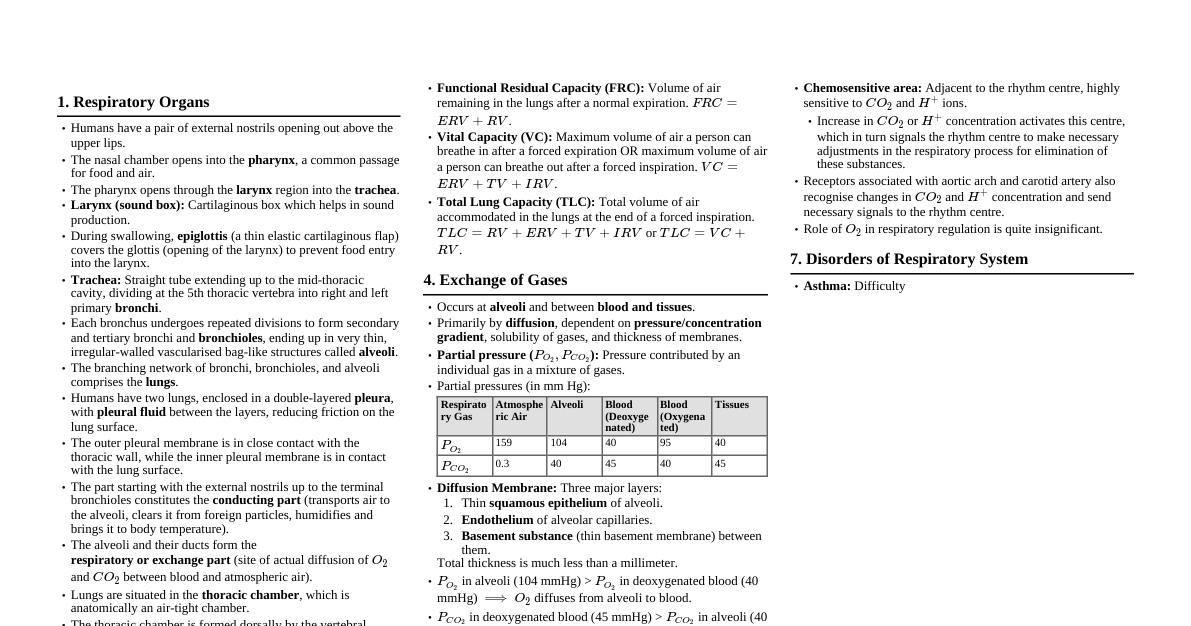
### Real Numbers - **Euclid's Division Lemma:** $a = bq + r$, where $0 \le r ### Polynomials - **Degree of a Polynomial:** The highest power of the variable in a polynomial. - **Types:** - Linear: $ax+b$, degree 1 - Quadratic: $ax^2+bx+c$, degree 2 - Cubic: $ax^3+bx^2+cx+d$, degree 3 - **Zeros of a Polynomial:** Values of $x$ for which $P(x) = 0$. Graphically, these are the x-intercepts. - **Relationship between Zeros and Coefficients (Quadratic):** - If $\alpha, \beta$ are the zeros of $ax^2+bx+c$: - Sum of zeros: $\alpha + \beta = -b/a$ - Product of zeros: $\alpha \beta = c/a$ - **Relationship between Zeros and Coefficients (Cubic):** - If $\alpha, \beta, \gamma$ are the zeros of $ax^3+bx^2+cx+d$: - Sum of zeros: $\alpha + \beta + \gamma = -b/a$ - Sum of products of zeros taken two at a time: $\alpha\beta + \beta\gamma + \gamma\alpha = c/a$ - Product of zeros: $\alpha\beta\gamma = -d/a$ - **Division Algorithm:** $P(x) = G(x) \cdot Q(x) + R(x)$, where $R(x)=0$ or degree of $R(x) ### Pair of Linear Equations in Two Variables - **General Form:** $a_1x + b_1y + c_1 = 0$ and $a_2x + b_2y + c_2 = 0$. - **Graphical Method:** - Intersecting lines: Unique solution ($a_1/a_2 \neq b_1/b_2$) - Coincident lines: Infinitely many solutions ($a_1/a_2 = b_1/b_2 = c_1/c_2$) - Parallel lines: No solution ($a_1/a_2 = b_1/b_2 \neq c_1/c_2$) - **Algebraic Methods:** - **Substitution Method:** Express one variable in terms of the other from one equation, substitute into the second. - **Elimination Method:** Multiply equations by suitable numbers to make coefficients of one variable equal, then add/subtract. - **Cross-Multiplication Method:** $$ \frac{x}{b_1c_2 - b_2c_1} = \frac{y}{c_1a_2 - c_2a_1} = \frac{1}{a_1b_2 - a_2b_1} $$ ### Quadratic Equations - **Standard Form:** $ax^2 + bx + c = 0$, where $a \neq 0$. - **Methods to Solve:** - **Factorisation:** Split the middle term. - **Completing the Square:** Convert to $(x+k)^2 = d$. - **Quadratic Formula:** $x = \frac{-b \pm \sqrt{b^2 - 4ac}}{2a}$ - **Discriminant (D):** $D = b^2 - 4ac$ - $D > 0$: Two distinct real roots. - $D = 0$: Two equal real roots. - $D ### Arithmetic Progressions (AP) - **Definition:** A sequence where the difference between consecutive terms is constant (common difference, $d$). - **General Form:** $a, a+d, a+2d, ...$ - **$n^{th}$ Term:** $a_n = a + (n-1)d$ - **Sum of First $n$ Terms:** - $S_n = \frac{n}{2}[2a + (n-1)d]$ - $S_n = \frac{n}{2}(a + a_n)$ (when last term $a_n$ is known) ### Triangles - **Similarity of Triangles:** - **AAA (Angle-Angle-Angle):** If corresponding angles are equal. - **SSS (Side-Side-Side):** If corresponding sides are proportional. - **SAS (Side-Angle-Side):** If one angle of a triangle is equal to one angle of the other triangle and the sides including these angles are proportional. - **Basic Proportionality Theorem (Thales Theorem):** If a line is drawn parallel to one side of a triangle to intersect the other two sides in distinct points, the other two sides are divided in the same ratio. - **Area of Similar Triangles:** The ratio of the areas of two similar triangles is equal to the square of the ratio of their corresponding sides. - $\frac{Area(\triangle ABC)}{Area(\triangle