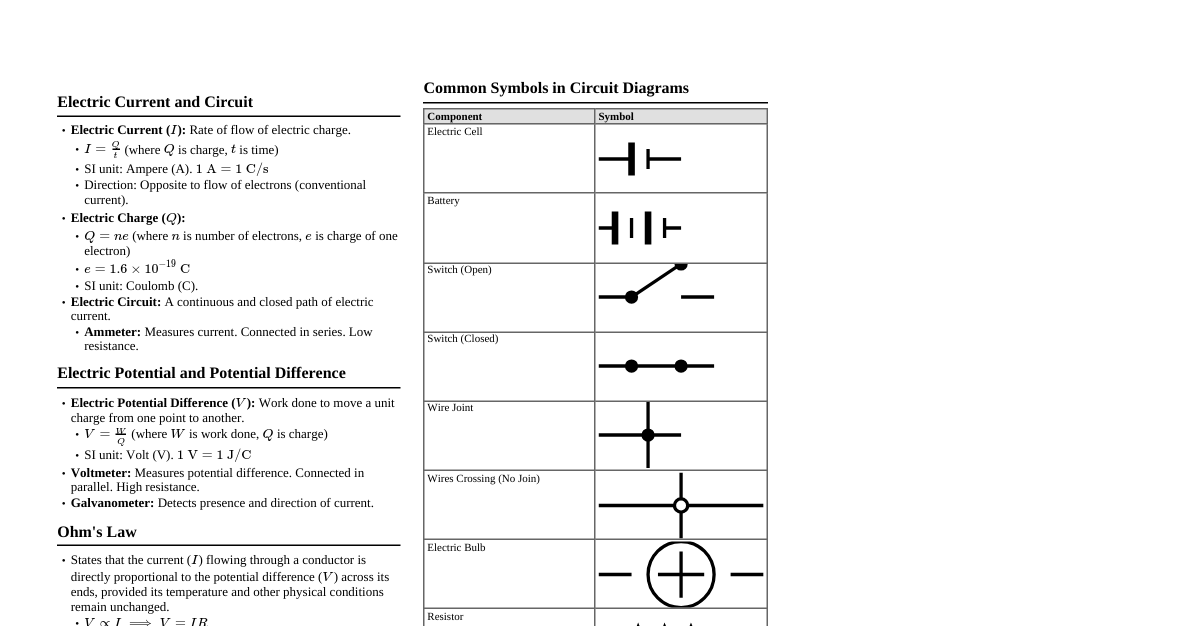
### Chemical Reactions & Equations - **Combination Reaction:** A + B → AB (e.g., C + O$_2$ → CO$_2$) - **Decomposition Reaction:** AB → A + B (e.g., CaCO$_3$ → CaO + CO$_2$) - **Displacement Reaction:** A + BC → AC + B (More reactive displaces less reactive) - **Double Displacement Reaction:** AB + CD → AD + CB (Exchange of ions) - **Redox Reaction:** Oxidation (gain O, lose H/e-), Reduction (lose O, gain H/e-) - **Corrosion:** Metals react with substances in atmosphere (e.g., rusting of iron) - **Rancidity:** Fats and oils oxidize, causing bad smell/taste. ### Acids, Bases & Salts - **Acids:** Sour taste, turn blue litmus red, pH 7. Release OH$^-$ ions. (e.g., NaOH, Ca(OH)$_2$) - **Neutralization:** Acid + Base → Salt + Water (e.g., HCl + NaOH → NaCl + H$_2$O) - **pH Scale:** 0 (highly acidic) to 14 (highly basic), 7 (neutral). - **Important Salts:** - Baking Soda: NaHCO$_3$ (Sodium Bicarbonate) - Washing Soda: Na$_2$CO$_3$.10H$_2$O (Sodium Carbonate Decahydrate) - Bleaching Powder: CaOCl$_2$ (Calcium Oxychloride) - Plaster of Paris (PoP): CaSO$_4$.$\frac{1}{2}$H$_2$O (Calcium Sulfate Hemihydrate) ### Metals & Non-metals - **Metals:** Lustrous, malleable, ductile, good conductors of heat/electricity. (e.g., Fe, Cu, Au) - React with oxygen to form basic oxides. - React with acids to produce H$_2$ gas (except noble metals). - **Non-metals:** Dull, brittle, poor conductors (except graphite). (e.g., C, O, S) - React with oxygen to form acidic or neutral oxides. - **Reactivity Series:** K > Na > Ca > Mg > Al > Zn > Fe > Pb > H > Cu > Hg > Ag > Au (Most to least reactive) - **Ionic Bonds:** Transfer of electrons (metal + non-metal). - **Covalent Bonds:** Sharing of electrons (non-metal + non-metal). ### Carbon & its Compounds - **Covalent Bonding:** Carbon forms covalent bonds by sharing electrons. - **Versatile Nature of Carbon:** - **Catenation:** Ability to form long chains, branches, and rings. - **Tetravalency:** Valency of 4, can bond with four other atoms. - **Hydrocarbons:** Compounds of Carbon and Hydrogen. - **Saturated:** Alkanes (C$_n$H$_{2n+2}$) - single bonds. - **Unsaturated:** Alkenes (C$_n$H$_{2n}$) - double bonds, Alkynes (C$_n$H$_{2n-2}$) - triple bonds. - **Functional Groups:** Atoms/groups that determine chemical properties. - Alcohol (-OH), Aldehyde (-CHO), Ketone (C=O), Carboxylic Acid (-COOH). - **Homologous Series:** Series of compounds with similar chemical properties and a general formula. - **Ethanol (C$_2$H$_5$OH):** Alcohol, used as fuel, solvent. - **Ethanoic Acid (CH$_3$COOH):** Carboxylic acid, main component of vinegar. ### Life Processes - **Nutrition:** - **Autotrophic:** Organisms make their own food (e.g., plants via Photosynthesis). - **Heterotrophic:** Organisms depend on others for food (e.g., animals). - **Photosynthesis:** 6CO$_2$ + 6H$_2$O $\xrightarrow{\text{Sunlight, Chlorophyll}}$ C$_6$H$_{12}$O$_6$ + 6O$_2$ - **Respiration:** - **Aerobic:** With oxygen, produces more energy (Glucose + O$_2$ → CO$_2$ + H$_2$O + Energy). - **Anaerobic:** Without oxygen, produces less energy (e.g., Ethanol in yeast, Lactic acid in muscles). - **Transportation:** - **Plants:** Xylem (water/minerals), Phloem (food). - **Humans:** Circulatory system (blood, heart, vessels). - **Excretion:** Removal of waste products. - **Humans:** Kidneys (filter blood), Lungs (CO$_2$), Skin (sweat). ### Control & Coordination - **Nervous System:** - **Brain:** Cerebrum (thought, memory), Cerebellum (balance), Medulla (involuntary actions). - **Spinal Cord:** Reflex actions. - **Neurons:** Structural and functional unit. - **Reflex Arc:** Stimulus → Receptor → Sensory neuron → Spinal cord → Motor neuron → Effector → Response. - **Endocrine System:** Glands secrete hormones. - **Thyroid:** Thyroxine (metabolism). - **Pancreas:** Insulin (blood sugar). - **Adrenal:** Adrenaline (fight or flight). - **Pituitary:** Growth hormone. - **Plant Hormones (Phytohormones):** - Auxins (growth), Gibberellins (stem growth), Cytokinins (cell division), Abscisic Acid (growth inhibition), Ethylene (fruit ripening). ### How do Organisms Reproduce? - **Asexual Reproduction:** Single parent. - Fission (Amoeba), Budding (Hydra), Fragmentation (Spirogyra), Spore Formation (Rhizopus), Vegetative Propagation (plants). - **Sexual Reproduction:** Two parents, gametes involved. - **Flowering Plants:** Pollination (transfer of pollen), Fertilization (fusion of male/female gametes), Seed formation. - **Humans:** - **Male:** Testes (sperm, testosterone), Vas deferens, Urethra. - **Female:** Ovaries (egg, estrogen, progesterone), Fallopian tubes, Uterus, Vagina. - **Menstrual Cycle:** Monthly cycle of egg release and uterine lining preparation. - **Contraception:** Methods to prevent pregnancy (e.g., condoms, pills, IUDs). ### Heredity & Evolution - **Heredity:** Transmission of traits from parents to offspring. - **Genetics:** Study of heredity. - **Genes:** Units of heredity, segments of DNA. - **Mendel's Laws:** - **Law of Dominance:** One trait masks another. - **Law of Segregation:** Alleles separate during gamete formation. - **Law of Independent Assortment:** Genes for different traits assort independently. - **Sex Determination:** In humans, XY (male), XX (female). Y chromosome determines maleness. - **Evolution:** Gradual change in living organisms over generations. - **Natural Selection:** Survival of the fittest. - **Speciation:** Formation of new species. - **Evidence of Evolution:** Fossils, Homologous/Analogous organs. ### Light: Reflection & Refraction - **Reflection:** Bouncing back of light. - **Laws:** Angle of incidence = Angle of reflection. Incident ray, reflected ray, normal lie in same plane. - **Mirrors:** Plane, Concave (converging), Convex (diverging). - **Mirror Formula:** $\frac{1}{f} = \frac{1}{v} + \frac{1}{u}$ (f=focal length, v=image dist, u=object dist) - **Magnification:** $m = -\frac{v}{u} = \frac{h'}{h}$ - **Refraction:** Bending of light as it passes from one medium to another. - **Laws (Snell's Law):** $\frac{\sin i}{\sin r} = \text{constant} = n$ (refractive index) - **Lenses:** Convex (converging), Concave (diverging). - **Lens Formula:** $\frac{1}{f} = \frac{1}{v} - \frac{1}{u}$ - **Power of Lens:** $P = \frac{1}{f}$ (in dioptres, if f in meters) ### The Human Eye & Colourful World - **Human Eye Parts:** Cornea, Iris, Pupil, Lens, Retina, Optic Nerve. - **Accommodation:** Ability of eye lens to adjust focal length. - **Defects of Vision:** - **Myopia (Nearsightedness):** Distant objects