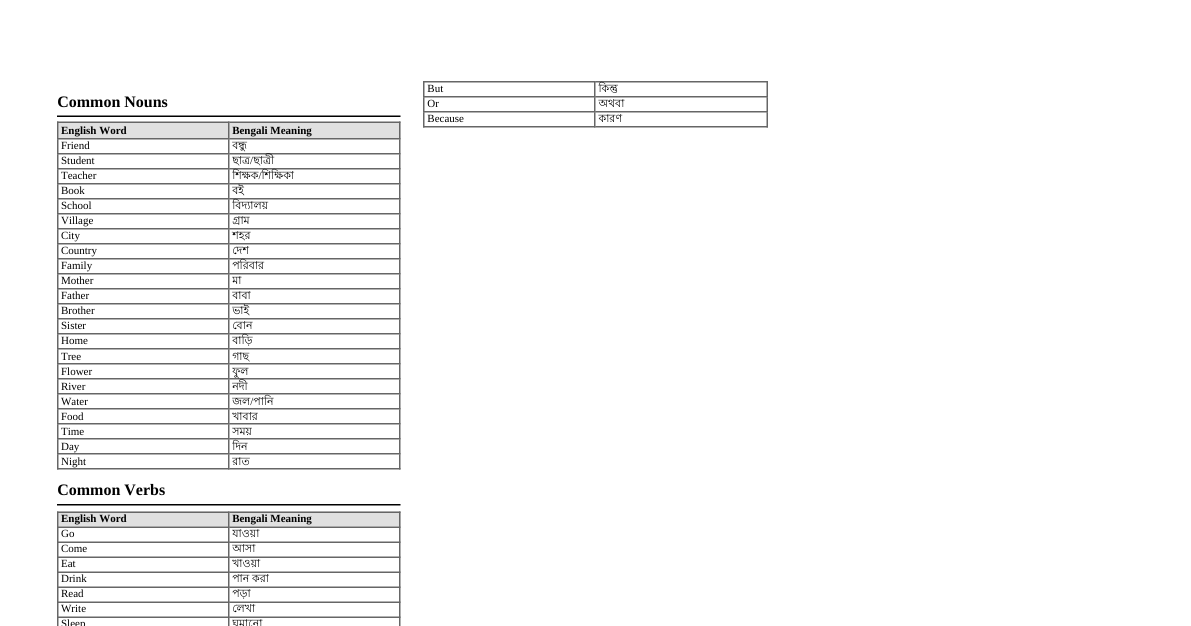
Verb (ক্রিয়া) Definition: A verb is a word that describes an action, state, or occurrence. (যে শব্দ দ্বারা কোনো কাজ করা, হওয়া বা ঘটা বোঝায় তাকে Verb বা ক্রিয়া বলে)। Example: go (যাওয়া), eat (খাওয়া), is (হয়), become (হওয়া), happen (ঘটা). Main Types of Verbs (ক্রিয়ার প্রধান প্রকারভেদ) Finite Verb (সমাপিকা ক্রিয়া): Completes the meaning of a sentence. (যে ক্রিয়া দ্বারা বাক্যের অর্থ সম্পূর্ণ হয়)। Example: He goes to school. (সে স্কুলে যায়।) Example: I am a student. (আমি একজন ছাত্র।) Non-Finite Verb (অসমাপিকা ক্রিয়া): Does not complete the meaning of a sentence; needs another verb. (যে ক্রিয়া দ্বারা বাক্যের অর্থ সম্পূর্ণ হয় না এবং অন্য একটি ক্রিয়ার সাহায্য নেয়)। Example: He wants to go . (সে যেতে চায়।) Example: Going there, he saw me. (সেখানে গিয়ে সে আমাকে দেখলো।) Types of Finite Verbs (সমাপিকা ক্রিয়ার প্রকারভেদ) 1. Principal/Main Verb (মূল ক্রিয়া) Performs the main action in a sentence. (বাক্যের প্রধান কাজ সম্পাদন করে)। Transitive Verb (সকর্মক ক্রিয়া): Requires an object to complete its meaning. (যে ক্রিয়ার কর্ম বা Object থাকে)। Example: He reads a book. (সে একটি বই পড়ে।) - 'a book' is the object. Intransitive Verb (অকর্মক ক্রিয়া): Does not require an object. (যে ক্রিয়ার কর্ম বা Object থাকে না)। Example: The baby sleeps . (বাচ্চাটি ঘুমায়।) Example: Birds fly . (পাখিরা ওড়ে।) Ditransitive Verb (দ্বিকর্মক ক্রিয়া): Takes two objects (direct and indirect). (যে ক্রিয়ার দুটি কর্ম থাকে)। Example: He gave me a pen. (সে আমাকে একটি কলম দিল।) - 'me' (indirect), 'a pen' (direct). Factitive Verb (পূরক ক্রিয়া): Takes an object and an object complement. (যে ক্রিয়া কর্ম ও কর্মের পূরক উভয়ই গ্রহণ করে)। Example: We made him captain . (আমরা তাকে অধিনায়ক বানিয়েছিলাম।) - 'captain' is the complement. Cognate Verb (সমধাতুজ ক্রিয়া): An intransitive verb followed by a cognate object (an object derived from the same root as the verb). (অকর্মক ক্রিয়া যার কর্ম একই ধাতু থেকে উৎপন্ন)। Example: He dreamt a strange dream. (সে একটি অদ্ভুত স্বপ্ন দেখেছিল।) Reflexive Verb (আত্মবাচক ক্রিয়া): The action performed by the subject reflects back on the subject itself, often with a reflexive pronoun. (যে ক্রিয়ার কাজ কর্তা নিজেই করে এবং তার ফল কর্তার উপরই ফিরে আসে)। Example: He killed himself. (সে নিজেকে হত্যা করলো।) 