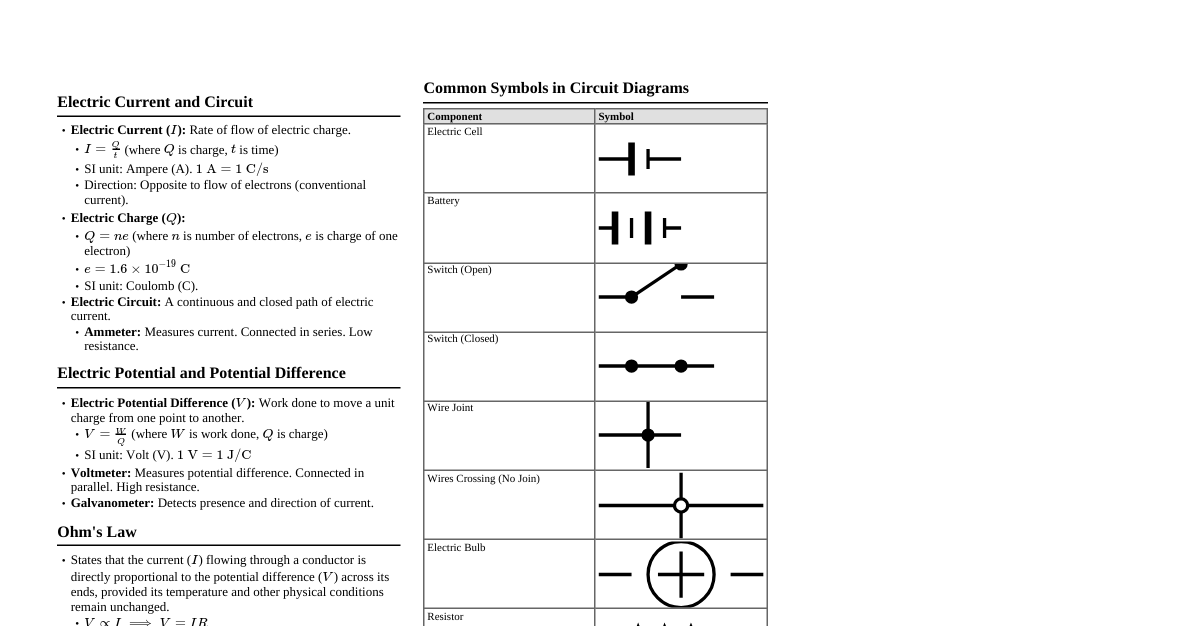
### Chemical Reactions & Equations - **Combination Reaction:** A + B → AB (e.g., $CaO + H_2O \rightarrow Ca(OH)_2$) - **Decomposition Reaction:** AB → A + B (e.g., $CaCO_3 \rightarrow CaO + CO_2$) - **Displacement Reaction:** A + BC → AC + B (More reactive displaces less reactive) - **Double Displacement Reaction:** AB + CD → AD + CB (Exchange of ions) - **Redox Reactions:** - **Oxidation:** Gain of oxygen, loss of hydrogen, loss of electrons. - **Reduction:** Loss of oxygen, gain of hydrogen, gain of electrons. - **Oxidizing Agent:** Substance that oxidizes another and gets reduced itself. - **Reducing Agent:** Substance that reduces another and gets oxidized itself. - **Exothermic Reaction:** Releases heat (e.g., respiration). - **Endothermic Reaction:** Absorbs heat (e.g., photosynthesis). - **Corrosion:** Rusting of iron ($Fe_2O_3 \cdot xH_2O$). - **Rancidity:** Oxidation of fats and oils in food, causing bad smell/taste. Prevented by antioxidants, nitrogen flushing, refrigeration. ### Acids, Bases & Salts - **Acids:** Sour taste, turn blue litmus red, release $H^+$ ions (Arrhenius), proton donors (Bronsted-Lowry). pH 7. - **Examples:** $NaOH$ (Strong), $Ca(OH)_2$ (Strong), $NH_4OH$ (Weak). - **Salts:** Formed by neutralization reaction ($Acid + Base \rightarrow Salt + Water$). - **pH Scale:** 0 (highly acidic) to 14 (highly basic). 7 is neutral. - **Common Chemicals:** - **Bleaching Powder:** $CaOCl_2$ (Used for bleaching, disinfectant). - **Baking Soda:** $NaHCO_3$ (Antacid, baking). - **Washing Soda:** $Na_2CO_3 \cdot 10H_2O$ (Cleaning agent, removes permanent hardness of water). - **Plaster of Paris (POP):** $CaSO_4 \cdot \frac{1}{2}H_2O$ (Fracture setting, decorative items). ### Metals & Non-metals - **Metals:** Malleable, ductile, lustrous, good conductors of heat and electricity, usually solid (except Hg). Form basic oxides. - **Reactivity Series:** K > Na > Ca > Mg > Al > Zn > Fe > Pb > H > Cu > Hg > Ag > Au. - **Extraction:** - High reactivity: Electrolytic reduction (Na, K, Al). - Medium reactivity: Roasting (sulfide ores), Calcination (carbonate ores), then reduction with carbon (Zn, Fe, Pb). - Low reactivity: Heating alone (Hg, Cu). - **Non-metals:** Brittle, non-lustrous, poor conductors (except graphite). Form acidic or neutral oxides. - **Examples:** Carbon, Sulfur, Oxygen, Nitrogen, Chlorine. - **Alloys:** Homogeneous mixtures of two or more metals, or a metal and a non-metal. (e.g., Brass (Cu+Zn), Bronze (Cu+Sn), Solder (Pb+Sn)). ### Carbon & Its Compounds - **Covalent Bonding:** Sharing of electrons to achieve stable configuration. Carbon forms 4 covalent bonds. - **Versatile Nature of Carbon:** - **Catenation:** Ability to form long chains, branched chains, and rings. - **Tetravalency:** Valency of 4, allowing bonding with various elements. - **Hydrocarbons:** Compounds of Carbon and Hydrogen. - **Saturated:** Alkanes (C-C single bonds, $C_nH_{2n+2}$). - **Unsaturated:** Alkenes (C=C double bonds, $C_nH_{2n}$), Alkynes (C≡C triple bonds, $C_nH_{2n-2}$). - **Functional Groups:** Atoms or groups of atoms that determine chemical