blurred. Corrected by concave lens. - **Hypermetropia (Farsightedness):** Near objects blurred. Corrected by convex lens. - **Presbyopia:** Age-related, difficulty seeing near. Corrected by bifocal lens. - **Dispersion:** Splitting of white light into its constituent colours (VIBGYOR). - **Atmospheric Refraction:** Twinkling of stars, early sunrise/late sunset. - **Scattering of Light:** Blue sky, red sunset/sunrise. ### Electricity - **Electric Current (I):** Rate of flow of charge. $I = \frac{Q}{t}$ (Ampere, A) - **Electric Potential Difference (V):** Work done per unit charge. $V = \frac{W}{Q}$ (Volt, V) - **Ohm's Law:** $V = IR$ (R=Resistance, Ohm, $\Omega$) - **Resistance:** Obstruction to flow of current. - **Series:** $R_{eq} = R_1 + R_2 + ...$ - **Parallel:** $\frac{1}{R_{eq}} = \frac{1}{R_1} + \frac{1}{R_2} + ...$ - **Heating Effect of Current (Joule's Law):** $H = I^2Rt = VIt = \frac{V^2}{R}t$ - **Electric Power (P):** Rate of doing work. $P = VI = I^2R = \frac{V^2}{R}$ (Watt, W) - **Household Circuits:** Parallel connection, Earth wire for safety. ### Magnetic Effects of Electric Current - **Magnetic Field:** Region around a magnet where its force is experienced. - **Magnetic Field Lines:** Originate from N pole, end at S pole, never intersect. - **Right-Hand Thumb Rule:** Direction of magnetic field around a current-carrying conductor. - **Fleming's Left-Hand Rule:** For force on a current-carrying conductor in a magnetic field (Motor principle). - **Fleming's Right-Hand Rule:** For induced current in a conductor moving in a magnetic field (Generator principle). - **Electromagnetic Induction:** Production of induced current due to change in magnetic field. - **Electric Motor:** Converts electrical energy to mechanical energy. - **Electric Generator:** Converts mechanical energy to electrical energy. - **AC (Alternating Current):** Changes direction periodically. - **DC (Direct Current):** Flows in one direction. ### Sources of Energy - **Conventional Sources:** - **Fossil Fuels:** Coal, Petroleum, Natural Gas (non-renewable, cause pollution). - **Thermal Power Plants:** Use fossil fuels to heat water, produce steam. - **Hydro Power Plants:** Convert kinetic energy of flowing water to electricity. - **Non-Conventional Sources (Renewable):** - **Solar Energy:** Solar cells, solar water heaters. - **Wind Energy:** Windmills. - **Biomass Energy:** Biogas plants. - **Ocean Energy:** Tidal energy, Wave energy, Ocean Thermal Energy Conversion (OTEC). - **Geothermal Energy:** Heat from Earth's interior. - **Nuclear Energy:** Fission of heavy nuclei (clean but radioactive waste). - **Environmental Consequences:** Pollution, global warming. ### Our Environment - **Ecosystem:** Biotic (living) and Abiotic (non-living) components interacting. - **Food Chain:** Producer → Primary Consumer → Secondary Consumer → Tertiary Consumer. - **Food Web:** Interconnected food chains. - **Trophic Levels:** Steps in a food chain (producers, consumers). - **10% Law:** Only 10% of energy is transferred to the next trophic level. - **Biomagnification:** Increase in concentration of toxic substances at higher trophic levels. - **Ozone Layer Depletion:** Caused by CFCs, leads to increased UV radiation. - **Waste Management:** Reduce, Reuse, Recycle.