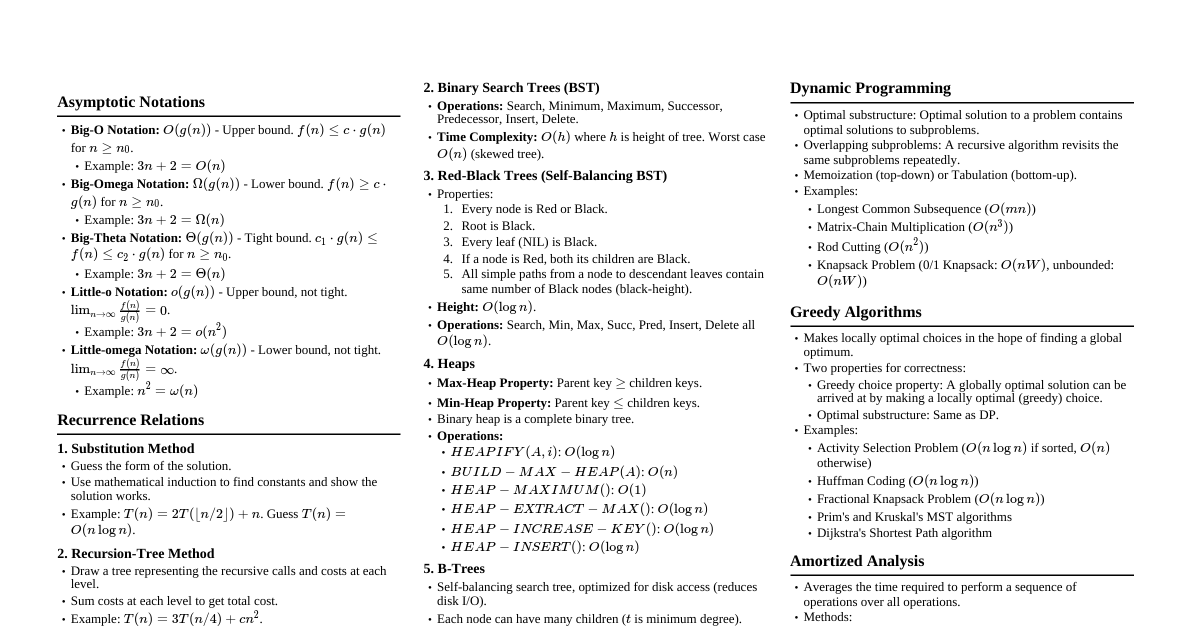
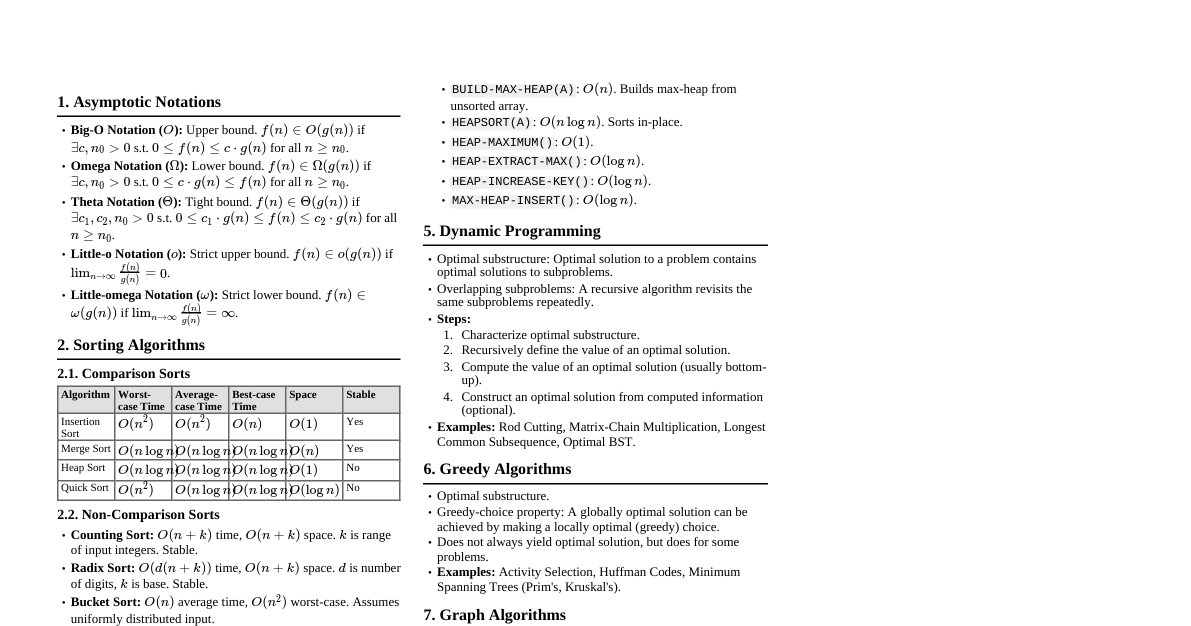
What is Artificial Intelligence? Definition: AI is a field of computer science dedicated to solving cognitive problems commonly associated with human intelligence, such as learning, problem-solving, and pattern recognition. Goal: To create intelligent agents that perceive their environment and take actions that maximize their chances of achieving their goals. Key Areas: Machine Learning, Deep Learning, Natural Language Processing, Computer Vision, Robotics, Expert Systems, Planning. Types of AI Narrow AI (Weak AI): Designed and trained for a specific task. Examples: Siri, Google Assistant, image recognition systems, recommendation engines. Most AI we interact with today is Narrow AI. General AI (Strong AI / Human-level AI): Hypothetical AI with human-like cognitive abilities across various tasks. Can understand, learn, and apply intelligence to any intellectual task that a human can. Currently theoretical and a subject of ongoing research. Superintelligence: Hypothetical AI far exceeding human intelligence across all aspects. Capable of performing tasks better than humans in virtually every field. Further in the future than AGI. Philosophical Foundations & History Turing Test (1950): Proposed by Alan Turing, a test of a machine's ability to exhibit intelligent behavior equivalent to, or indistinguishable from, that of a human. Dartmouth Workshop (1956): Often considered the birth of AI as a field. Coined the term "Artificial Intelligence." AI Winters: Periods of reduced funding and interest in AI research due to overly optimistic predictions and limited progress. Recent Revival: Driven by increased data availability, powerful computing (GPUs), and advancements in machine learning algorithms (especially deep learning). Key Concepts in AI Agent: Anything that can perceive its environment through sensors and act upon that environment through actuators. Rational Agent: An agent that acts to achieve the best possible outcome or, when there is uncertainty, the best expected outcome. Environment: The world in which an agent operates. Can be fully observable/partially observable, deterministic/stochastic, episodic/sequential, static/dynamic, discrete/continuous, single-agent/multi-agent. State Space Search: A process used in AI to find a path from an initial state to a goal state in a problem's state space. Machine Learning (ML) Overview Supervised Learning: Learns from labeled data (input-output pairs). Goal: Predict output for new inputs. Tasks: Classification (predict categories), Regression (predict continuous