properties. - **Alcohol:** -OH (e.g., Ethanol $CH_3CH_2OH$) - **Aldehyde:** -CHO (e.g., Ethanal $CH_3CHO$) - **Ketone:** >C=O (e.g., Propanone $CH_3COCH_3$) - **Carboxylic Acid:** -COOH (e.g., Ethanoic Acid $CH_3COOH$) - **Ethanol:** $CH_3CH_2OH$. Used as solvent, fuel, in alcoholic beverages. - **Ethanoic Acid:** $CH_3COOH$. Also called Acetic Acid. Used as vinegar. - **Soaps & Detergents:** Cleansing agents. Soaps are sodium/potassium salts of long-chain fatty acids. Detergents are ammonium/sulfonate salts of long-chain carboxylic acids. - **Micelle Formation:** Hydrophobic tail (hydrocarbon) attracts dirt, hydrophilic head (ionic) attracts water. ### Periodic Classification of Elements - **Mendeleev's Periodic Law:** Properties of elements are a periodic function of their atomic masses. - **Limitations:** Position of isotopes, hydrogen, anomalous pairs. - **Modern Periodic Law:** Properties of elements are a periodic function of their atomic numbers. - **Periods:** Horizontal rows (7). Number of shells. - **Groups:** Vertical columns (18). Number of valence electrons (for main group elements). - **Trends:** - **Valency:** First increases, then decreases across a period. Remains same in a group. - **Atomic Size:** Decreases across a period, increases down a group. - **Metallic Character:** Decreases across a period, increases down a group. - **Non-metallic Character:** Increases across a period, decreases down a group. - **Electronegativity:** Increases across a period, decreases down a group. ### Life Processes - **Nutrition:** - **Autotrophic:** Organisms make their own food (e.g., plants via photosynthesis: $6CO_2 + 6H_2O \xrightarrow{Sunlight/Chlorophyll} C_6H_{12}O_6 + 6O_2$). - **Heterotrophic:** Organisms depend on others for food (e.g., animals). - **Respiration:** Release of energy from food. - **Aerobic:** With oxygen ($C_6H_{12}O_6 + 6O_2 \rightarrow 6CO_2 + 6H_2O + Energy (ATP)$). Occurs in mitochondria. - **Anaerobic:** Without oxygen (e.g., in yeast: ethanol + $CO_2$; in muscle cells: lactic acid). - **Transportation:** - **Plants:** Xylem (water & minerals from roots to leaves), Phloem (food from leaves to other parts). - **Humans:** - **Blood:** Red Blood Cells (oxygen transport), White Blood Cells (immunity), Platelets (clotting), Plasma (fluid matrix). - **Heart:** Four chambers (Right Atrium, Right Ventricle, Left Atrium, Left Ventricle). Double circulation. - **Blood Vessels:** Arteries (carry blood away from heart), Veins (carry blood towards heart), Capillaries (exchange). - **Excretion:** Removal of metabolic waste products. - **Humans:** Kidneys (filter blood, form urine), Ureters, Urinary Bladder, Urethra. Nephron is functional unit of kidney. ### Control & Coordination - **Nervous System:** - **Neurons:** Structural and functional unit. Dendrite (receives), Cell Body, Axon (transmits), Nerve Ending. - **Synapse:** Gap between two neurons. - **Reflex Arc:** Quick, involuntary response (sensory neuron → spinal cord → motor neuron). - **Brain:** - **Forebrain:** Cerebrum (thought, memory, voluntary actions), Hypothalamus (hunger, thirst, temp). - **Midbrain:** Reflexes involving