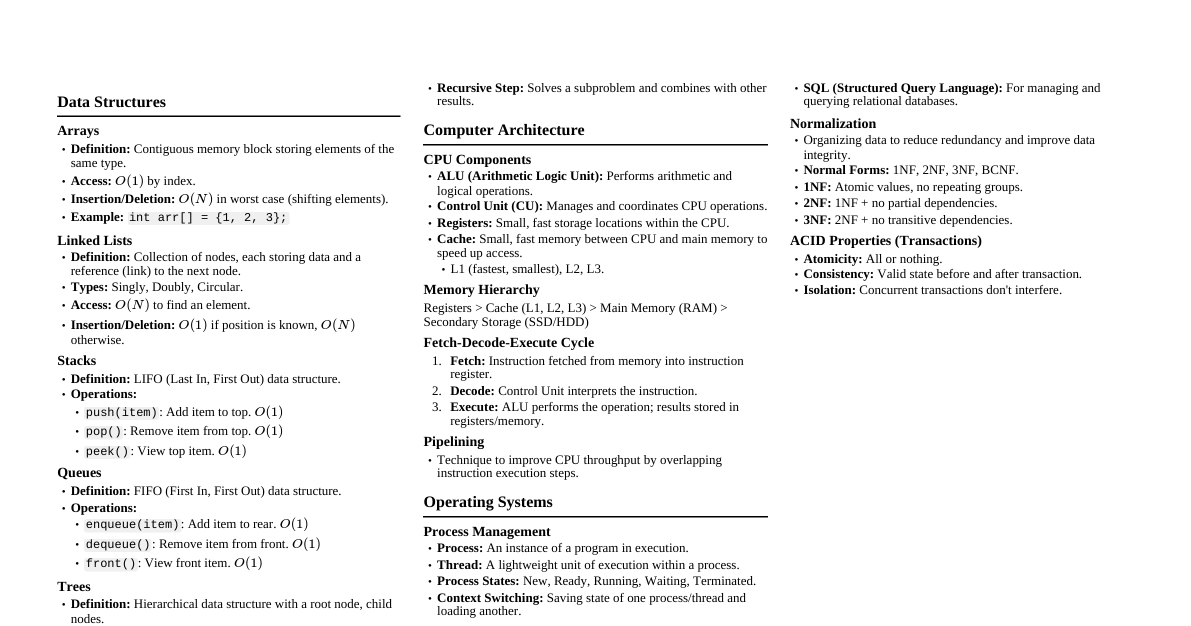
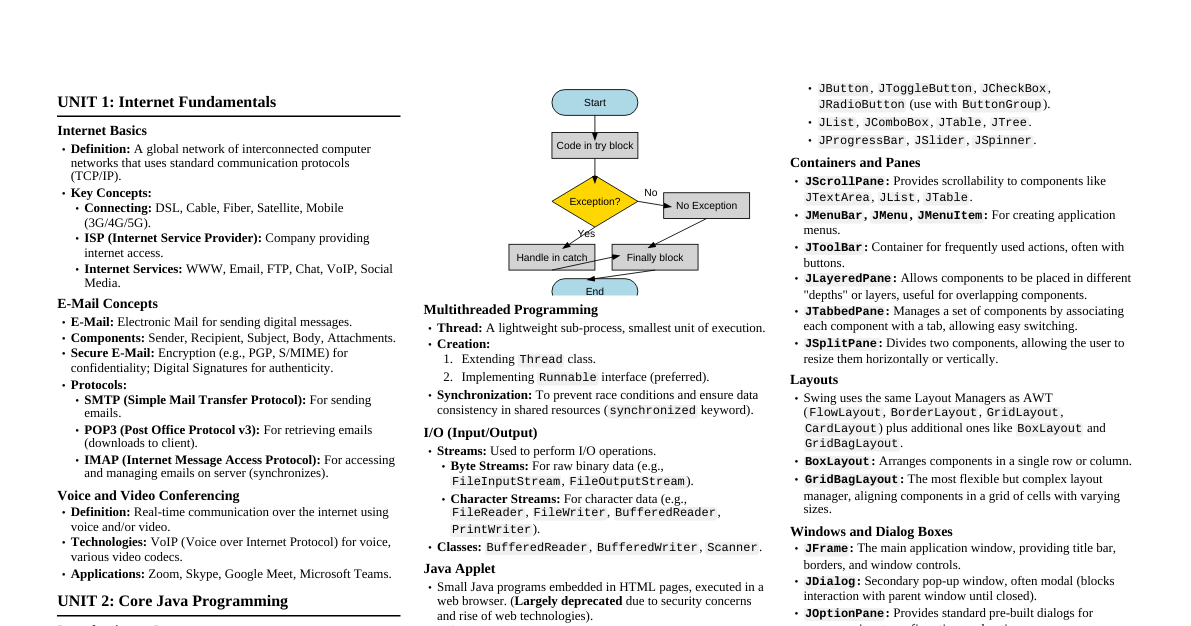
### Earth's Structure - **Crust:** Outermost layer, solid rock. - Continental crust: Thicker, less dense (granite). - Oceanic crust: Thinner, more dense (basalt). - **Mantle:** Thickest layer, semi-solid rock (silicates). Convection currents drive plate tectonics. - Lithosphere: Rigid outer part (crust + upper mantle). - Asthenosphere: Plastic layer below lithosphere. - **Core:** Innermost layers. - Outer core: Liquid iron and nickel, generates Earth's magnetic field. - Inner core: Solid iron and nickel, extreme pressure. ### Plate Tectonics - **Theory:** Earth's lithosphere is divided into large plates that move over the asthenosphere. - **Driving Force:** Convection currents in the mantle. - **Plate Boundaries:** - **Divergent:** Plates move apart (mid-ocean ridges, rift valleys). New crust forms. - **Convergent:** Plates move together. - Oceanic-continental: Oceanic plate subducts (volcanoes, trenches). - Oceanic-oceanic: One oceanic plate subducts (island arcs, trenches). - Continental-continental: Plates collide (mountain ranges). - **Transform:** Plates slide past each other (faults, earthquakes). ### Rock Cycle - **Igneous Rocks:** Formed from cooling and solidification of magma/lava. - Intrusive: Cools slowly underground (e.g., granite). - Extrusive: Cools quickly on surface (e.g., basalt). - **Sedimentary Rocks:** Formed from compaction and