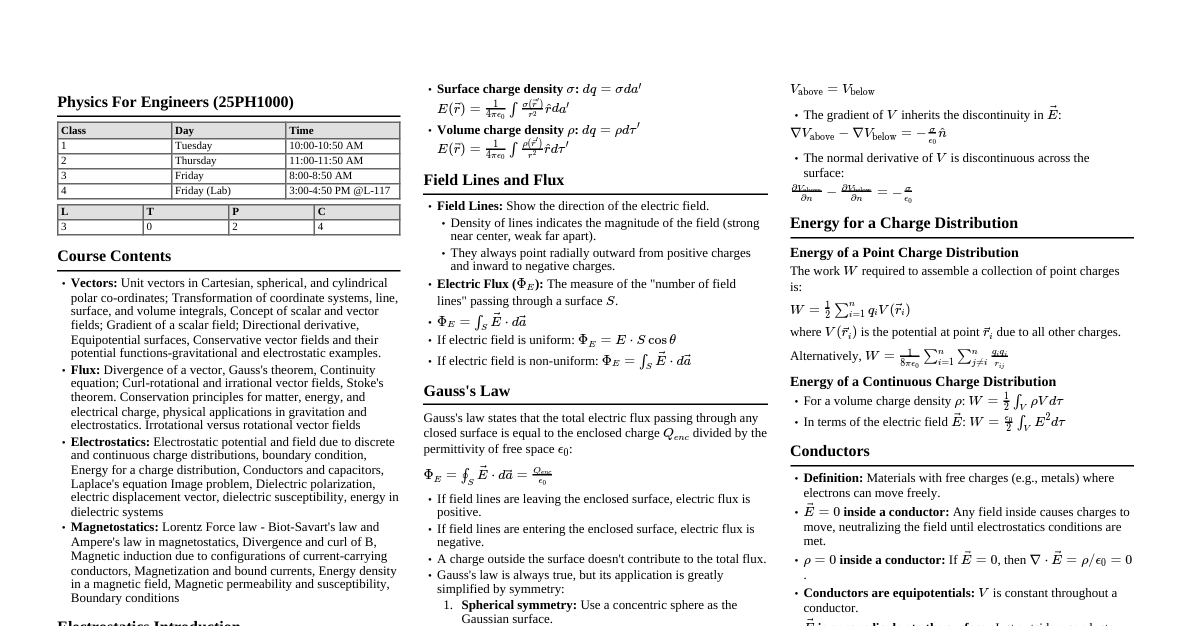
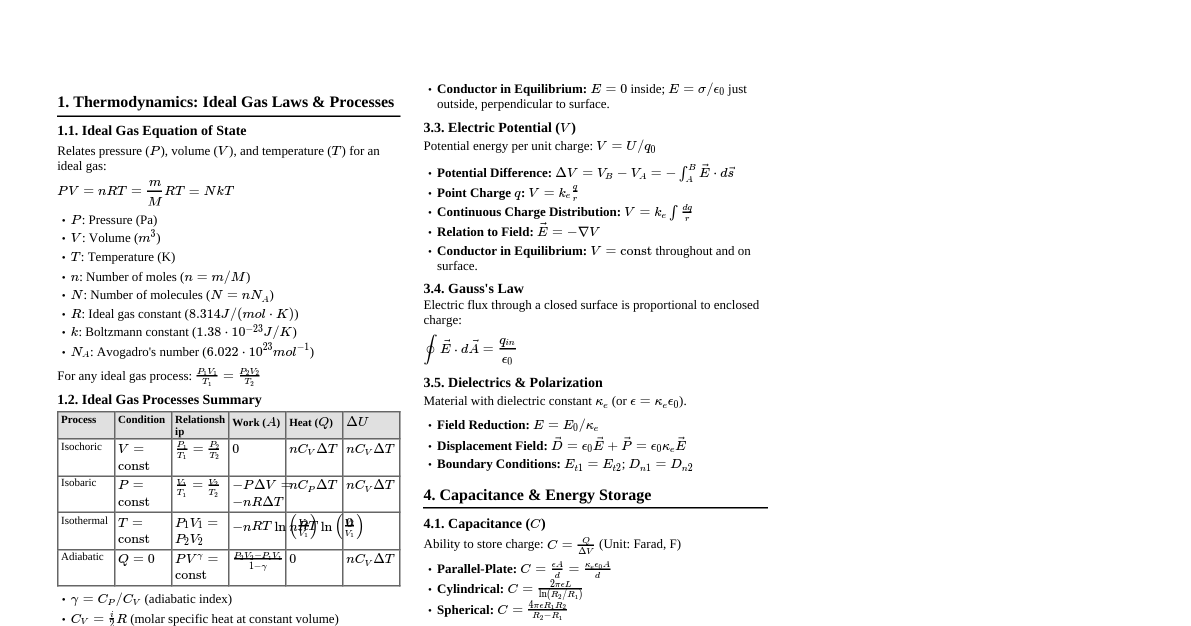
1. Physical Quantities and Measurement Scalar Quantity: Has magnitude only (e.g., mass, time, distance, speed). Vector Quantity: Has magnitude and direction (e.g., displacement, velocity, acceleration, force). SI Units: Length: meter (m) Mass: kilogram (kg) Time: second (s) Current: ampere (A) Temperature: Kelvin (K) Amount of substance: mole (mol) Luminous intensity: candela (cd) Prefixes: Prefix Symbol Factor Giga G $10^9$ Mega M $10^6$ Kilo k $10^3$ Centi c $10^{-2}$ Milli m $10^{-3}$ Micro $\mu$ $10^{-6}$ Nano n $10^{-9}$ 2. Motion Distance: Total path length covered (scalar). Displacement: Change in position (vector). Speed: Rate of change of distance, $v = \frac{d}{t}$ (scalar). Velocity: Rate of change of displacement, $\vec{v} = \frac{\Delta \vec{x}}{\Delta t}$ (vector). Acceleration: Rate of change of velocity, $\vec{a} = \frac{\Delta \vec{v}}{\Delta t}$ (vector). Equations of Motion (Constant Acceleration): $v = u + at$ $s = ut + \frac{1}{2}at^2$ $v^2 = u^2 + 2as$ Where $u$ = initial velocity, $v$ = final velocity, $a$ = acceleration, $t$ = time, $s$ = displacement. Free Fall: $a = g \approx 9.8 \text{ m/s}^2$ (downwards). 3. Force Newton's Laws of Motion: First Law (Inertia): An object remains at rest or in uniform motion unless acted upon by an external force. Second Law: Force equals mass times acceleration, $F = ma$. Third Law: For every action, there is an equal and opposite reaction. Weight: Force of gravity on an object, $W = mg$. Friction: Force opposing motion. Momentum: Product of mass and velocity, $p = mv$. Impulse: Change in momentum, $J = F\Delta t = \Delta p$. Conservation of Momentum: Total momentum of an isolated system remains constant. $m_1u_1 + m_2u_2 = m_1v_1 + m_2v_2$. 4. Work, Power and Energy Work Done: Force times distance in the direction of force, $W = Fd \cos \theta$. Unit: Joule (J). Energy: Capacity to do work. Kinetic Energy: $KE = \frac{1}{2}mv^2$. Gravitational Potential Energy: $PE_g = mgh$. Elastic Potential Energy: $PE_e = \frac{1}{2}kx^2$ (for a spring). Conservation of Energy: Energy cannot be created or destroyed, only transformed. Power: Rate of doing work or transferring energy, $P = \frac{W}{t} = Fv$. Unit: Watt (W). Efficiency: $\text{Efficiency} = \frac{\text{Useful Energy Output}}{\text{Total Energy Input}} \times 100\%$. 