eyes/ears. - **Hindbrain:** Cerebellum (balance, posture), Pons (respiration), Medulla (heartbeat, BP, vomiting). - **Endocrine System (Hormones):** Chemical messengers. - **Thyroid:** Thyroxine (metabolism). - **Pancreas:** Insulin (lowers blood sugar), Glucagon (raises blood sugar). - **Adrenal:** Adrenaline (fight or flight). - **Pituitary:** Growth hormone, Master gland. - **Testes (males):** Testosterone. - **Ovaries (females):** Estrogen, Progesterone. - **Coordination in Plants:** - **Phytohormones:** Auxins (growth, phototropism), Gibberellins (stem elongation), Cytokinins (cell division), Abscisic Acid (growth inhibition), Ethylene (fruit ripening). - **Tropism:** Directional growth in response to stimulus. Phototropism (light), Geotropism (gravity), Hydrotropism (water), Chemotropism (chemicals). ### How Do Organisms Reproduce? - **Asexual Reproduction:** Single parent, no gamete fusion, genetically identical offspring. - **Fission:** Binary (Amoeba), Multiple (Plasmodium). - **Budding:** Yeast, Hydra. - **Spore Formation:** Rhizopus. - **Fragmentation:** Spirogyra. - **Vegetative Propagation:** Plants (roots, stems, leaves - e.g., potato, rose). - **Sexual Reproduction:** Two parents, gamete fusion, genetically varied offspring. - **Flowering Plants:** - **Flower Parts:** Sepals, Petals, Stamens (male - anther, filament), Pistil/Carpel (female - stigma, style, ovary). - **Pollination:** Transfer of pollen. Self/Cross. - **Fertilization:** Fusion of male gamete with egg cell in ovary. Forms zygote. Ovary develops into fruit, ovule into seed. - **Human Reproduction:** - **Male:** Testes (sperm, testosterone), Vas deferens, Urethra, Penis. - **Female:** Ovaries (egg, estrogen, progesterone), Fallopian tubes, Uterus, Vagina. - **Menstrual Cycle:** Monthly cycle of changes in uterus lining. - **Fertilization:** In fallopian tube. Zygote implants in uterus. - **Birth Control:** Barrier methods, pills, IUDs, surgical methods (vasectomy, tubectomy). - **STDs:** Bacterial (Gonorrhea, Syphilis), Viral (Warts, HIV/AIDS). ### Heredity & Evolution - **Heredity:** Transmission of traits from parents to offspring. - **Variations:** Differences among individuals of a species. Important for evolution. - **Mendel's Laws:** - **Law of Dominance:** Dominant trait expresses over recessive. - **Law of Segregation:** Alleles separate during gamete formation. - **Law of Independent Assortment:** Genes for different traits assort independently. - **Sex Determination:** In humans, XY (male), XX (female). Male decides sex of offspring. - **Evolution:** Gradual change in living organisms over generations. - **Evidence:** Fossils, Homologous organs (same structure, different function), Analogous organs (different structure, same function), Vestigial organs. - **Natural Selection (Darwin):** Survival of the fittest. - **Speciation:** Formation of new species due to genetic drift, natural selection, geographical isolation. ### Light: Reflection & Refraction - **Reflection:** Bouncing back of light. - **Laws:** Angle of incidence = Angle of reflection; Incident ray, reflected ray, normal lie in same