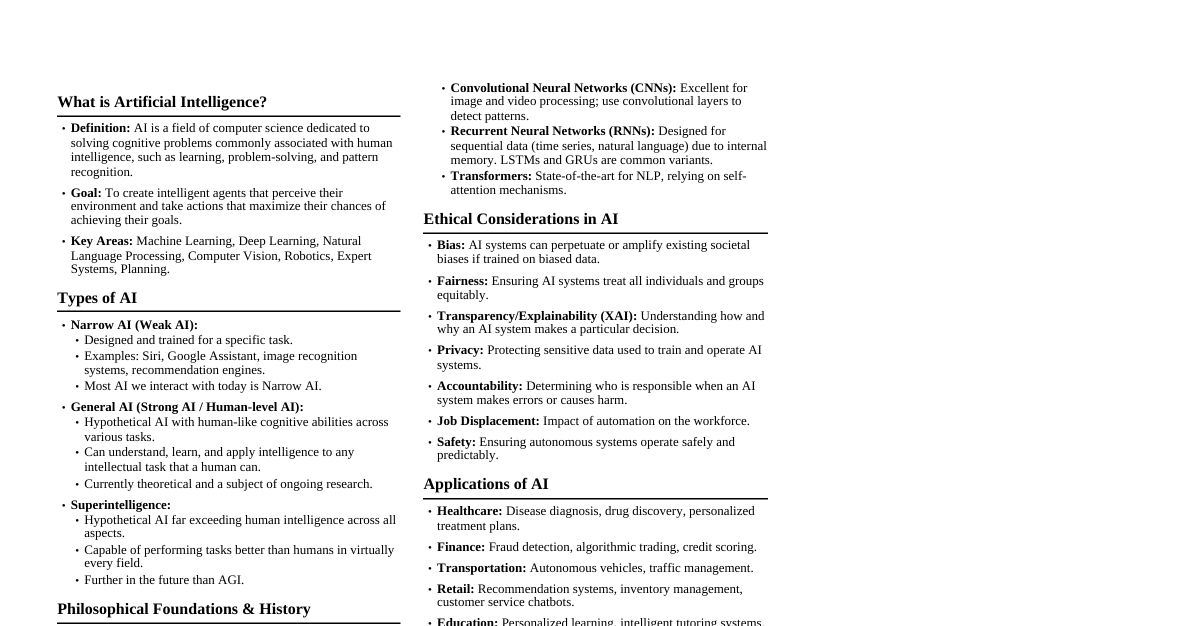
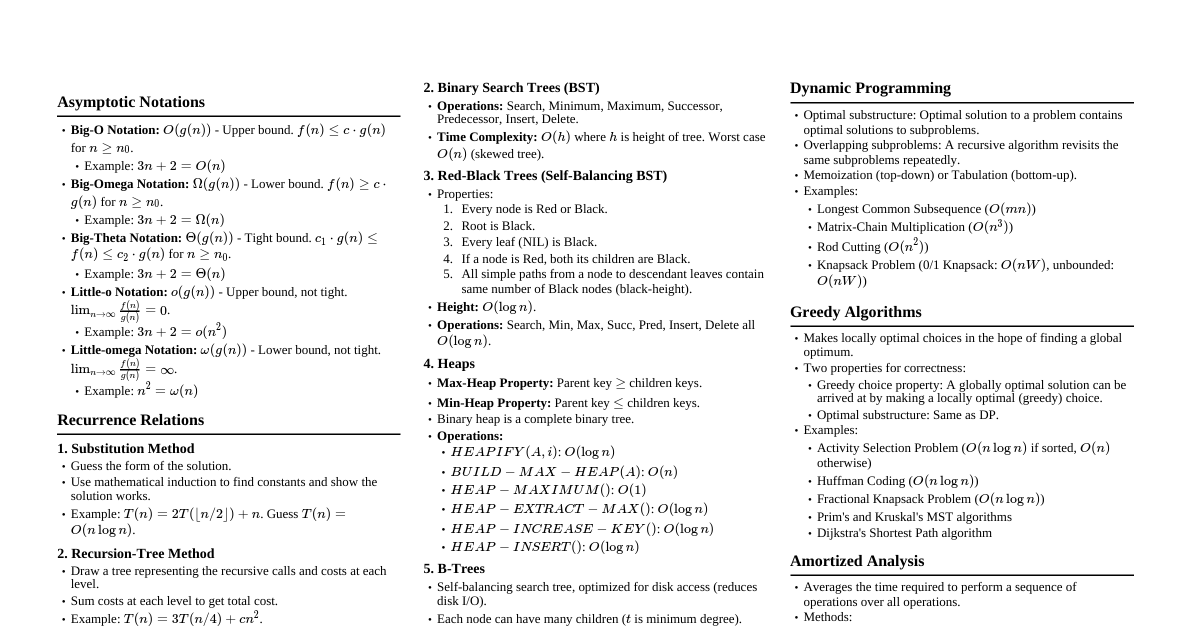
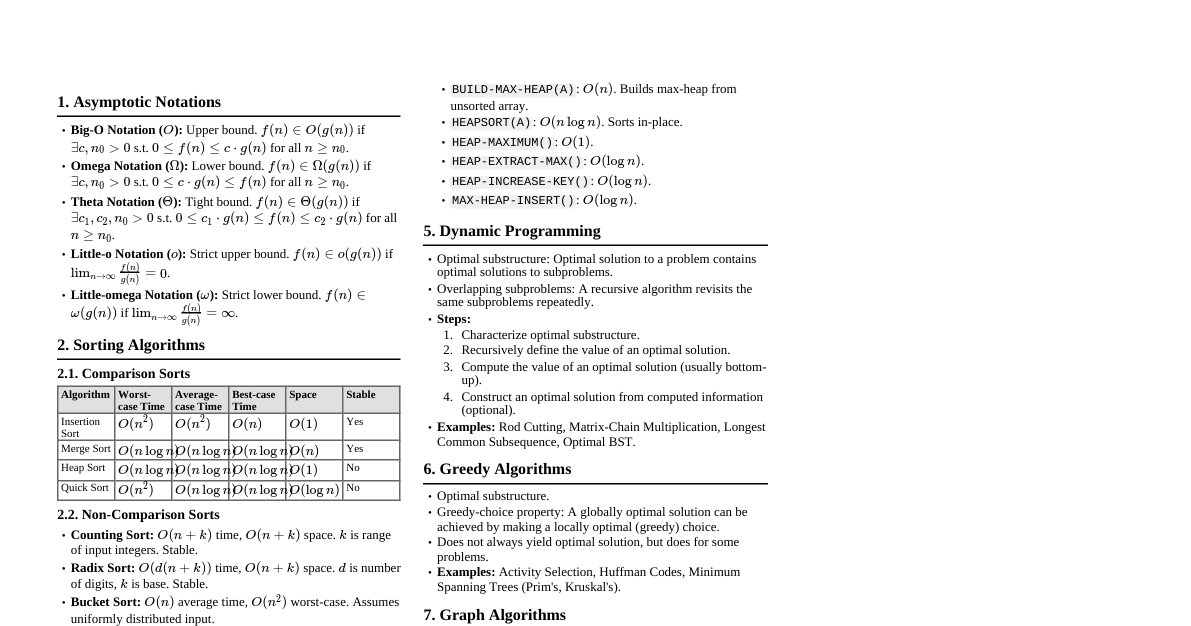
### AI Fundamentals #### Definition - **Artificial Intelligence (AI):** A machine's ability to think, learn, and act like humans. - AI enables computers to study data, analyze patterns, make decisions, and solve problems without human intervention. #### History of AI - **Early Ideas (Before 1950s):** Concepts of smart machines in science fiction. - **1950s - The Beginning of AI:** - 1950: Alan Turing introduces the Turing Test. - 1956: John McCarthy coins the term "Artificial Intelligence." - **1960s-1970s – Early Computer Programs:** AI solves small problems and plays simple games based on rules. - **1980s - Start of Machine Learning:** - Computers begin to learn from data. - Expert systems developed for medicine and banking. - **2000s - Internet and Big Data:** AI applications in mobiles, websites, search engines, speech tools, and chatbots emerge. - **2010s-Present – Modern AI:** AI becomes integrated into everyday life and various industries. #### AI Subfields - Knowledge Engineering - Machine Learning - Computer Vision - Natural Language Processing (NLP) - Robotics #### Industry Applications of AI - **Healthcare:** Disease diagnosis, treatment planning, drug discovery, surgery support, virtual health assistants, hospital management. - **Finance:** Fraud detection, customer support, loan/credit decisions, insurance policy work, personalized services, quick claim processing. - **Retail:** (Not detailed in provided text, but generally includes personalized shopping, inventory management). - **Agriculture:** Crop monitoring, soil/weather analysis, smart irrigation, pest/disease control, harvesting/sorting, market price prediction. - **Education:** Personalized learning, smart tutoring systems, automatic grading, virtual classrooms, language translation/support, career guidance. - **Transportation:** (Not detailed in provided text, but generally includes self-driving cars, traffic management). ### Challenges in AI AI helps in doing things faster and easier but also brings new challenges, primarily related to how AI behaves, makes decisions, and ensures fairness and safety. #### Ethics in AI - AI systems should adhere to moral values and human principles to ensure technology benefits society without causing harm. - **Example:** AI in hospitals should assist doctors, not replace medical decisions. #### Bias