5. Pressure and States of Matter Pressure: Force per unit area, $P = \frac{F}{A}$. Unit: Pascal (Pa). Pressure in Liquids: $P = \rho gh$ (where $\rho$ is density, $g$ is acceleration due to gravity, $h$ is depth). Archimedes' Principle: Buoyant force equals the weight of the fluid displaced. Pascal's Principle: Pressure applied to an enclosed fluid is transmitted undiminished to every portion of the fluid and the walls of the containing vessel. States of Matter: Solid, Liquid, Gas, Plasma. Solid: Fixed shape and volume. Liquid: Fixed volume, takes shape of container. Gas: No fixed shape or volume. Kinetic Theory of Gases: Explains gas properties based on particle motion. 6. Effect of Heat on Substances Temperature: Measure of average kinetic energy of particles. Unit: Kelvin (K), Celsius ($^\circ$C). Heat: Transfer of thermal energy. Unit: Joule (J). Specific Heat Capacity (c): Energy required to raise 1 kg of substance by $1^\circ$C/K. $Q = mc\Delta T$. Latent Heat (L): Energy absorbed/released during phase change without temperature change. $Q = mL$. Specific Latent Heat of Fusion ($L_f$): Solid to liquid. Specific Latent Heat of Vaporization ($L_v$): Liquid to gas. Modes of Heat Transfer: Conduction: Through direct contact (solids). Convection: Through fluid movement (liquids, gases). Radiation: Through electromagnetic waves (vacuum, all states). 7. Waves and Sound Wave: Disturbance that transfers energy without transferring matter. Transverse Wave: Oscillations perpendicular to wave propagation (e.g., light). Longitudinal Wave: Oscillations parallel to wave propagation (e.g., sound). Wave Equation: $v = f\lambda$ (velocity = frequency $\times$ wavelength). Period (T): Time for one complete oscillation, $T = \frac{1}{f}$. Amplitude: Maximum displacement from equilibrium. Sound Waves: Longitudinal waves, require a medium. Speed of sound in air $\approx 330-340 \text{ m/s}$. Loudness relates to amplitude. Pitch relates to frequency. Echo: Reflected sound. 8. Reflection of Light Law of Reflection: Incident ray, reflected ray, and normal lie in the same plane. Angle of incidence ($i$) = Angle of reflection ($r$). Plane Mirror: Forms virtual, erect, laterally inverted image, same size as object, same distance behind mirror as object in front. Spherical Mirrors (Concave/Convex): Concave: Converging mirror. Can form real or virtual images. Convex: Diverging mirror. Always forms virtual, erect, diminished images. Mirror Formula: $\frac{1}{f} = \frac{1}{u} + \frac{1}{v}$ (where $f$ = focal length, $u$ = object distance, $v$ = image distance). Magnification (M): $M = \frac{h_i}{h_o} = -\frac{v}{u}$. Sign Convention: Real is positive, virtual is negative. Light from left to right. 