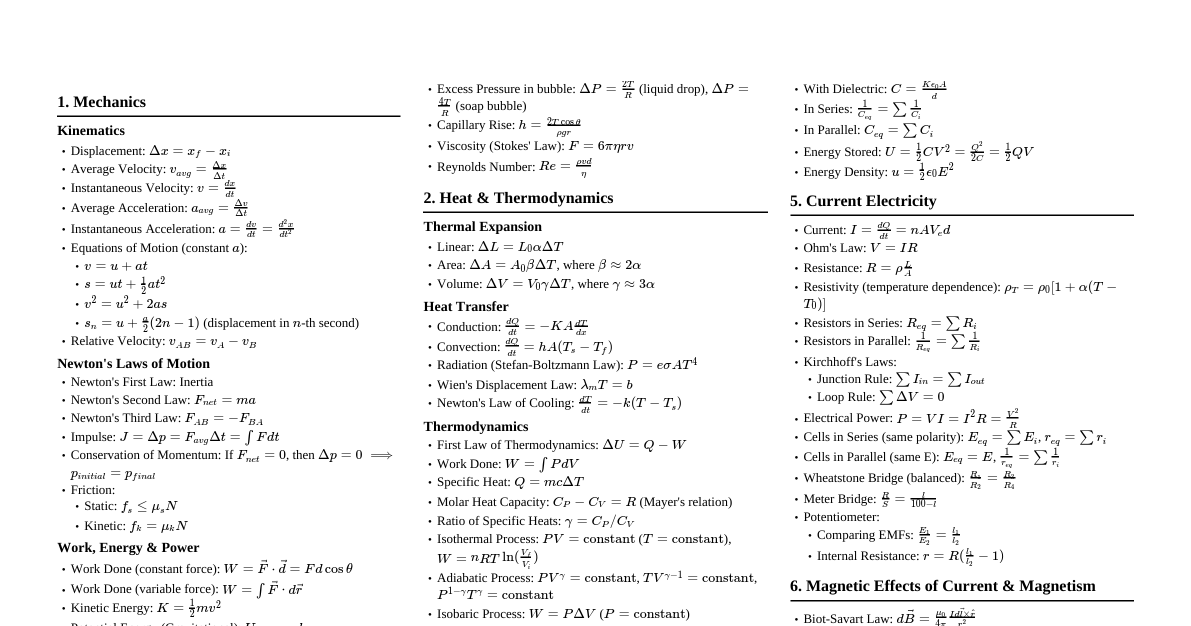
### Position-Time Graphs ($x-t$) - **Definition:** Shows an object's position as a function of time. - **Slope:** Represents velocity ($v = \frac{\Delta x}{\Delta t}$). - **Key Features:** - **Horizontal line:** Object is at rest ($v=0$). - **Straight line with constant slope:** Constant velocity (uniform motion). - **Curved line:** Changing velocity (acceleration). - **Slope increasing:** Increasing velocity (positive acceleration if moving in positive direction). - **Slope decreasing:** Decreasing velocity (negative acceleration if moving in positive direction). | Motion Type | Graph Shape | Slope | |--------------------|-------------------------------------------|---------------------------------------| | At Rest | Horizontal line | Zero slope ($v=0$) | | Constant Velocity | Straight line (non-horizontal) | Constant slope ($v \ne 0$) | | Constant Positive Accel. | Upward curving parabola (concave up) | Increasing positive slope | | Constant Negative Accel. | Downward curving parabola (concave down)| Decreasing positive, or increasing negative slope | ### Velocity-Time Graphs ($v-t$) - **Definition:** Shows an object's velocity as a function of time. - **Slope:** Represents acceleration ($a = \frac{\Delta v}{\Delta t}$). - **Area under curve:** Represents displacement ($\Delta x = \int v \, dt$). - **Key Features:** - **Horizontal line:** Constant velocity ($a=0$). - **Straight line with constant slope:** Constant acceleration. - **Line above x-axis:** Moving in positive direction. - **Line below x-axis:** Moving in negative direction. - **Crossing x-axis:** Momentarily at rest, reversing direction. | Motion Type | Graph Shape | Slope | Area Under Curve | |--------------------|-------------------------------------------|---------------------------------------|----------------------------------| | Constant Velocity | Horizontal line (non-zero) | Zero slope ($a=0$) | Displacement ($\Delta x$) | | Constant Positive Accel. | Straight line (upward slope) | Constant positive slope ($a>0$) | Displacement ($\Delta x$) | | Constant Negative Accel. | Straight line (downward slope) | Constant negative slope ($a ### Acceleration-Time Graphs ($a-t$) - **Definition:** Shows an object's acceleration as a function of time. - **Slope:** Represents "jerk" (rate of change of acceleration). - **Area under curve:** Represents change in velocity ($\Delta v = \int a \, dt$). - **Key Features:** - **Horizontal line at zero:** Constant velocity. - **Horizontal line (non-zero):** Constant acceleration. - **Line above x-axis:** Positive acceleration. - **Line below x-axis:** Negative acceleration. | Motion Type | Graph Shape | Area Under Curve | |--------------------|-------------------------------------------|----------------------------------| | Constant Velocity | Horizontal line at $a=0$ | Zero change in velocity | | Constant Accel. | Horizontal line (non-zero) | Change in velocity ($\Delta v$) | | Changing Accel. | Non-horizontal line or curved line | Change in velocity ($\Delta v$) | ### Relationships Between Graphs - **From $x-t$ to $v-t$:** Slope of $x-t$ graph gives $v-t$ graph. - **From $v-t$ to $a-t$:** Slope of $v-t$ graph gives $a-t$ graph. - **From $a-t$ to $v-t$:** Area under $a-t$ graph gives change in velocity. - **From $v-t$ to $x-t$:** Area under $v-t$ graph gives change in displacement. #### Example: Ball Thrown Upwards - **$x-t$:** Parabola opening downwards (goes up, slows, comes down, speeds up). Peak is max height. - **$v-t$:** Straight line with negative slope (starts positive, crosses zero at peak height, becomes negative). - **$a-t$:** Horizontal line below x-axis (constant negative acceleration due to gravity, $-g$).