PQR)} = (\frac{AB}{PQ})^2 = (\frac{BC}{QR})^2 = (\frac{CA}{RP})^2$ - **Pythagoras Theorem:** In a right-angled triangle, the square of the hypotenuse is equal to the sum of the squares of the other two sides ($h^2 = p^2 + b^2$). - **Converse:** If in a triangle, square of one side is equal to the sum of the squares of the other two sides, then the angle opposite the first side is a right angle. ### Coordinate Geometry - **Distance Formula:** Distance between $(x_1, y_1)$ and $(x_2, y_2)$ is $\sqrt{(x_2-x_1)^2 + (y_2-y_1)^2}$. - **Section Formula:** Coordinates of a point $P(x,y)$ dividing the line segment joining $A(x_1, y_1)$ and $B(x_2, y_2)$ internally in the ratio $m:n$: - $x = \frac{mx_2 + nx_1}{m+n}$ - $y = \frac{my_2 + ny_1}{m+n}$ - **Mid-point Formula:** For $m=n=1$: $x = \frac{x_1+x_2}{2}$, $y = \frac{y_1+y_2}{2}$. - **Area of a Triangle:** Area of $\triangle ABC$ with vertices $(x_1, y_1)$, $(x_2, y_2)$, $(x_3, y_3)$: - Area $= \frac{1}{2} |x_1(y_2-y_3) + x_2(y_3-y_1) + x_3(y_1-y_2)|$ - If Area $= 0$, points are collinear. ### Introduction to Trigonometry - **Trigonometric Ratios (Right-angled triangle):** - $\sin A = \frac{\text{Opposite}}{\text{Hypotenuse}}$ - $\cos A = \frac{\text{Adjacent}}{\text{Hypotenuse}}$ - $\tan A = \frac{\text{Opposite}}{\text{Adjacent}}$ - $\csc A = \frac{1}{\sin A}$ - $\sec A = \frac{1}{\cos A}$ - $\cot A = \frac{1}{\tan A}$ - **Trigonometric Ratios of Specific Angles:** | Angle $(\theta)$ | $0^\circ$ | $30^\circ$ | $45^\circ$ | $60^\circ$ | $90^\circ$ | |------------------|-----------|------------|------------|------------|------------| | $\sin \theta$ | 0 | $1/2$ | $1/\sqrt{2}$ | $\sqrt{3}/2$ | 1 | | $\cos \theta$ | 1 | $\sqrt{3}/2$ | $1/\sqrt{2}$ | $1/2$ | 0 | | $\tan \theta$ | 0 | $1/\sqrt{3}$ | 1 | $\sqrt{3}$ | Undefined | - **Trigonometric Identities:** - $\sin^2 A + \cos^2 A = 1$ - $1 + \tan^2 A = \sec^2 A$ - $1 + \cot^2 A = \csc^2 A$ - **Complementary Angles:** - $\sin(90^\circ - A) = \cos A$ - $\cos(90^\circ - A) = \sin A$ - $\tan(90^\circ - A) = \cot A$ - $\cot(90^\circ - A) = \tan A$ - $\sec(90^\circ - A) = \csc A$ - $\csc(90^\circ - A) = \sec A$ ### Applications of Trigonometry - **Heights and Distances:** Using trigonometric ratios to find heights of objects or distances between objects based on angles of elevation and depression. - **Angle of Elevation:** Angle formed by the line of sight with the horizontal when the object is above the horizontal level. - **Angle of Depression:** Angle formed by the line of sight with the horizontal when the object is below the horizontal level. ### Circles - **Tangent to a Circle:** A line that intersects the circle at only one point. - **Properties of Tangents:** - The tangent at any point of a circle is perpendicular to the radius through the point of contact. - The lengths of tangents drawn from an external point to a circle are equal. - There can be at most two parallel tangents to a circle. - From an external point, two tangents can be drawn to a circle. - From an internal point, no tangent can be drawn to a circle. ### Constructions - **Division of a Line Segment:** Divide a line segment in a given ratio (internally). - **Tangent to a Circle:** - From a point on the circle (using radius perpendicularity). - From a