9. Refraction of Light Refraction: Bending of light as it passes from one medium to another. Snell's Law: $n_1 \sin \theta_1 = n_2 \sin \theta_2$. Refractive Index (n): $n = \frac{\text{speed of light in vacuum}}{\text{speed of light in medium}} = \frac{c}{v}$. Also $n = \frac{\sin i}{\sin r}$. Total Internal Reflection (TIR): Occurs when light goes from denser to rarer medium at an angle greater than critical angle ($C = \sin^{-1}(\frac{n_2}{n_1})$). Lenses (Converging/Diverging): Converging (Convex): Forms real or virtual images. Diverging (Concave): Always forms virtual, erect, diminished images. Lens Formula: $\frac{1}{f} = \frac{1}{u} + \frac{1}{v}$. Power of a Lens (P): $P = \frac{1}{f}$ (in diopters, $f$ in meters). 10. Static Electricity Charge: Property of matter, positive or negative. Unit: Coulomb (C). Law of Conservation of Charge: Net charge in an isolated system remains constant. Coulomb's Law: Force between two point charges, $F = k \frac{q_1 q_2}{r^2}$. Electric Field (E): Force per unit charge, $E = \frac{F}{q}$. Unit: N/C or V/m. Electric Potential (V): Work done per unit charge to move a charge from infinity to a point. Unit: Volt (V). Capacitance (C): Ability to store charge, $C = \frac{Q}{V}$. Unit: Farad (F). Energy Stored in Capacitor: $E = \frac{1}{2}CV^2 = \frac{1}{2}QV = \frac{1}{2}\frac{Q^2}{C}$. 11. Current Electricity Electric Current (I): Rate of flow of charge, $I = \frac{\Delta Q}{\Delta t}$. Unit: Ampere (A). Voltage/Potential Difference (V): Energy per unit charge, $V = \frac{W}{Q}$. Unit: Volt (V). Resistance (R): Opposition to current flow. Unit: Ohm ($\Omega$). Ohm's Law: $V = IR$. Resistivity ($\rho$): Intrinsic property of material, $R = \rho \frac{L}{A}$. Resistors in Series: $R_{total} = R_1 + R_2 + ...$ Resistors in Parallel: $\frac{1}{R_{total}} = \frac{1}{R_1} + \frac{1}{R_2} + ...