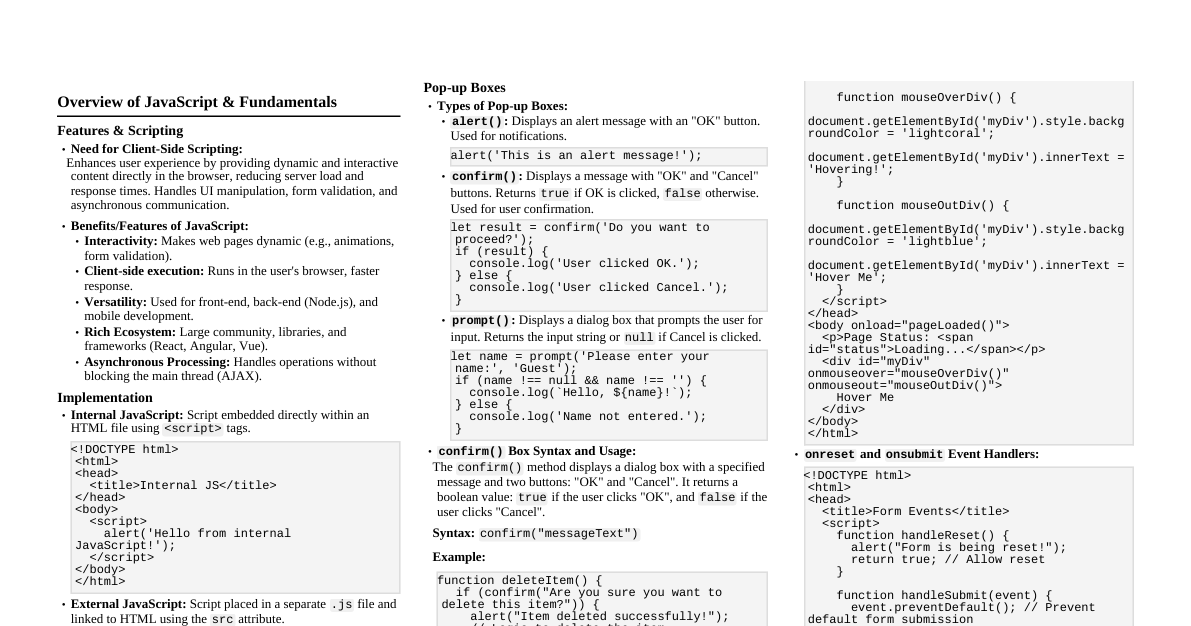
Chapter 12: Linking Resources 12.1 JavaScript Synchronous: <script src="path/to.js"></script> Standard practice is to place scripts just before the closing $</body>$ tag. Asynchronous: <script src="path/to.js" async></script> Loads script in parallel, interrupts HTML parsing once downloaded to parse script. Deferred: <script src="path/to.js" defer></script> Like async, but parsing occurs only after HTML is fully parsed. Guaranteed load order. NoScript: <noscript>JavaScript disabled</noscript> Content displayed if scripts are disabled or not supported. 12.2 External CSS Stylesheet <link rel="stylesheet" href="path/to.css" type="text/css"> Place in $<head>$ for faster loading. $type$ attribute is optional in HTML5. CDN Example: <link rel="stylesheet" href="https://maxcdn.bootstrapcdn.com/bootstrap/3.3.7/css/bootstrap.min.css" integrity="..." crossorigin="anonymous"> @import (less common): <style type="text/css">@import("path/to.css")</style> 12.3 Favicon <link rel="icon" type="image/png" href="/favicon.png"> <link rel="shortcut icon" type="image/x-icon" href="/favicon.ico"> $favicon.ico$ at root is often loaded automatically. 12.4 Alternative CSS <link rel="alternate stylesheet" href="path/to/style.css" title="yourTitle"> Allows user to select stylesheets in supported browsers. 12.5 Resource Hint: dns-prefetch, prefetch, prerender Preconnect: $<link rel="preconnect" href="URL">$ (Resolves DNS, TCP handshake, TLS) DNS-Prefetch: $<link rel="dns-prefetch" href="URL">$ (Resolves DNS for faster asset loading) Prefetch: $<link rel="prefetch" href="URL">$ (Prefetches resources for quicker loading) Prerender: $<link rel="prerender" href="URL">$ (Renders URL in background for instant display) Chapter 17: Input Control Elements Parameter Details type Identifies the type of input control to display. Values: hidden, text, tel, url, email, password, date, time, number, range, color, checkbox, radio, file, submit, image, reset, button . Defaults to text . name Indicates the name of the input. disabled Boolean value; input cannot be edited, not sent on form submission, cannot receive focus. checked Boolean; for radio / checkbox , indicates control is selected by default. multiple HTML5: Indicates multiple files or values can be passed (for file and email types). placeholder HTML5: Hint for user of what can be entered. autocomplete HTML5: Indicates whether value can be automatically completed by browser. readonly Boolean; input is not editable. Sent on submission, but won't receive focus. Ignored for hidden, range, color, checkbox, radio, file, button . required HTML5: Value must be present or element checked for form submission. alt Alternative text for images not displayed. autofocus Input element should get focus when page loads. value Specifies the value of input element. step Specifies legal number intervals (for number, range, date, datetime-local, month, time, week ). 17.1 Text Basic input type, default if no type specified. Single-line text field. Syntax: <input type="text"> or <input> Default width is 20 characters, adjustable with size attribute (e.g., $<input type="text" size="50">$). For multi-line text, use $<textarea>$. 