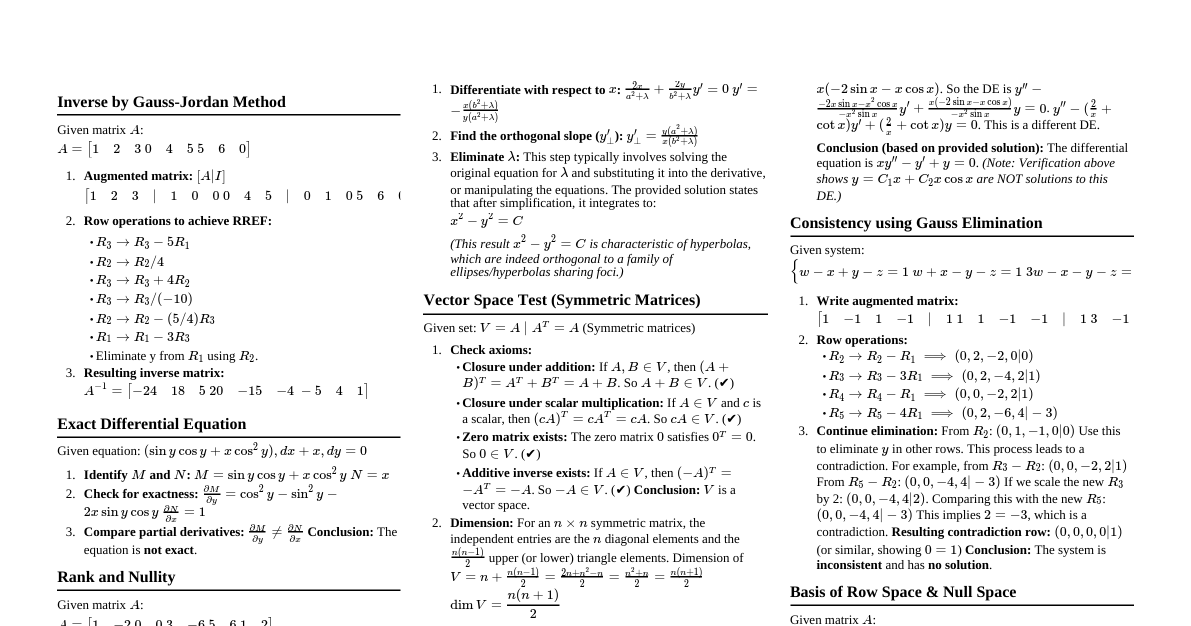
### Fundamental Shapes & Angles - **Point:** A location with no size. - **Line:** Extends infinitely in two directions. - **Line Segment:** Part of a line with two endpoints. - **Ray:** Part of a line with one endpoint, extending infinitely in one direction. - **Angle:** Formed by two rays sharing a common endpoint (vertex). - **Acute:** $0^\circ ### Parallel Lines & Transversals When a transversal line intersects two parallel lines: - **Alternate Interior Angles:** Equal (e.g., $\angle 3 = \angle 6$, $\angle 4 = \angle 5$) - **Alternate Exterior Angles:** Equal (e.g., $\angle 1 = \angle 8$, $\angle 2 = \angle 7$) - **Corresponding Angles:** Equal (e.g., $\angle 1 = \angle 5$, $\angle 2 = \angle 6$) - **Consecutive Interior Angles (Same-Side Interior):** Supplementary (sum to $180^\circ$) (e.g., $\angle 3 + \angle 5 = 180^\circ$, $\angle 4 + \angle 6 = 180^\circ$) ### Triangles - **Sum of Interior Angles:** Always $180^\circ$. - **Exterior Angle Theorem:** An exterior angle equals the sum of the two non-adjacent interior angles. - **Area:** $A = \frac{1}{2}bh$, where $b$ is the base and $h$ is the height perpendicular to the base. - **Perimeter:** Sum of all three side lengths. - **Triangle Inequality Theorem:** The sum of the lengths of any two sides of a triangle must be greater than the length of the third side ($a+b > c$). - **Types of Triangles:** - **Equilateral:** All 3 sides equal, all 3 angles $60^\circ$. - **Isosceles:** 2 sides equal, angles opposite those sides are equal. - **Scalene:** All 3 sides different lengths, all 3 angles different. - **Right:** Contains one $90^\circ$ angle. - **Pythagorean Theorem (for Right Triangles):** $a^2 + b^2 = c^2$, where $a$ and $b$ are legs, and $c$ is the hypotenuse. - **Pythagorean Triples:** Common integer side lengths (e.g., 3-4-5, 5-12-13, 8-15-17). - **Special Right Triangles:** - **$45^\circ$-$45^\circ$-$90^\circ$ (Isosceles Right Triangle):** Sides are in ratio $x : x : x\sqrt{2}$. - **$30^\circ$-$60^\circ$-$90^\circ$:** Sides are in ratio $x : x\sqrt{3} : 2x$. - **Similar Triangles:** - Corresponding angles are equal. - Corresponding sides are proportional. - If two angles of one triangle are congruent to two angles of another, the triangles are similar (AA Similarity). ### Polygons - **Definition:** Closed planar figure made of line segments. - **Quadrilaterals (4 Sides):** - **Sum of Interior Angles:** $360^\circ$. - **Parallelogram:** Opposite sides parallel and equal, opposite angles equal, diagonals bisect each other. - **Rectangle:** Parallelogram with 4 right angles. Diagonals are equal. Area = $lw$. - **Rhombus:** Parallelogram with 4 equal sides. Diagonals are perpendicular bisectors and bisect angles. Area = $\frac{1}{2}d_1 d_2$. - **Square:** Rectangle and Rhombus. Area = $s^2$. - **Trapezoid:** Exactly one pair of parallel sides (bases). Area = $\frac{1}{2}(b_1+b_2)h$. - **General Polygons:** - **Sum of Interior Angles:** $(n-2) \times 180^\circ$, where $n$ is the number of sides. - **Sum of Exterior Angles:** Always $360^\circ$. - **Regular Polygon:** All sides equal, all angles equal. - Each Interior Angle: $\frac{(n-2) \times 180^\circ}{n}$ ### Circles - **Radius ($r$):** Distance from center to any point on the circle. - **Diameter ($d$):** Distance across the circle through the center ($d=2r$). - **Circumference:** $C = 2\pi r = \pi d$ - **Area:** $A = \pi r^2$ - **Arc:** A portion of the circumference. - **Arc