$ Electric Power: $P = VI = I^2R = \frac{V^2}{R}$. Unit: Watt (W). Electrical Energy: $E = Pt = VIt$. Unit: Joule (J) or kWh. Kirchhoff's Laws: Junction Rule: Sum of currents entering a junction equals sum of currents leaving. Loop Rule: Sum of potential differences around any closed loop is zero. 12. Magnetic Effect of Current Magnetic Field: Region where magnetic forces are exerted. Represented by magnetic field lines. Right-Hand Grip Rule: For current-carrying wire, thumb in current direction, fingers curl in magnetic field direction. Force on a Current-Carrying Wire in Magnetic Field: $F = BIL \sin \theta$. (B = magnetic field strength, I = current, L = length of wire). Force on a Moving Charge in Magnetic Field: $F = qvB \sin \theta$. Electromagnetic Induction (Faraday's Law): Induced EMF is proportional to the rate of change of magnetic flux, $\mathcal{E} = -N \frac{\Delta \Phi}{\Delta t}$. Lenz's Law: Induced current flows in a direction that opposes the change in magnetic flux that caused it. Transformers: Change AC voltage. $\frac{V_s}{V_p} = \frac{N_s}{N_p} = \frac{I_p}{I_s}$. 13. Modern Physics and Electronics Atomic Structure: Nucleus (protons, neutrons) and electrons. Radioactivity: Spontaneous decay of unstable nuclei. Alpha ($\alpha$): Helium nucleus ($_2^4\text{He}$). Beta ($\beta$): Electron or positron. Gamma ($\gamma$): High-energy electromagnetic radiation. Half-Life ($T_{1/2}$): Time for half of radioactive nuclei to decay. $N = N_0 (\frac{1}{2})^{n}$ where $n = \frac{t}{T_{1/2}}$. Mass-Energy Equivalence: $E = mc^2$. Photoelectric Effect: Emission of electrons when light shines on a material. $KE_{max} = hf - \Phi$. (h = Planck's constant, f = frequency, $\Phi$ = work function). Semiconductors: Materials with conductivity between conductors and insulators (e.g., Silicon, Germanium). Doping: Adding impurities to change conductivity (n-type, p-type). p-n Junction: Forms a diode, allows current in one direction. Logic Gates: Basic building blocks of digital circuits (AND, OR, NOT, NAND, NOR, XOR, XNOR). 14. Physics to Save Life Medical Imaging: X-rays: For bones, dense structures. Ultrasound: High-frequency sound waves for soft tissues, fetal imaging. MRI (Magnetic Resonance Imaging): Uses strong magnetic fields and radio waves for detailed soft tissue images. CT Scans (Computed Tomography): Multiple X-ray images for cross-sectional views. Radiation Therapy: Using controlled doses of radiation to destroy cancer cells. Lasers in Medicine: Precision surgery, ophthalmology, dermatology. Defibrillators: Use controlled electric shocks to restore normal heart rhythm. Pacemakers: Electronic devices to regulate heartbeats. Fiber Optics: Used in endoscopes for internal viewing. Biophysics: Application of physics principles to biological systems.