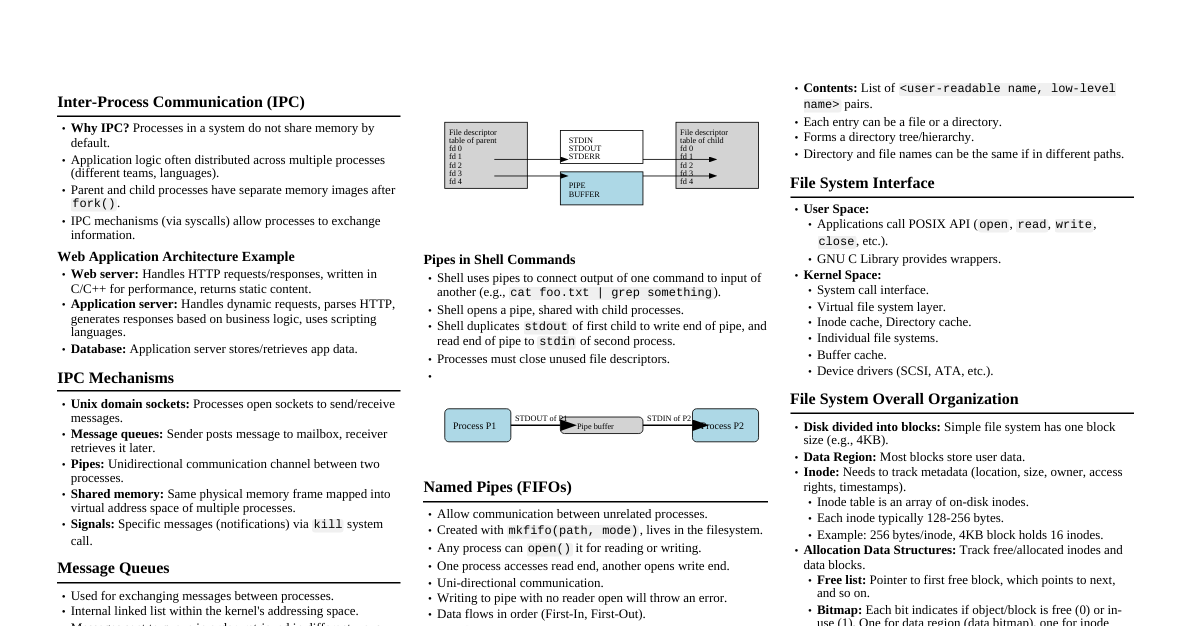
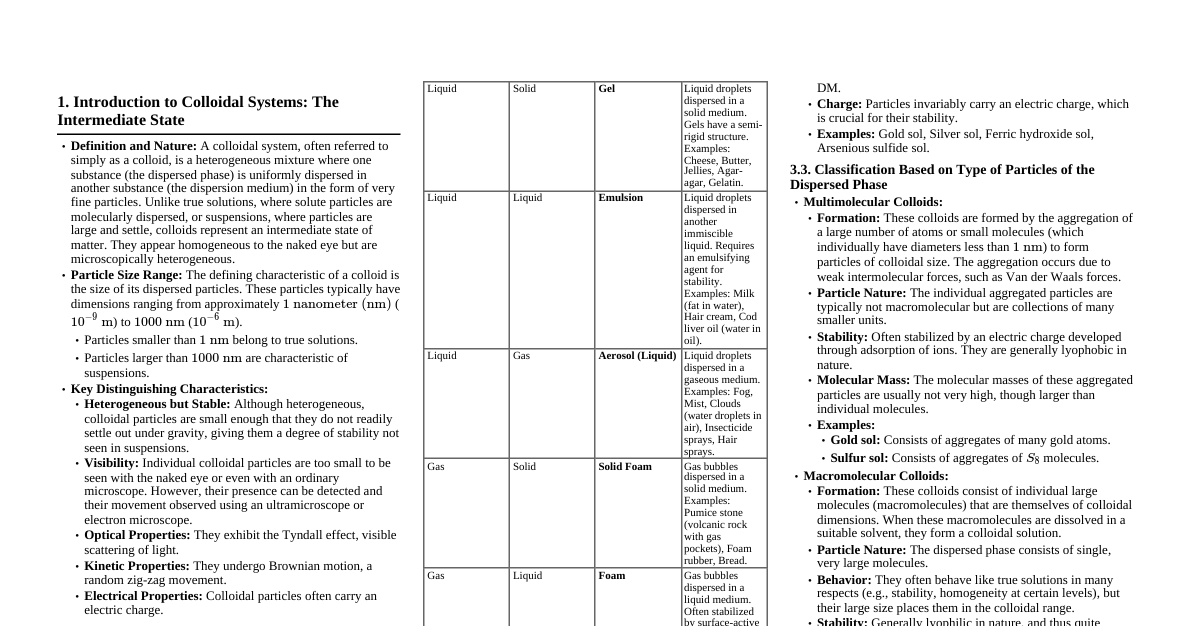
### Types of Numbers - **Natural Numbers** ($\mathbb{N}$): $\{1, 2, 3, ...\}$ (Counting numbers) - **Whole Numbers** ($\mathbb{W}$): $\{0, 1, 2, 3, ...\}$ (Natural numbers + zero) - **Integers** ($\mathbb{Z}$): $\{..., -2, -1, 0, 1, 2, ...\}$ (Whole numbers + negative counterparts) - **Rational Numbers** ($\mathbb{Q}$): Numbers that can be expressed as a fraction $p/q$, where $p, q \in \mathbb{Z}$ and $q \neq 0$. E.g., $1/2, -3/4, 5$. - **Irrational Numbers** ($\mathbb{P}$ or $\mathbb{I}$): Numbers that cannot be expressed as a simple fraction. Their decimal representation is non-terminating and non-repeating. E.g., $\pi, \sqrt{2}, e$. - **Real Numbers** ($\mathbb{R}$): All rational and irrational numbers. They can be represented on a number line. - **Complex Numbers** ($\mathbb{C}$): Numbers of the form $a + bi$, where $a, b \in \mathbb{R}$ and $i = \sqrt{-1}$ is the imaginary unit. #### Relationship between Number Sets $$\mathbb{N} \subset \mathbb{W} \subset \mathbb{Z} \subset \mathbb{Q} \subset \mathbb{R} \subset \mathbb{C}$$ ### Number System Visualization *Conceptual diagram showing sets of numbers nested within each other.* ### Decimal & Binary Conversion #### Decimal to Binary **Method:** Repeated division by 2, collect remainders in reverse order. **Example: Convert 13 (Decimal) to Binary** 1. $13 \div 2 = 6$ R $1$ 2. $6 \div 2 = 3$ R $0$ 3. $3 \div 2 = 1$ R $1$ 4. $1 \div 2 = 0$ R $1$ Result: $13_{10} = 1101_2$ #### Binary to Decimal **Method:** Sum of (digit * $2^{\text{position}}$), starting from right with position 0. **Example: Convert $1101_2$ to Decimal** $1 \cdot 2^3 + 1 \cdot 2^2 + 0 \cdot 2^1 + 1 \cdot 2^0$ $= 1 \cdot 8 + 1 \cdot 4 + 0 \cdot 2 + 1 \cdot 1$ $= 8 + 4 + 0 + 1 = 13_{10}$ ### Octal & Hexadecimal #### Octal (Base 8) - Digits: 0-7 - **Binary to Octal:** Group binary digits into sets of 3 from right. - $1101_2 \rightarrow 001 \ 101_2 \rightarrow 1_8 \ 5_8 \rightarrow 15_8$ - **Octal to Binary:** Convert each octal digit to 3 binary digits. - $15_8 \rightarrow 001 \ 101_2 \rightarrow 1101_2$ #### Hexadecimal (Base 16) - Digits: 0-9, A-F (A=10, B=11, C=12, D=13, E=14, F=15) - **Binary to Hexadecimal:** Group binary digits into sets of 4 from right. - $1101_2 \rightarrow 1101_2 \rightarrow D_{16}$ - **Hexadecimal to Binary:** Convert each hex digit to 4 binary digits. - $D_{16} \rightarrow 1101_2$ ### Common Number Bases Comparison | Base | Name | Digits/Symbols | Example ($10_{base}$) | | :--- | :---------- | :----------------------------------- | :-------------------- | | 2 | Binary | 0, 1 | $10_2 = 2_{10}$ | | 8 | Octal | 0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7 | $10_8 = 8_{10}$ | | 10 | Decimal | 0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9 | $10_{10} = 10_{10}$ | | 16 | Hexadecimal | 0-9, A, B, C, D, E, F | $10_{16} = 16_{10}$ |