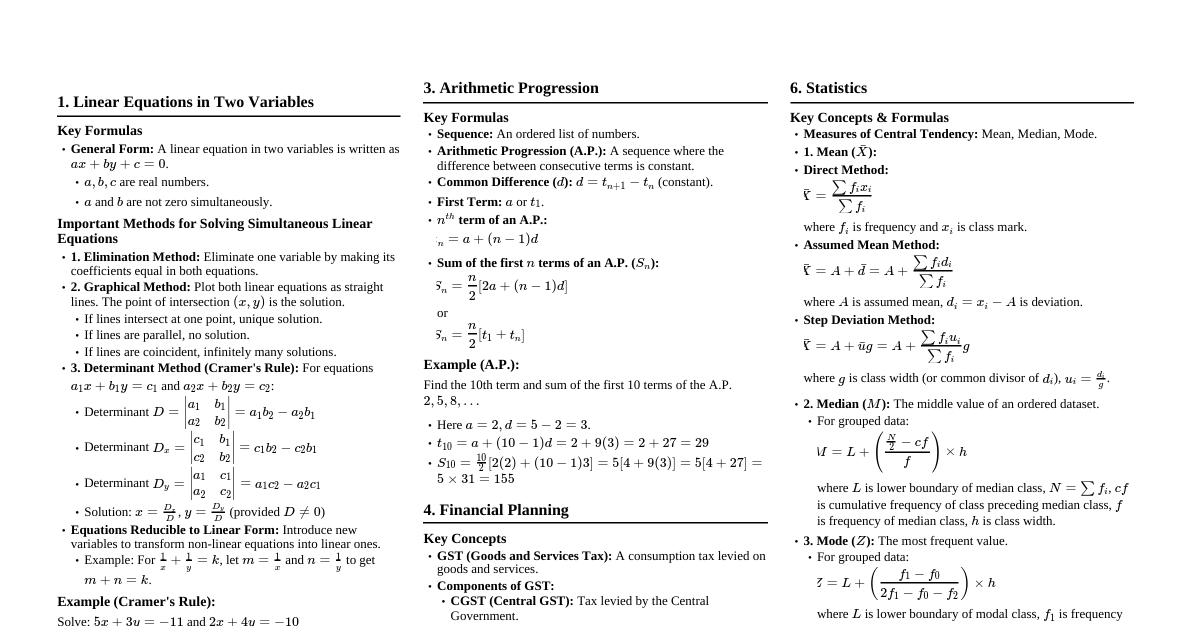
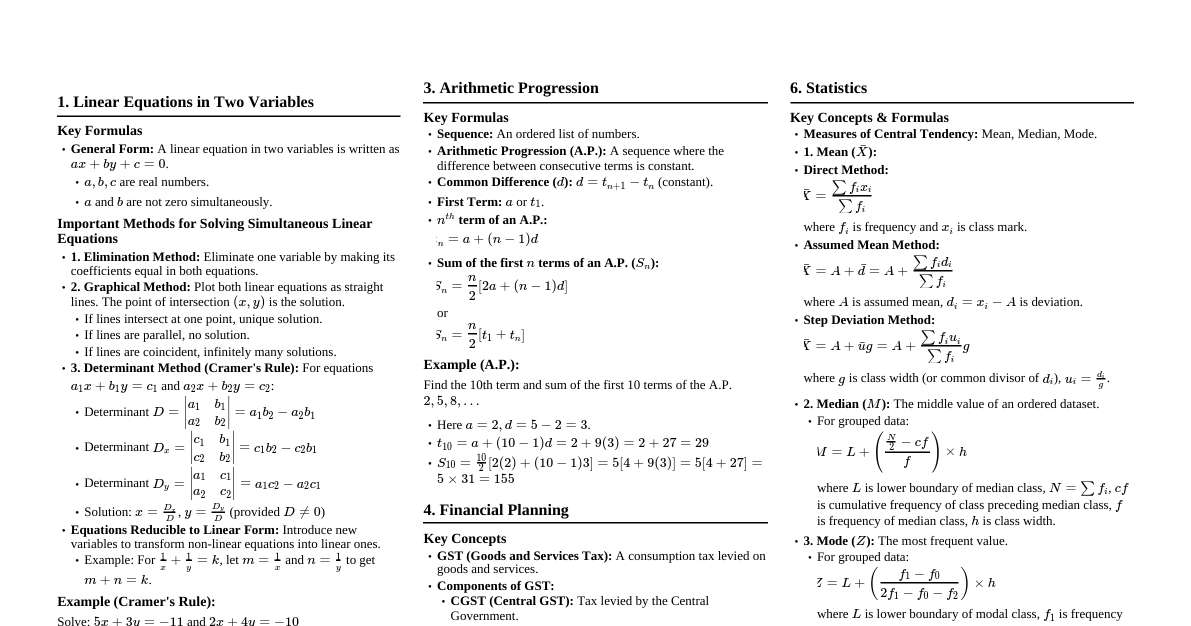
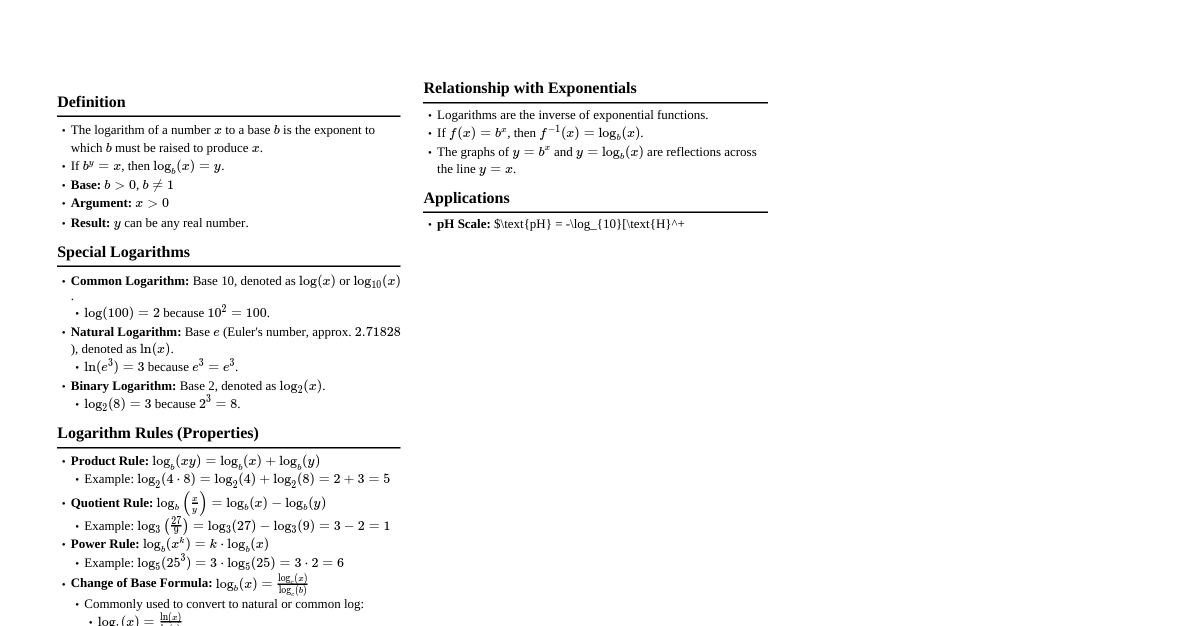
Basic Algebra Commutative Property: Addition: $a + b = b + a$ Multiplication: $a \cdot b = b \cdot a$ Associative Property: Addition: $(a + b) + c = a + (b + c)$ Multiplication: $(a \cdot b) \cdot c = a \cdot (b \cdot c)$ Distributive Property: $a \cdot (b + c) = a \cdot b + a \cdot c$ Order of Operations (PEMDAS/BODMAS): Parentheses/Brackets Exponents/Orders Multiplication and Division (from left to right) Addition and Subtraction (from left to right) Exponents and Radicals $a^m \cdot a^n = a^{m+n}$ $\frac{a^m}{a^n} = a^{m-n}$ $(a^m)^n = a^{mn}$ $(ab)^n = a^n b^n$ $(\frac{a}{b})^n = \frac{a^n}{b^n}$ $a^0 = 1$ (for $a \neq 0$) $a^{-n} = \frac{1}{a^n}$ $\sqrt[n]{a} = a^{1/n}$ $\sqrt[n]{ab} = \sqrt[n]{a} \cdot \sqrt[n]{b}$ $\sqrt[n]{\frac{a}{b}} = \frac{\sqrt[n]{a}}{\sqrt[n]{b}}$ Factoring Formulas Difference of Squares: $a^2 - b^2 = (a - b)(a + b)$ Perfect Square Trinomials: $a^2 + 2ab + b^2 = (a + b)^2$ $a^2 - 2ab + b^2 = (a - b)^2$ Sum of Cubes: $a^3 + b^3 = (a + b)(a^2 - ab + b^2)$ Difference of Cubes: $a^3 - b^3 = (a - b)(a^2 + ab + b^2)$ Quadratic Equations Standard Form: $ax^2 + bx + c = 0$ Quadratic Formula: $x = \frac{-b \pm \sqrt{b^2 - 4ac}}{2a}$ Discriminant: $\Delta = b^2 - 4ac$ If $\Delta > 0$, two distinct real roots If $\Delta = 0$, one real root (repeated) If $\Delta Logarithms Definition: $y = \log_b(x) \iff b^y = x$ Product Rule: $\log_b(MN) = \log_b(M) + \log_b(N)$ Quotient Rule: $\log_b(\frac{M}{N}) = \log_b(M) - \log_b(N)$ Power Rule: $\log_b(M^p) = p \cdot \log_b(M)$ Change of Base: $\log_b(M) = \frac{\log_c(M)}{\log_c(b)}$ $\log_b(b) = 1$ $\log_b(1) = 0$ $\log_b(b^x) = x$ $b^{\log_b(x)} = x$ Geometry Formulas Area Square: $A = s^2$ Rectangle: $A = lw$ Triangle: $A = \frac{1}{2}bh$ Circle: $A = \pi r^2$ Trapezoid: $A = \frac{1}{2}(b_1 + b_2)h$ Volume Cube: $V = s^3$ Rectangular Prism: $V = lwh$ Cylinder: $V = \pi r^2 h$ Cone: $V = \frac{1}{3}\pi r^2 h$ Sphere: $V = \frac{4}{3}\pi r^3$ Perimeter/Circumference Square: $P = 4s$ Rectangle: $P = 2(l + w)$ Circle (Circumference): $C = 2\pi r = \pi d$ Pythagorean Theorem For a right triangle with legs $a, b$ and hypotenuse $c$: $a^2 + b^2 = c^2$ Trigonometry Basic Ratios (SOH CAH TOA) $\sin(\theta) = \frac{\text{Opposite}}{\text{Hypotenuse}}$ $\cos(\theta) = \frac{\text{Adjacent}}{\text{Hypotenuse}}$ $\tan(\theta) = \frac{\text{Opposite}}{\text{Adjacent}} = \frac{\sin(\theta)}{\cos(\theta)}$ Reciprocal Identities $\csc(\theta) = \frac{1}{\sin(\theta)}$ $\sec(\theta) = \frac{1}{\cos(\theta)}$ $\cot(\theta) = \frac{1}{\tan(\theta)}$ Pythagorean Identities $\sin^2(\theta) + \cos^2(\theta) = 1$ $1 + \tan^2(\theta) = \sec^2(\theta)$ $1 + \cot^2(\theta) = \csc^2(\theta)$ Angle Sum and Difference $\sin(A \pm B) = \sin A \cos B \pm \cos A \sin B$ $\cos(A \pm B) = \cos A \cos B \mp \sin A \sin B$ $\tan(A \pm B) = \frac{\tan A \pm \tan B}{1 \mp \tan A \tan B}$ Calculus - Derivatives Basic Rules Constant Rule: $\frac{d}{dx}(c) = 