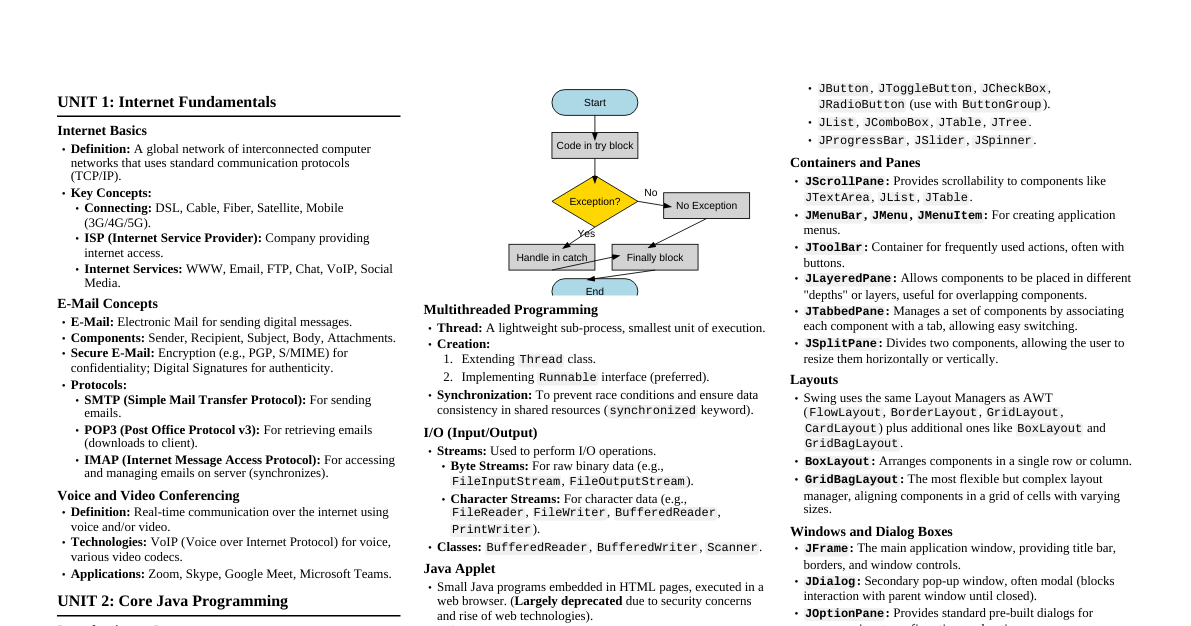
### Basic Electrical Concepts - **Charge (Q):** Fundamental property of matter, measured in Coulombs (C). - Electron charge: $-1.602 \times 10^{-19}$ C - **Current (I):** Rate of flow of charge, measured in Amperes (A). - $I = \frac{dQ}{dt}$ - Conventional current flows from positive to negative. - **Voltage (V) / Electromotive Force (EMF):** Electrical potential difference, measured in Volts (V). - Work done per unit charge: $V = \frac{dW}{dQ}$ - **Resistance (R):** Opposition to current flow, measured in Ohms ($\Omega$). - Depends on material, length, cross-sectional area, and temperature. - $R = \rho \frac{L}{A}$ (where $\rho$ is resistivity) - **Power (P):** Rate at which energy is transferred or consumed, measured in Watts (W). - $P = VI = I^2R = \frac{V^2}{R}$ - **Energy (E):** Capacity to do work, measured in Joules (J). - $E = Pt$ ### Ohm's Law - **Relationship:** $V = IR$ - Describes the relationship between voltage, current, and resistance in a DC circuit. ### Kirchhoff's Laws - **Kirchhoff's Current Law (KCL):** The algebraic sum of currents entering a node (junction) is zero. - $\sum I_{in} = \sum I_{out}$ - **Kirchhoff's Voltage Law (KVL):** The algebraic sum of voltages around any closed loop in a circuit is zero. - $\sum V = 0$ ### Series and Parallel Circuits #### Series Circuits - **Current:** Same through all components ($I_{total} = I_1 = I_2 = ...$) - **Voltage:** Divides across components ($V_{total} = V_1 + V_2 + ...$) - **Resistance:** Sum of individual resistances ($R_{total} = R_1 + R_2 + ...$) #### Parallel Circuits - **Current:** Divides among branches ($I_{total} = I_1 + I_2 + ...$) - **Voltage:** Same across all components ($V_{total} = V_1 = V_2 = ...$) - **Resistance:** Reciprocal of sum of reciprocals ($\frac{1}{R_{total}} = \frac{1}{R_1} + \frac{1}{R_2} + ...$) ### Capacitance - **Capacitor:** Stores electrical energy in an electric field. - **Definition:** $C = \frac{Q}{V}$ (Charge stored per unit voltage), measured in Farads (F). - **Energy Stored:** $E = \frac{1}{2}CV^2$ - **Series Capacitors:** $\frac{1}{C_{total}} = \frac{1}{C_1} + \frac{1}{C_2} + ...$ - **Parallel Capacitors:** $C_{total} = C_1 + C_2 + ...