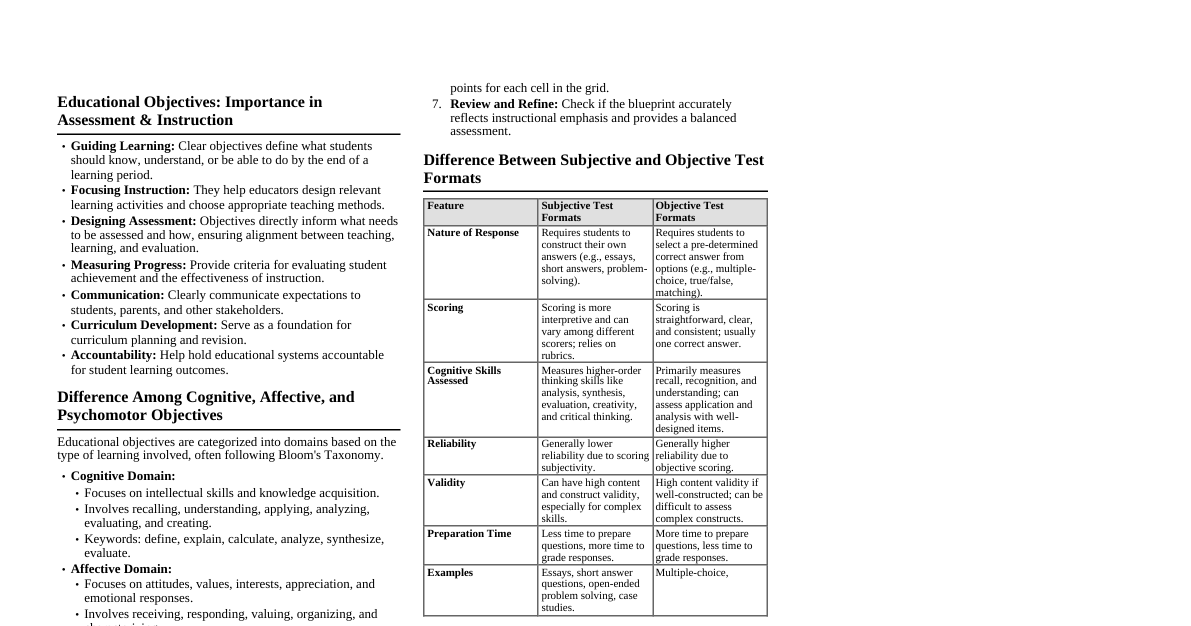
### SQL Basics - **What is SQL?** Standard language for managing relational databases. - **Key Concepts:** - **Database:** Organized collection of data. - **Table:** Collection of related data held in a structured format (rows & columns). - **Column (Field):** A set of data values of a particular type. - **Row (Record):** A single entry in a table. - **Primary Key:** Uniquely identifies each row in a table. - **Foreign Key:** Links two tables together. - **SQL Data Types:** - `INT`: Integer numbers. - `VARCHAR(size)`: Variable-length string. - `TEXT`: Large text data. - `DATE`: Date value. - `BOOLEAN`: True/False. - `DECIMAL(P,S)`: Exact numeric value. ### DDL Commands (Data Definition Language) - **Purpose:** Define and manage database structure. #### CREATE - `CREATE DATABASE database_name;` - `CREATE TABLE table_name (column1 datatype PRIMARY KEY, column2 datatype, ...);` #### ALTER - `ALTER TABLE table_name ADD column_name datatype;` - `ALTER TABLE table_name DROP COLUMN column_name;` - `ALTER TABLE table_name MODIFY COLUMN column_name new_datatype;` (Syntax varies by DB) #### DROP - `DROP DATABASE database_name;` - `DROP TABLE table_name;` #### TRUNCATE - `TRUNCATE TABLE table_name;` (Removes all rows, keeps table structure) ### DML Commands (Data Manipulation Language) - **Purpose:** Manage data within database objects. #### SELECT - `SELECT column1, column2 FROM table_name;` - `SELECT * FROM table_name;` (Select all columns) - `SELECT DISTINCT column_name FROM table_name;` (Unique values) - `SELECT column_name AS alias_name FROM table_name;` (Rename column) #### WHERE Clause (Filtering) - `SELECT * FROM table_name WHERE condition;` - **Operators:** `=`, `!=`, `>`, ` =`, ` ### Advanced SQL #### Joins - **INNER JOIN:** Returns rows when there is a match in both tables. `SELECT * FROM Orders INNER JOIN Customers ON Orders.CustomerID = Customers.CustomerID;` - **LEFT JOIN (LEFT OUTER JOIN):** Returns all rows from the left table, and the matching rows from the right table. - **RIGHT JOIN (RIGHT OUTER JOIN):** Returns all rows from the right table, and the matching rows from the left table. - **FULL JOIN (FULL OUTER JOIN):** Returns rows when there is a match in one of the tables. #### Aggregate Functions - `COUNT(column)`: Number of rows. - `SUM(column)`: Sum of values. - `AVG(column)`: Average of values. - `MIN(column)`: Minimum value. - `MAX(column)`: Maximum value. #### GROUP BY - `SELECT column_name, COUNT(*) FROM table_name GROUP BY column_name;` - Used with aggregate functions to group result-set by one or more columns. #### HAVING Clause - `SELECT column_name, COUNT(*) FROM table_name GROUP BY column_name HAVING COUNT(*) > 1;` - Filters groups based on aggregate conditions (like `WHERE` for `GROUP BY`). #### Subqueries (Nested Queries) - `SELECT column1 FROM table_name WHERE column2 IN (SELECT column3 FROM another_table WHERE condition);` - A query within another SQL query. #### UNION (Combining Result Sets) - `SELECT column1 FROM table1 UNION SELECT column1 FROM table2;` - Combines the result-set of two or more SELECT statements (removes duplicates). - `UNION ALL` includes duplicates. ### Important Notes - **Case Sensitivity:** Varies by database system (e.g., MySQL is case-insensitive for table names on Windows, sensitive on Unix). Keywords are usually case-insensitive. - **Semicolons:** Required to terminate statements in some systems (e.g., PostgreSQL, Oracle), optional in others (e.g., MySQL). Good practice to include. - **Comments:** - `-- This is a single-line comment` - `/* This is a multi-line comment */` - **Practice!** The best way to learn is by writing and experimenting with SQL queries.