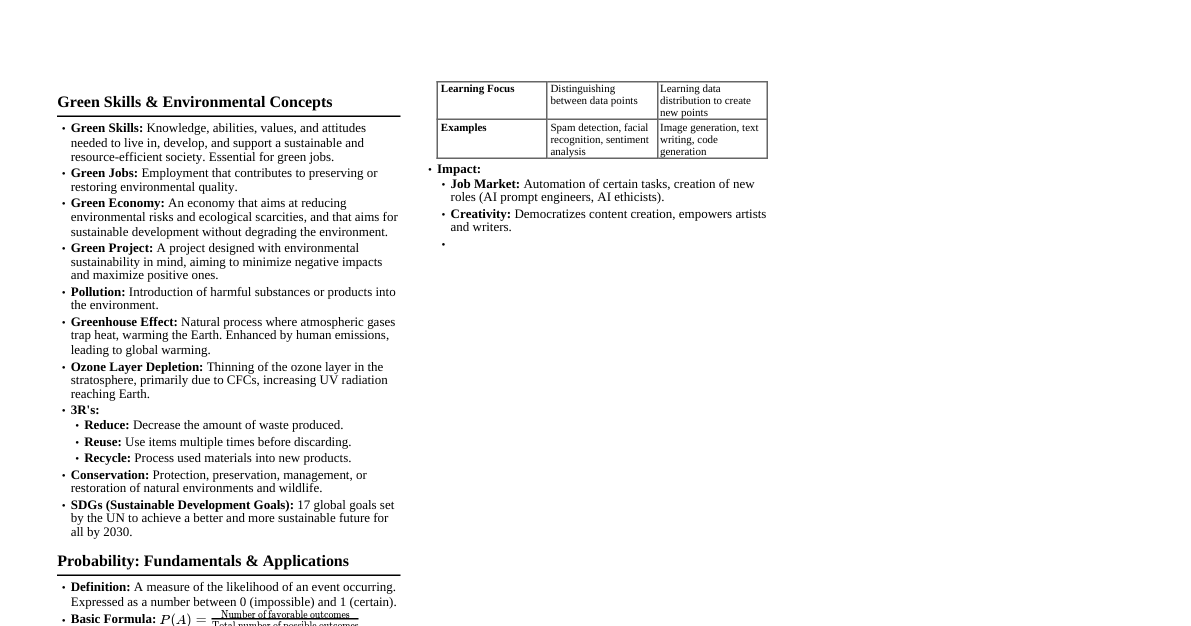
Concept of Sustainability: A Historical Review on UN Level 1. Early Roots & Conservation (Pre-1970s) Conservation Movement: Focus on protecting natural resources (forests, wildlife). Environmental Awareness: Growing concerns about pollution and resource depletion. Key Thinkers: Rachel Carson's "Silent Spring" (1962) highlights ecological damage. 2. Emergence of "Environment" on UN Agenda (1970s) 1972 Stockholm Conference (UN Conference on the Human Environment): First major international conference on environmental issues. Declaration: Links environmental protection with human well-being and development. Key Outcome: Establishment of the United Nations Environment Programme (UNEP). Shift from purely conservationist view to a broader environmental perspective. Concept of "Eco-development": Proposed by Maurice Strong, linking development with ecological considerations. 3. "Sustainable Development" Defined (1980s) 1980 IUCN World Conservation Strategy: Introduced the term "sustainable development." 1987 Brundtland Report (Our Common Future) by WCED: Landmark Definition: "Development that meets the needs of the present without compromising the ability of future generations to meet their own needs." Emphasized the interconnectedness of environmental protection, social equity, and economic development. Introduced the concept of intergenerational equity . Called for a new era of economic growth that is "socially and environmentally sustainable." 4. Operationalizing Sustainable Development (1990s) 1992 Rio Earth Summit (UN Conference on Environment and Development - UNCED): Key Outcomes: Rio Declaration: 27 principles of sustainable development. Agenda 21: A comprehensive action plan for sustainable development into the 21st century. Framework Convention on Climate Change (UNFCCC): Sets objective to stabilize greenhouse gas concentrations. Convention on Biological Diversity (CBD): Aims for conservation of biodiversity, sustainable use, and fair sharing of benefits. Statement on Forest Principles: Non-legally binding document on sustainable forest management. Emphasized global partnership and common but differentiated responsibilities. Commission on Sustainable Development (CSD): Established to monitor and review Agenda 21 implementation. 5. Global Partnerships & Implementation Challenges (2000s) 2000 Millennium Development Goals (MDGs): Eight goals focusing on poverty, hunger, disease, lack of adequate shelter, and environmental degradation by 2015. Though not explicitly "sustainable development," MDG 7 (Environmental Sustainability) was a direct link. 2002 World Summit on Sustainable Development (WSSD) in Johannesburg: Reviewed progress since Rio. Focused on implementation, particularly through partnerships (Type II outcomes). Emphasized water, sanitation, energy, health, agriculture, and biodiversity (WEHAB framework). 6. Future We Want & SDGs (2010s) 2012 Rio+20 (UN Conference on Sustainable Development): Reviewed 20 years since Rio '92. Key Outcomes: "The Future We Want" outcome document. Agreement to develop Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs). Emphasis on Green Economy in the context of sustainable development and poverty eradication. Strengthening UNEP and establishing a High-Level Political Forum on Sustainable Development (HLPF). 