values). Algorithms: Linear Regression, Logistic Regression, Support Vector Machines (SVM), Decision Trees, Random Forests, Neural Networks. Unsupervised Learning: Learns from unlabeled data. Goal: Find hidden patterns or structures in data. Tasks: Clustering (grouping similar data points), Dimensionality Reduction (reducing number of features). Algorithms: K-Means, Hierarchical Clustering, PCA (Principal Component Analysis), Autoencoders. Reinforcement Learning (RL): Learns by interacting with an environment. Agent receives rewards for desired actions and penalties for undesired ones. Goal: Maximize cumulative reward over time. Components: Agent, Environment, State, Action, Reward, Policy, Value Function. Algorithms: Q-Learning, SARSA, Deep Q-Networks (DQN). Deep Learning (DL) Overview Subset of ML: Uses artificial neural networks with multiple layers ("deep" networks). Inspired by Brain: Loosely modeled after the structure and function of the human brain. Key Advantage: Can automatically learn hierarchical features from raw data. Types of Neural Networks: Feedforward Neural Networks (FNN/MLP): Basic structure, information flows in one direction. Convolutional Neural Networks (CNNs): Excellent for image and video processing; use convolutional layers to detect patterns. Recurrent Neural Networks (RNNs): Designed for sequential data (time series, natural language) due to internal memory. LSTMs and GRUs are common variants. Transformers: State-of-the-art for NLP, relying on self-attention mechanisms. Ethical Considerations in AI Bias: AI systems can perpetuate or amplify existing societal biases if trained on biased data. Fairness: Ensuring AI systems treat all individuals and groups equitably. Transparency/Explainability (XAI): Understanding how and why an AI system makes a particular decision. Privacy: Protecting sensitive data used to train and operate AI systems. Accountability: Determining who is responsible when an AI system makes errors or causes harm. Job Displacement: Impact of automation on the workforce. Safety: Ensuring autonomous systems operate safely and predictably. Applications of AI Healthcare: Disease diagnosis, drug discovery, personalized treatment plans. Finance: Fraud detection, algorithmic trading, credit scoring. Transportation: Autonomous vehicles, traffic management. Retail: Recommendation systems, inventory management, customer service chatbots. Education: Personalized learning, intelligent tutoring systems. Manufacturing: Predictive maintenance, quality control, robot automation. Environmental Science: Climate modeling, wildlife monitoring, disaster prediction.