and Fairness in AI Systems - **Bias:** Showing preference or discrimination. If AI is trained on biased data, its output will be biased. - **Fairness:** Providing equal treatment and avoiding discrimination. - **Example:** An AI trained on male-dominated job application data might unfairly reject female candidates. #### Transparency in AI Systems - **Transparency:** Being open and clear about how AI systems work and make decisions. - Users should understand the reasoning behind AI's results and suggestions. - **Example:** A bank's AI rejecting a loan application must clearly state the reasons (e.g., low credit score). ### AI in Research #### AI in Experimentation - AI plays a crucial role in scientific experiments, making them more efficient. - **Data Collection & Analysis:** Collects and studies large datasets, identifies patterns and trends. - **Simulation:** Conducts experiments on computers before real-life trials. - **Method Suggestion:** Proposes better experimental methods or settings. - **Accuracy Improvement:** Reduces human errors, provides precise readings. - **Benefits:** Faster, cheaper, more reliable experiments. - **Examples:** - **Chemistry & Physics:** Predicts material reactions. - **Medicine:** Tests new drugs safely using computer models. - **Space Research:** Analyzes satellite data, predicts weather/planet conditions. #### AI in Multi-disciplinary Research - AI facilitates collaboration among different subjects to solve complex problems. - **Integration:** Brings together experts from various fields (science, technology, medicine, social sciences). - **Problem Solving:** Helps address complex issues requiring diverse perspectives. - **Teamwork:** Supports collaboration by analyzing data from all fields. - **Examples:** - **Medical Research:** Develops better tools for robotic surgeries. - **Agricultural Research:** Improves crop growth and irrigation systems. - **Educational Research:** Studies student learning and skill improvement. - **Environmental Research:** Predicts floods, droughts, and pollution. - AI acts as a bridge, enabling data sharing and new knowledge discovery across disciplines. ### Generative AI #### Meaning of Generative AI - AI that generates new content (text, images, videos, music, code) by learning from existing data. #### Uses of Generative AI - **Education:** Helps students/teachers prepare notes, essays, study materials. - **Programming:** Assists in writing and correcting