2. Auxiliary/Helping Verb (সাহায্যকারী ক্রিয়া) Helps the main verb to form various tenses, moods, and voices. (মূল ক্রিয়াকে বিভিন্ন Tense, Mood ও Voice গঠন করতে সাহায্য করে)। Primary Auxiliaries (প্রাথমিক সাহায্যকারী ক্রিয়া): To Be: am, is, are, was, were, be, being, been (হওয়া) To Have: have, has, had (থাকা/অধিকার করা) To Do: do, does, did (করা) Example: He is reading. (সে পড়ছে।) Example: They have finished. (তারা শেষ করেছে।) Example: Do you understand? (তুমি কি বোঝো?) Modal Auxiliaries (নিয়মসূচক সাহায্যকারী ক্রিয়া): Expresses ability, possibility, permission, obligation, etc. (সামর্থ্য, সম্ভাবনা, অনুমতি, বাধ্যবাধকতা ইত্যাদি প্রকাশ করে)। can, could, may, might, shall, should, will, would, must, ought to, used to, need, dare Example: I can swim. (আমি সাঁতার কাটতে পারি।) Example: You should study. (তোমার পড়া উচিত।) Types of Non-Finite Verbs (অসমাপিকা ক্রিয়ার প্রকারভেদ) These verbs do not change form according to the subject or tense and do not act as the main verb of a sentence. (এই ক্রিয়াগুলি কর্তা বা কাল অনুযায়ী রূপ পরিবর্তন করে না এবং বাক্যের প্রধান ক্রিয়া হিসাবে কাজ করে না)। Infinitive (ক্রিয়ার ভাবসূচক রূপ): 'To' + base form of the verb. (ক্রিয়ার মূল রূপের পূর্বে 'to' বসে)। Example: I want to eat . (আমি খেতে চাই।) Can also be 'bare infinitive' (without 'to') after certain verbs (e.g., make, let, help, see, hear). Example: Let me go . (আমাকে যেতে দাও।) Gerund (ক্রিয়া-বিশেষ্য): Verb + -ing, functions as a noun. (ক্রিয়ার সাথে '-ing' যুক্ত হয়ে বিশেষ্যের কাজ করে)। Example: Swimming is good for health. (সাঁতার কাটা স্বাস্থ্যের জন্য ভালো।) Example: I enjoy reading . (আমি পড়া উপভোগ করি।) Participle (ক্রিয়া-বিশেষণ): Functions as an adjective or part of a verb phrase. (ক্রিয়া ও বিশেষণের কাজ করে)। Present Participle: Verb + -ing (বর্তমান কৃদন্ত)। Example: A running train. (একটি চলন্ত ট্রেন।) Example: He is playing . (সে খেলছে।) Past Participle: Verb in its -ed/-en form (অতীত কৃদন্ত)। Example: A broken chair. (একটি ভাঙা চেয়ার।) Example: I have eaten . (আমি খেয়েছি।) Perfect Participle: Having + past participle (পূর্ণ কৃদন্ত)। Example: Having finished his work, he went home. (কাজ শেষ করে সে বাড়ি গেল।) Linking Verbs (সংযোজক ক্রিয়া) Connects the subject to a subject complement (a word or phrase that describes or identifies the subject). (যে ক্রিয়া কর্তা ও তার পূরক (complement) কে সংযুক্ত করে)। Most common: be (am, is, are, was, were), become, seem, appear, feel, look, smell, sound, taste . Example: She is happy. (সে সুখী।) - 'happy' describes 'she'. Example: He became a doctor. (সে একজন ডাক্তার হয়েছিল।) - 'a doctor' identifies 'he'. Phrasal Verbs (গুচ্ছ ক্রিয়া) A verb combined with a preposition or adverb (or both), which creates a new meaning. (একটি ক্রিয়া যখন একটি preposition বা adverb এর সাথে যুক্ত হয়ে নতুন অর্থ প্রকাশ করে)। Example: look up (খোঁজা), give up (ছেড়ে দেওয়া), take off (উড়ান দেওয়া/খুলে ফেলা). Example: He gave up smoking. (সে ধূমপান ছেড়ে দিল।)