plane. - **Mirrors:** - **Plane:** Virtual, erect, same size, laterally inverted. - **Concave:** Converging. Real & inverted (mostly), virtual & erect (when object between P & F). Used in headlights, shaving mirrors. - **Convex:** Diverging. Virtual, erect, diminished. Used as rear-view mirrors. - **Refraction:** Bending of light as it passes from one medium to another. - **Snell's Law:** $\frac{\sin i}{\sin r} = \text{constant} = n$ (refractive index). - **Lenses:** - **Convex:** Converging. Real & inverted (mostly), virtual & erect (when object between O & F). Used in magnifying glasses, cameras. - **Concave:** Diverging. Virtual, erect, diminished. Used to correct myopia. - **Power of Lens:** $P = \frac{1}{f}$ (in dioptres, f in meters). ### Human Eye & Colorful World - **Human Eye:** - **Cornea:** Transparent outer layer. - **Iris:** Controls pupil size. - **Pupil:** Regulates light entering. - **Lens:** Focuses light on retina. - **Retina:** Light-sensitive screen (rods for dim light, cones for color). - **Optic Nerve:** Transmits signals to brain. - **Defects of Vision:** - **Myopia (Nearsightedness):** Distant objects blurred. Corrected by concave lens. - **Hypermetropia (Farsightedness):** Near objects blurred. Corrected by convex lens. - **Presbyopia:** Age-related, difficulty seeing near objects. Corrected by bifocal lenses. - **Cataract:** Clouding of lens. - **Dispersion of Light:** Splitting of white light into its constituent colors (VIBGYOR) by a prism. - **Atmospheric Refraction:** Twinkling of stars, advanced sunrise & delayed sunset. - **Scattering of Light:** Blue sky, red sun at sunrise/sunset (Tyndall effect). ### Electricity - **Electric Current:** Flow of charge ($I = \frac{Q}{t}$). Unit: Ampere (A). - **Potential Difference:** Work done per unit charge ($V = \frac{W}{Q}$). Unit: Volt (V). - **Ohm's Law:** $V = IR$. - **Resistance:** Opposition to current flow. Unit: Ohm ($\Omega$). - $R = \rho \frac{L}{A}$ ($\rho$ = resistivity). - **Resistors in Series:** $R_{eq} = R_1 + R_2 + ...$ - **Resistors in Parallel:** $\frac{1}{R_{eq}} = \frac{1}{R_1} + \frac{1}{R_2} + ...$ - **Heating Effect of Current (Joule's Law):** $H = I^2Rt = VIt = \frac{V^2}{R}t$. - **Electric Power:** $P = VI = I^2R = \frac{V^2}{R}$. Unit: Watt (W). - Commercial unit: kilowatt-hour (kWh). $1 kWh = 3.6 \times 10^6 J$. ### Magnetic Effects of Electric Current - **Magnetic Field:** Region around a magnet or current-carrying conductor where its magnetic effect can be felt. - **Magnetic Field Lines:** Originate from North pole, end at South pole. Never intersect. - **Right-Hand Thumb Rule:** Direction of magnetic field around a straight current-carrying conductor. - **Solenoid:** Coil of many circular turns. Acts like a bar magnet. - **Electromagnet:** Temporary magnet created by passing current through a solenoid. - **Fleming's Left-Hand Rule:** For force on a current-carrying conductor in a magnetic field (Motor Rule). - Thumb: Force (Motion) - Forefinger: Magnetic Field - Middle finger: Current - **Electric Motor:** Converts electrical energy to mechanical energy. Principle: Force on current-carrying conductor in