code. - **Research:** Creates summaries and reports. - **Professional Tasks:** Prepares presentations and documents. - **Overall:** Makes work faster, easier, and more creative. #### Popular Generative AI Tools - **ChatGPT (by OpenAI):** - Advanced AI chatbot for writing essays, answering questions, solving problems. - Supports students, teachers, and professionals in learning and writing. - **Example:** Prepares short notes and explanations for study topics. - **Hugging Face:** - Free, open platform for using AI models. - Translates text, summarizes passages, creates new content. - Supports teachers, researchers, developers in language and research. - **Example:** Helps researchers analyze large data and build AI projects. - **Gemini (by Google):** - Advanced AI tool to understand text, images, and voice. - Supports learners, teachers, and creators in problem-solving. - **Example:** Explains images and answers questions. - **Perplexity AI:** - Smart AI assistant acting as a search helper. - Finds correct and clear answers from trusted online sources. - **Example:** Summarizes long articles and collects facts. #### Benefits of Generative AI Tools - Saves time and reduces workload. - Improves creativity and idea generation. - Aids in education, research, and communication. - Provides accurate and easy-to-understand information. - Makes learning and working faster and smarter. ### Prompt Engineering #### Definition - Giving clear and simple instructions to AI to get the best answers or results. - Helps AI understand better and provide more accurate assistance. #### Benefits of Prompt Engineering - Helps AI give right and useful answers. - Saves time by getting quick results. - Makes AI easier to use for everyone. - Enables AI to perform various tasks (writing, drawing, problem-solving). - Allows control over the type of answers AI provides. #### Applications of Prompt Engineering ##### Education - Teachers and students use prompt engineering for easier learning. - Students ask AI for explanations and practice questions. - Teachers use AI for lesson plans and grading. - Clear prompts ensure consistent, good answers, saving time and improving understanding. ##### Business & Commerce - **Business:** Helps employees work faster (e.g., writing emails, preparing reports, customer support). - **Commerce:** Improves advertisements and marketing. - Business owners ask AI for product descriptions and marketing ideas. - AI analyzes