial x}\right)_y$ (treat $y$ as constant) Maxima/Minima: Find $x$ where $\frac{df}{dx} = 0$. Check $\frac{d^2f}{dx^2} > 0$ (min) or $ 3. Integration Definition: Inverse of differentiation. $\int f(x) dx = F(x) + C$ if $\frac{dF}{dx} = f(x)$ Basic Integrals: $\int x^n dx = \frac{x^{n+1}}{n+1} + C \quad (n \ne -1)$ $\int \frac{1}{x} dx = \ln|x| + C$ $\int e^{ax} dx = \frac{1}{a}e^{ax} + C$ $\int \sin x dx = -\cos x + C$ $\int \cos x dx = \sin x + C$ Definite Integral: $\int_a^b f(x) dx = F(b) - F(a)$ Integration by Parts: $\int u \, dv = uv - \int v \, du$ Area under curve: $\int_a^b f(x) dx$ 4. Differential Equations First Order, Separable: $\frac{dy}{dx} = f(x)g(y) \implies \int \frac{dy}{g(y)} = \int f(x) dx$ First Order, Linear: $\frac{dy}{dx} + P(x)y = Q(x)$. Integrating factor $e^{\int P(x)dx}$. Homogeneous: $\frac{dy}{dx} = f(y/x)$. Substitute $y=vx$. Second Order Homogeneous (Constant Coefficients): $ay'' + by' + cy = 0$. Characteristic equation $ar^2 + br + c = 0$. Distinct real roots $r_1, r_2$: $y = C_1e^{r_1x} + C_2e^{r_2x}$ Repeated real root $r$: $y = (C_1 + C_2x)e^{rx}$ Complex conjugate roots $\alpha \pm i\beta$: $y = e^{\alpha x}(C_1\cos(\beta x) + C_2\sin(\beta x))$ 5. Matrices & Determinants Matrix Addition/Subtraction: Element-wise. Requires same dimensions. Matrix Multiplication: $(AB)_{ij} = \sum_k A_{ik} B_{kj}$. $A_{m \times n} B_{n \times p} \implies C_{m \times p}$. Not commutative ($AB \ne BA$). Determinant of $2 \times 2$: $\begin{vmatrix} a & b \\ c & d \end{vmatrix} = ad - bc$ Determinant of $3 \times 3$: $$ \begin{vmatrix} a & b & c \\ d & e & f \\ g & h & i \end{vmatrix} = a(ei-fh) - b(di-fg) + c(dh-eg) $$ Inverse of a Matrix $A$: $A^{-1}$ such that $AA^{-1} = A^{-1}A = I$. $A^{-1} = \frac{1}{\det(A)} \text{adj}(A)$. Eigenvalues & Eigenvectors: $Ax = \lambda x$. $\det(A - \lambda I) = 0$ to find eigenvalues $\lambda$. Solving Linear Systems: $Ax=b$. Use Cramer's rule ($\det$), matrix inverse, or Gaussian elimination. 6. Probability & Statistics (Basic) Mean: $\bar{x} = \frac{\sum x_i}{N}$ Median: Middle value when data is ordered. Mode: Most frequent value. Standard Deviation: $s = \sqrt{\frac{\sum (x_i - \bar{x})^2}{N-1}}$ (sample) or $\sqrt{\frac{\sum (x_i - \bar{x})^2}{N}}$ (population) Variance: $s^2$ Probability: $P(A) = \frac{\text{Number of favorable outcomes}}{\text{Total number of outcomes}}$ Mutually Exclusive Events: $P(A \text{ or } B) = P(A) + P(B)$ Independent Events: $P(A \text{ and } B) = P(A)P(B)$ 7. Vectors (Advanced) Dot Product: $\vec{A} \cdot \vec{B} = |\vec{A}||\vec{B}|\cos\theta = A_x B_x + A_y B_y + A_z B_z$. Scalar result. Cross Product: $\vec{A} \times \vec{B} = |\vec{A}||\vec{B}|\sin\theta \hat{n}$. Vector result. $$ \vec{A} \times \vec{B} = \begin{vmatrix} \mathbf{i} & \mathbf{j} & \mathbf{k} \\ A_x & A_y & A_z \\ B_x & B_y & B_z \end{vmatrix} $$ Gradient: $\nabla f = \left(\frac{\partial f}{\partial x}\right)\mathbf{i} + \left(\frac{\partial f}{\partial y}\right)\mathbf{j} + \left(\frac{\partial f}{\partial z}\right)\mathbf{k}$. Direction of max increase. Divergence: $\nabla \cdot \vec{F} = \frac{\partial F_x}{\partial x} + \frac{\partial F_y}{\partial y} + \frac{\partial F_z}{\partial z}$. Scalar field. Curl: $\nabla \times \vec{F} = \begin{vmatrix} \mathbf{i} & \mathbf{j} & \mathbf{k} \\ \partial/\partial x & \partial/\partial y & \partial/\partial z \\ F_x & F_y & F_z \end{vmatrix}$. Vector field. 8. Complex Numbers Definition: $z = x + iy$, where $i = \sqrt{-1}$. Conjugate: $\bar{z} = x - iy$. Modulus: $|z| = \sqrt{x^2 + y^2}$. Polar Form: $z = r(\cos\theta + i\sin\theta) = re^{i\theta}$, where $r=|z|$ and $\theta = \arg(z)$. De Moivre's Theorem: $(re^{i\theta})^n = r^n e^{in\theta} = r^n (\cos(n\theta) + i\sin(n\theta))$. 9. Series Expansions Taylor Series: $f(x) = \sum_{n=0}^{\infty} \frac{f^{(n)}(a)}{n!}(x-a)^n$ Maclaurin Series (Taylor at $a=0$): $f(x) = \sum_{n=0}^{\infty} \frac{f^{(n)}(0)}{n!}x^n$ Common Expansions: $e^x = 1 + x + \frac{x^2}{2!} + \frac{x^3}{3!} + \dots$ $\sin x = x - \frac{x^3}{3!} + \frac{x^5}{5!} - \dots$ $\cos x = 1 - \frac{x^2}{2!} + \frac{x^4}{4!} - \dots$ $\ln(1+x) = x - \frac{x^2}{2} + \frac{x^3}{3} - \dots \quad (|x| $(1+x)^n = 1 + nx + \frac{n(n-1)}{2!}x^2 + \dots$ (Binomial series) 10. Units & Conversions SI Base Units: m, kg, s, A, K, mol, cd. Prefixes: Giga ($10^9$), Mega ($10^6$), Kilo ($10^3$), Centi ($10^{-2}$), Milli ($10^{-3}$), Micro ($10^{-6}$), Nano ($10^{-9}$), Pico ($10^{-12}$). Common Conversions: 1 atm = 101325 Pa = 760 mmHg = 760 Torr 1 L = $1 \text{ dm}^3 = 1000 \text{ cm}^3$ 1 cal = 4.184 J 1 eV = $1.602 \times 10^{-19}$ J $0^\circ \text{C} = 273.15 \text{ K}$