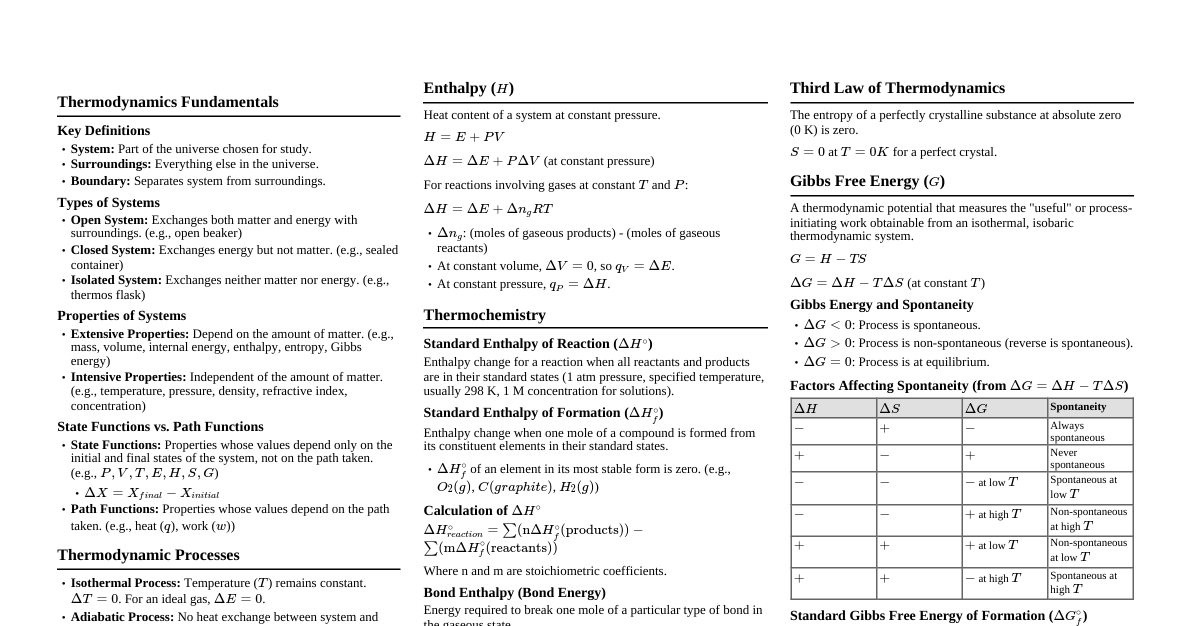
First Law of Thermodynamics The First Law of Thermodynamics is a statement of the conservation of energy. It states that energy cannot be created or destroyed, only transferred or changed from one form to another. Mathematical Formulation The most common form of the First Law is: $$ \Delta U = Q - W $$ $\Delta U$: Change in the internal energy of the system (J) $Q$: Net heat transferred to the system (J) $W$: Net work done by the system (J) Alternative forms for Work: If $W$ is work done on the system: $\Delta U = Q + W$ For infinitesimal changes: $dU = \delta Q - \delta W$ Internal Energy ($U$) Definition: The total energy contained within a thermodynamic system, including kinetic and potential energies of its molecules. State Function: Internal energy is a state function, meaning its change ($\Delta U$) depends only on the initial and final states of the system, not on the path taken. For an ideal gas, internal energy depends primarily on temperature: $U = U(T)$. Heat ($Q$) Definition: Energy transferred due to a temperature difference between the system and its surroundings. Sign Convention: $Q > 0$: Heat absorbed by the system (endothermic) $Q Not a State Function: Heat transfer depends on the path taken. Work ($W$) Definition: Energy transferred due to a force acting over a distance. In thermodynamics, it often refers to mechanical work (e.g., expansion/compression). Sign Convention (Work done BY the system): $W > 0$: Work done by the system on the surroundings (e.g., gas expansion) $W Pressure-Volume Work: For a quasi-static process: $W = \int P dV$ Not a State Function: Work depends on the path taken. Thermodynamic Processes The First Law applies to various processes: Process Type Description First Law ($\Delta U = Q - W$) Isothermal Constant temperature ($\Delta T = 0$) For ideal gas: $\Delta U = 0 \implies Q = W$ Adiabatic No heat exchange ($Q = 0$) $\Delta U = -W$ Isobaric Constant pressure ($\Delta P = 0$) $\Delta U = Q - P\Delta V$ Isochoric Constant volume ($\Delta V = 0$) $W = 0 \implies \Delta U = Q$ Cyclic Returns to initial state ($\Delta U = 0$) $Q = W$ Enthalpy ($H$) Definition: $H = U + PV$ Change in Enthalpy: $\Delta H = \Delta U + \Delta(PV)$ For isobaric processes (constant pressure): $\Delta H = Q_P$ (Heat at constant pressure) Useful for chemical reactions and phase changes at constant pressure. Specific Heat Capacities Constant Volume ($C_V$): $$ C_V = \left(\frac{\partial U}{\partial T}\right)_V $$ For isochoric process: $Q_V = \Delta U = n C_V \Delta T$ Constant Pressure ($C_P$): $$ C_P = \left(\frac{\partial H}{\partial T}\right)_P $$ For isobaric process: $Q_P = \Delta H = n C_P \Delta T$ Relation for Ideal Gas (Mayer's Relation): $C_P - C_V = R$ (where $R$ is the ideal gas constant) Perpetual Motion Machines of the First Kind The First Law implies that it is impossible to create a perpetual motion machine of the first kind, which would produce work without any energy input.