2015 Adoption of the 2030 Agenda for Sustainable Development & SDGs: 17 Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs): Universal call to action to end poverty, protect the planet, and ensure prosperity for all. 5 Ps: People, Planet, Prosperity, Peace, Partnership. Integrates economic, social, and environmental dimensions comprehensively. Universal applicability to all countries, developed and developing. Includes targets (169) and indicators for monitoring progress. 2015 Paris Agreement on Climate Change (under UNFCCC): A legally binding international treaty on climate change. Goal to limit global warming to well below 2, preferably to 1.5 degrees Celsius, compared to pre-industrial levels. Crucial for achieving SDG 13 (Climate Action). 7. Current & Future Directions (2020s onwards) Acceleration of SDG Implementation: Global efforts to achieve the 2030 Agenda. Addressing Global Crises: Climate change, biodiversity loss, pollution, pandemics (e.g., COVID-19) as interconnected challenges. Role of Technology & Innovation: Leveraging digital solutions for sustainability. Circular Economy Principles: Moving beyond linear "take-make-dispose" models. Just Transition: Ensuring social equity in the transition to sustainable economies. Multilateralism & International Cooperation: Renewed emphasis on global collaboration to tackle shared challenges. Integration: Further integration of environmental, social, and economic considerations in all policy sectors. Key Concepts & Interconnections Three Pillars of Sustainability: Environmental: Protecting natural resources, ecosystems, biodiversity, climate. Social: Equity, human rights, poverty eradication, health, education, community well-being. Economic: Sustainable growth, fair trade, resource efficiency, employment, stable economies. Intergenerational Equity: Ensuring future generations have the resources and opportunities we have today. Intragenerational Equity: Addressing inequalities within the current generation. Common but Differentiated Responsibilities (CBDR): Developed countries have a greater responsibility due to historical emissions and capacity. Planetary Boundaries: Concept defining safe operating space for humanity with respect to Earth's systems. Green Economy: Economic growth that is environmentally sustainable and socially inclusive. Resilience: The capacity of systems (social, ecological, economic) to absorb disturbance and reorganize while undergoing change. Evolution of UN's Approach to Sustainability Era Focus Key UN Events/Reports Core Idea Pre-1970s Conservation Protecting nature from human impact. 1970s Environment 1972 Stockholm Conference Human impact on environment; need for environmental management. 1980s Sustainable Development Defined 1987 Brundtland Report Meeting present needs without compromising future generations. 1990s Action & Frameworks 1992 Rio Earth Summit (Agenda 21, UNFCCC, CBD) Global action plans and conventions. 2000s Implementation & Goals 2000 MDGs, 2002 Johannesburg Summit Addressing poverty, specific targets, partnerships. 2010s Transformative Agenda 2012 Rio+20, 2015 SDGs, 2015 Paris Agreement Integrated, universal goals for people, planet, prosperity. 2020s+ Acceleration & Resilience SDG acceleration, climate action, circular economy Holistic systems thinking, just transition. Source, MINO Takashii Sensei