cementation of sediments. - Clastic: From fragments of other rocks (e.g., sandstone). - Chemical: From precipitation of minerals (e.g., limestone). - Organic: From accumulation of organic matter (e.g., coal). - **Metamorphic Rocks:** Formed when existing rocks are changed by heat, pressure, or chemical reactions. - Foliated: Minerals aligned in layers (e.g., slate, schist). - Non-foliated: No distinct layers (e.g., marble, quartzite). ### Earth's Atmosphere - **Composition:** ~78% Nitrogen, ~21% Oxygen, ~1% Argon, CO2, water vapor, etc. - **Layers (from surface up):** - **Troposphere:** Weather occurs, temperature decreases with altitude. - **Stratosphere:** Contains ozone layer (absorbs UV), temperature increases with altitude. - **Mesosphere:** Temperature decreases with altitude, meteors burn up. - **Thermosphere:** High temperatures, aurora occurs. - **Exosphere:** Outermost layer, merges with space. - **Greenhouse Effect:** Natural process where atmospheric gases trap heat, warming the Earth. ### Water Cycle (Hydrologic Cycle) - **Evaporation:** Liquid water to water vapor (from oceans, lakes, etc.). - **Transpiration:** Water vapor released by plants. - **Condensation:** Water vapor to liquid droplets (forms clouds). - **Precipitation:** Water falls back to Earth (rain, snow, hail). - **Runoff:** Water flows over land surface. - **Infiltration:** Water seeps into the ground. - **Groundwater:** Water stored beneath Earth's surface.