Length:** $L = \frac{\text{central angle}}{360^\circ} \times 2\pi r$ - **Sector:** A portion of the circle's area. - **Area of Sector:** $A = \frac{\text{central angle}}{360^\circ} \times \pi r^2$ - **Chords:** A line segment connecting two points on the circle. - **Tangent Line:** A line that touches the circle at exactly one point; perpendicular to the radius at that point. - **Inscribed Angle:** Angle formed by two chords with its vertex on the circle. Measure is half the measure of its intercepted arc. - **Central Angle:** Angle with its vertex at the center of the circle. Measure is equal to the measure of its intercepted arc. - **Equation of a Circle:** $(x-h)^2 + (y-k)^2 = r^2$, where $(h,k)$ is the center and $r$ is the radius. ### Coordinate Geometry - **Distance Formula:** Given two points $(x_1, y_1)$ and $(x_2, y_2)$, the distance $D = \sqrt{(x_2-x_1)^2 + (y_2-y_1)^2}$. - **Midpoint Formula:** Given two points $(x_1, y_1)$ and $(x_2, y_2)$, the midpoint $M = \left(\frac{x_1+x_2}{2}, \frac{y_1+y_2}{2}\right)$. - **Slope Formula:** Given two points $(x_1, y_1)$ and $(x_2, y_2)$, the slope $m = \frac{y_2-y_1}{x_2-x_1} = \frac{\text{rise}}{\text{run}}$. - **Equation of a Line:** - **Slope-Intercept Form:** $y = mx + b$, where $m$ is the slope and $b$ is the y-intercept. - **Point-Slope Form:** $y - y_1 = m(x - x_1)$, where $m$ is the slope and $(x_1, y_1)$ is a point on the line. - **Parallel Lines:** Have the same slope ($m_1 = m_2$). - **Perpendicular Lines:** Slopes are negative reciprocals ($m_1 \cdot m_2 = -1$). ### Solids (3D Shapes) - **Volume ($V$):** Amount of space a 3D object occupies. - **Surface Area ($SA$):** Total area of all faces/surfaces. - **Rectangular Prism:** - $V = lwh$ - $SA = 2lw + 2lh + 2wh$ - **Cube:** - $V = s^3$ - $SA = 6s^2$ - **Cylinder:** - $V = \pi r^2 h$ - $SA = 2\pi r^2 + 2\pi rh$ (two bases + lateral surface) - **Cone (Formulas provided on SAT reference sheet):** - $V = \frac{1}{3}\pi r^2 h$ - **Sphere (Formulas provided on SAT reference sheet):** - $V = \frac{4}{3}\pi r^3$ - $SA = 4\pi r^2$ - **Pyramid (Formulas provided on SAT reference sheet):** - $V = \frac{1}{3} \text{ (Base Area)} h$ ### Trigonometry Basics (SOH CAH TOA) - Applies to **Right Triangles** only. - **SOH:** $\sin(\theta) = \frac{\text{Opposite}}{\text{Hypotenuse}}$ - **CAH:** $\cos(\theta) = \frac{\text{Adjacent}}{\text{Hypotenuse}}$ - **TOA:** $\tan(\theta) = \frac{\text{Opposite}}{\text{Adjacent}}$ - **Identifying Sides:** - **Hypotenuse:** Longest side, opposite the $90^\circ$ angle. - **Opposite:** Side across from angle $\theta$. - **Adjacent:** Side next to angle $\theta$ (not the hypotenuse). ### Trigonometric Identities - **Complementary Angle Relationship:** - $\sin(x^\circ) = \cos(90^\circ - x^\circ)$ - $\cos(x^\circ) = \sin(90^\circ - x^\circ)$ - This means if $\sin(A) = \cos(B)$, then $A+B=90^\circ$. - **Tangent in terms of Sine and Cosine:** - $\tan(\theta) = \frac{\sin(\theta)}{\cos(\theta)}$ - **Pythagorean Identity (less common on SAT):** - $\sin^2(\theta) + \cos^2(\theta) = 1$ ### Radians - A unit for measuring angles, where $2\pi \text{ radians} = 360^\circ$. - $\pi \text{ radians} = 180^\circ$. - To convert degrees to radians: multiply by $\frac{\pi}{180^\circ}$. - To convert radians to degrees: multiply by $\frac{180^\circ}{\pi}$. - Arc Length with Radians: $L = r\theta$ (where $\theta$ is in radians). - Area of Sector with Radians: $A = \frac{1}{2}r^2\theta$ (where $\theta$ is in radians).