point outside the circle (using perpendicular bisector of the line joining the center and the external point). - **Construction of Similar Triangles:** Construct a triangle similar to a given triangle as per a given scale factor. ### Areas Related to Circles - **Circumference of a Circle:** $2\pi r$ - **Area of a Circle:** $\pi r^2$ - **Area of a Sector:** $\frac{\theta}{360^\circ} \times \pi r^2$ (where $\theta$ is the angle in degrees) - **Length of an Arc:** $\frac{\theta}{360^\circ} \times 2\pi r$ - **Area of a Segment:** Area of sector - Area of corresponding triangle. ### Surface Areas and Volumes - **Combinations of Solids:** Calculating surface areas and volumes of objects formed by combining two or more basic solids (e.g., cylinder with hemispherical ends). - **Conversion of Solids:** Volume remains constant when a solid is reshaped from one form to another. - **Formulas:** - **Cuboid:** - Volume: $l \times b \times h$ - Surface Area: $2(lb + bh + hl)$ - **Cube:** - Volume: $a^3$ - Surface Area: $6a^2$ - **Cylinder:** - Volume: $\pi r^2 h$ - Curved Surface Area (CSA): $2\pi rh$ - Total Surface Area (TSA): $2\pi r(r+h)$ - **Cone:** - Volume: $\frac{1}{3}\pi r^2 h$ - CSA: $\pi rl$ (where $l = \sqrt{r^2+h^2}$ is slant height) - TSA: $\pi r(l+r)$ - **Sphere:** - Volume: $\frac{4}{3}\pi r^3$ - Surface Area: $4\pi r^2$ - **Hemisphere:** - Volume: $\frac{2}{3}\pi r^3$ - CSA: $2\pi r^2$ - TSA: $3\pi r^2$ - **Frustum of a Cone:** (If included in syllabus) - Volume: $\frac{1}{3}\pi h (R^2 + r^2 + Rr)$ - CSA: $\pi l (R+r)$ where $l = \sqrt{h^2 + (R-r)^2}$ ### Statistics - **Measures of Central Tendency:** - **Mean ($\bar{x}$):** - Direct Method: $\bar{x} = \frac{\sum f_i x_i}{\sum f_i}$ - Assumed Mean Method: $\bar{x} = a + \frac{\sum f_i d_i}{\sum f_i}$ where $d_i = x_i - a$ - Step-Deviation Method: $\bar{x} = a + \left(\frac{\sum f_i u_i}{\sum f_i}\right) h$ where $u_i = \frac{x_i - a}{h}$ - **Median:** The middle-most value when data is arranged in ascending/descending order. - For grouped data: Median $= L + \left(\frac{N/2 - cf}{f}\right) h$ - $L$: lower limit of median class - $N$: sum of frequencies - $cf$: cumulative frequency of class preceding median class - $f$: frequency of median class - $h$: class size - **Mode:** The most frequently occurring value. - For grouped data: Mode $= L + \left(\frac{f_1 - f_0}{2f_1 - f_0 - f_2}\right) h$ - $L$: lower limit of modal class - $f_1$: frequency of modal class - $f_0$: frequency of class preceding modal class - $f_2$: frequency of class succeeding modal class - $h$: class size - **Empirical Relationship:** $3 \text{ Median } = \text{ Mode } + 2 \text{ Mean }$ - **Ogives (Cumulative Frequency Curves):** - "Less than" ogive: Plots upper class limits vs. less than cumulative frequencies. - "More than" ogive: Plots lower class limits vs. more than cumulative frequencies. - The intersection of the two ogives gives the median. ### Probability - **Definition:** $P(E) = \frac{\text{Number of favourable outcomes}}{\text{Total number of possible outcomes}}$ - **Range of Probability:** $0 \le P(E) \le 1$ - **Complementary Events:** $P(E) + P(\text{not } E) = 1$ - **Impossible Event:** $P(\text{impossible event}) = 0$ - **Sure/Certain Event:** $P(\text{sure event}) = 1$