customer feedback to understand buyer needs. - Simple instructions make AI creative and useful for sales. ### Creative Content Creation #### AI for Creative Writing - AI can generate stories, poems, or essays quickly with simple prompts. - Helps writers get new ideas. - Changes writing style or mood. - Fixes grammar and improves sentence clarity. - Creates speeches, dialogues, conversations. - Makes writing sound natural. #### AI for Creative Design - AI can draw pictures or art from descriptions. - Creates logos, posters, banners quickly. - Chooses colors, shapes, and styles for attractive designs. - Helps organize layouts for books, magazines, websites, advertisements. - Customizes designs to match branding or event themes. #### AI Scripts for Videos ##### Definition - Scripts generated by AI tools from a given topic, idea, or keywords, including dialogues and narration, used for video content. - Used by students, teachers, content creators, and professionals to save time and improve content quality. ##### Steps to Create AI Scripts 1. **Provide Topic/Keywords:** Input the video's subject. 2. **AI Generates Draft Script:** AI creates a draft with introduction, main points, and conclusion. 3. **Edit and Finalize:** Human users edit to add examples, dialogues, or emotions. 4. **Use in Video Production:** Final script used for recording, animations, or presentations. ##### Uses of AI Scripts - Educational videos (schools, colleges, online learning). - YouTube or social media content (advertisements, explainer videos, tutorials). - Professional-quality scripts. - Supporting teachers in online classes and presentations. ##### Advantages of AI Scripts - Saves time and effort. - Generates creative ideas and examples. - Makes content organized, clear, and professional. - Easy to edit and customize. - Reduces writer's block and simplifies video planning. ##### Limitations of AI Scripts - Lack emotions/personal touch, leading to mechanical output. - Can give general, repetitive, or false content. - Requires human review, editing, and creativity. - Cannot fully replace human judgment, experience, and storytelling. ##### Real-Life Examples of AI Tools for Scripts - **ChatGPT:** Writes detailed scripts based on topic input. - **Jasper AI:** Creates marketing or educational content scripts. - **Synthesia:** Generates AI video scripts with avatars and voiceover. - **Copy.ai:** Provides ready-to-use content for short or long videos.