$ - **RC Time Constant ($\tau$):** Time taken for voltage across capacitor to reach 63.2% of final value during charging, or drop to 36.8% during discharging. - $\tau = RC$ ### Inductance - **Inductor:** Stores energy in a magnetic field. - **Definition:** $L = \frac{N\Phi}{I}$ (Flux linkage per unit current), measured in Henrys (H). - **Induced EMF:** $V_L = -L \frac{dI}{dt}$ (Lenz's Law) - **Energy Stored:** $E = \frac{1}{2}LI^2$ - **Series Inductors:** $L_{total} = L_1 + L_2 + ...$ (if no mutual inductance) - **Parallel Inductors:** $\frac{1}{L_{total}} = \frac{1}{L_1} + \frac{1}{L_2} + ...$ (if no mutual inductance) - **RL Time Constant ($\tau$):** Time taken for current through inductor to reach 63.2% of final value. - $\tau = \frac{L}{R}$ ### AC Circuits Fundamentals - **Alternating Current (AC):** Current that periodically reverses direction. - **Frequency (f):** Number of cycles per second, measured in Hertz (Hz). - **Period (T):** Time for one complete cycle, $T = \frac{1}{f}$. - **Peak Value ($V_P, I_P$):** Maximum value of voltage or current. - **RMS Value ($V_{RMS}, I_{RMS}$):** Effective value, equivalent to DC for power dissipation. - For sine wave: $V_{RMS} = \frac{V_P}{\sqrt{2}}$, $I_{RMS} = \frac{I_P}{\sqrt{2}}$ - **Phase Angle ($\phi$):** Angular difference between two AC waveforms (e.g., voltage and current). - **Reactance (X):** Opposition to AC current flow by capacitors ($X_C$) and inductors ($X_L$). - **Capacitive Reactance:** $X_C = \frac{1}{2\pi fC}$ - **Inductive Reactance:** $X_L = 2\pi fL$ - **Impedance (Z):** Total opposition to AC current, combining resistance and reactance. - $Z = \sqrt{R^2 + (X_L - X_C)^2}$ (for series RLC) - **Power Factor (PF):** $\cos\phi = \frac{R}{Z}$. Indicates how much of the apparent power is real power. - **Resonance:** Occurs when $X_L = X_C$. - Resonant Frequency: $f_r = \frac{1}{2\pi\sqrt{LC}}$ ### Transformers - **Principle:** Transfers electrical energy between circuits through electromagnetic induction. - **Turns Ratio:** $\frac{V_S}{V_P} = \frac{N_S}{N_P} = \frac{I_P}{I_S}$ - $N_P$: Primary turns, $N_S$: Secondary turns - $V_P, I_P$: Primary voltage/current - $V_S, I_S$: Secondary voltage/current - **Types:** Step-up (increases voltage), Step-down (decreases voltage). - **Losses:** Copper losses, Eddy current losses, Hysteresis losses, Flux leakage. ### Electrical Safety - **Hazards:** Electric shock, burns, fire, arc flash. - **Protective Devices:** Fuses, Circuit Breakers (MCB, ELCB/RCCB), Grounding/Earthing. - **Insulation:** Prevents current flow through unintended paths. - **Lockout/Tagout:** Procedures to ensure equipment is de-energized before maintenance.