magnetic field. - **Electromagnetic Induction (Faraday's Law):** Production of induced current due to change in magnetic flux. - **Fleming's Right-Hand Rule:** For direction of induced current (Generator Rule). - Thumb: Motion - Forefinger: Magnetic Field - Middle finger: Induced Current - **Electric Generator:** Converts mechanical energy to electrical energy. Principle: EMI. - **AC vs DC:** Alternating Current (direction changes periodically) vs Direct Current (constant direction). ### Sources of Energy - **Conventional Sources:** - **Fossil Fuels:** Coal, Petroleum, Natural Gas (non-renewable, cause pollution). - **Thermal Power Plants:** Use fossil fuels to heat water, produce steam to run turbines. - **Hydro Power Plants:** Convert potential energy of falling water into electricity. Renewable, but environmental impact. - **Biomass:** Organic matter (wood, agricultural waste). Renewable, but inefficient. - **Wind Energy:** Wind turbines convert kinetic energy of wind into electricity. Renewable, clean. - **Non-Conventional Sources:** - **Solar Energy:** Solar cells (photovoltaic effect), solar heaters. Clean, renewable. - **Ocean Energy:** Tidal energy, wave energy, Ocean Thermal Energy Conversion (OTEC). - **Geothermal Energy:** Heat from Earth's interior. - **Nuclear Energy:** Fission of heavy nuclei (Uranium). High energy yield, but radioactive waste disposal issues. - **Good Source of Energy:** High calorific value, easily accessible, safe to transport, economical, causes less pollution. ### Our Environment - **Ecosystem:** All living organisms in an area along with non-living components. - **Components:** Producers (autotrophs), Consumers (herbivores, carnivores, omnivores), Decomposers (bacteria, fungi). - **Food Chain:** Transfer of energy (e.g., Grass → Deer → Tiger). - **Food Web:** Interconnected food chains. - **10% Law:** Only 10% of energy is transferred from one trophic level to the next. - **Trophic Levels:** Producers (1st), Primary Consumers (2nd), Secondary Consumers (3rd), Tertiary Consumers (4th). - **Environmental Problems:** - **Ozone Depletion:** Depletion of ozone layer ($O_3$) by CFCs. Causes skin cancer, cataract. - **Waste Management:** Biodegradable (decomposed by microbes) vs Non-biodegradable (plastics, glass). - **Recycling, Reuse, Reduce:** The 3 R's for waste management. ### Management of Natural Resources - **Natural Resources:** Coal, Petroleum, Forests, Wildlife, Water. - **Sustainable Management:** Using resources wisely to meet present needs without compromising future generations. - **Forests & Wildlife:** - **Conservation:** Protecting biodiversity. - **Stakeholders:** Local people, Forest Department, Industrialists, Wildlife enthusiasts. - **Chipko Andolan:** Movement to protect trees. - **Water Resources:** - **Rainwater Harvesting:** Collecting and storing rainwater. - **Dams:** For irrigation, electricity, water supply. - **Coal & Petroleum:** - **Formation:** From degradation of biomass over millions of years. - **Conservation:** Use public transport, carpooling, switch off lights, use efficient appliances. - **The 3 R's:** Reduce, Reuse, Recycle.