0$ Power Rule: $\frac{d}{dx}(x^n) = nx^{n-1}$ Constant Multiple Rule: $\frac{d}{dx}(cf(x)) = c\frac{d}{dx}(f(x))$ Sum/Difference Rule: $\frac{d}{dx}(f(x) \pm g(x)) = \frac{d}{dx}(f(x)) \pm \frac{d}{dx}(g(x))$ Product Rule: $\frac{d}{dx}(f(x)g(x)) = f'(x)g(x) + f(x)g'(x)$ Quotient Rule: $\frac{d}{dx}\left(\frac{f(x)}{g(x)}\right) = \frac{f'(x)g(x) - f(x)g'(x)}{(g(x))^2}$ Chain Rule: $\frac{d}{dx}(f(g(x))) = f'(g(x))g'(x)$ Common Derivatives $\frac{d}{dx}(e^x) = e^x$ $\frac{d}{dx}(a^x) = a^x \ln a$ $\frac{d}{dx}(\ln x) = \frac{1}{x}$ $\frac{d}{dx}(\log_a x) = \frac{1}{x \ln a}$ $\frac{d}{dx}(\sin x) = \cos x$ $\frac{d}{dx}(\cos x) = -\sin x$ $\frac{d}{dx}(\tan x) = \sec^2 x$ $\frac{d}{dx}(\cot x) = -\csc^2 x$ $\frac{d}{dx}(\sec x) = \sec x \tan x$ $\frac{d}{dx}(\csc x) = -\csc x \cot x$ Calculus - Integrals Basic Rules Power Rule: $\int x^n dx = \frac{x^{n+1}}{n+1} + C$ (for $n \neq -1$) $\int \frac{1}{x} dx = \ln|x| + C$ $\int cf(x) dx = c \int f(x) dx$ $\int (f(x) \pm g(x)) dx = \int f(x) dx \pm \int g(x) dx$ Common Integrals $\int e^x dx = e^x + C$ $\int a^x dx = \frac{a^x}{\ln a} + C$ $\int \sin x dx = -\cos x + C$ $\int \cos x dx = \sin x + C$ $\int \sec^2 x dx = \tan x + C$ $\int \csc^2 x dx = -\cot x + C$ $\int \sec x \tan x dx = \sec x + C$ $\int \csc x \cot x dx = -\csc x + C$ $\int \frac{1}{\sqrt{a^2 - x^2}} dx = \arcsin(\frac{x}{a}) + C$ $\int \frac{1}{a^2 + x^2} dx = \frac{1}{a}\arctan(\frac{x}{a}) + C$ Fundamental Theorem of Calculus $\int_a^b f(x) dx = F(b) - F(a)$, where $F'(x) = f(x)$