17.2 Checkbox and Radio Buttons Checkbox: <input type="checkbox"> Independent choices. Radio Button: <input type="radio"> Mutually exclusive choices within a group (same name attribute). Attributes: value : String value associated with button on form submission (defaults to "on" if omitted). checked : Boolean, initial state (checked or unchecked). Accessibility (Labels): Wrap input: <label><input type="radio" name="color" value="#F00"> Red</label> Using for attribute: <input type="checkbox" name="color" value="#F00" id="red"><label for="red">Red</label> Button Groups: Use $<fieldset>$ and $<legend>$ for grouping and labeling radio buttons. 17.3 Input Validation Required: <input required> Field must be completed. Min/Max Length: <input minlength="3" maxlength="15"> Prevents user from typing more than maxlength characters. Specifying a Range: Use min and max for number/range inputs. Example: $<input type="number" name="marks" min="0" max="100">$. Match a Pattern: Use pattern attribute with a regular expression. Example: $<input pattern="\d*" title="Numbers only, please.">$. Accept File Type: <input type="file" accept="image/*,.rar"> Specifies allowed file types. 17.4 Color <input type="color" name="favcolor" value="#ff0000"> Creates a color picker. Falls back to text input if not supported. 17.5 Password <input type="password" name="password" placeholder="Password"> Single-line text field where input is hidden. 17.6 File <input type="file" name="fileSubmission"> Allows users to select files from local filesystem. Used with forms for uploading. Multiple files: Add multiple attribute: <input type="file" multiple> Accept files: Use accept attribute to specify types (e.g., image/png, image/jpeg ). 17.7 Button <input type="button" value="Button Text"> <button type="button">Button Text</button> Used for triggering actions without submitting forms. Attributes: name : Submitted with form data. type : submit (default), reset , button , menu . value : Initial value of button. 17.8 Submit <input type="submit" value="Submit"> Creates a button that submits the form. Can use $<button type="submit">...</button>$ for more styling flexibility. Extra Attributes: form, formaction, formenctype, formmethod, formnovalidate, formtarget . 17.9 Reset <input type="reset" value="Reset"> Resets all form inputs to their default state. Must be inside or attached to a $<form>$ element. 17.10 Hidden <input type="hidden" name="inputName" value="inputValue"> Not visible to user, but its value is sent on form submission. 17.11 Tel <input type="tel" value="+8400000000"> One-line text control for telephone numbers. 17.12 Email <input type="email" name="email"> Input field for email addresses, automatically validated by browser. 17.13 Number <input type="number" value="0" name="quantity"> Input for numbers. Allows symbols like 'e' for scientific notation. 17.14 Range <input type="range" min="" max="" step=""> Control for entering a number where exact value isn't important. Attributes: min (default 0), max (default 100), step (default 1). 17.15 Search <input type="search" name="googlesearch"> Textual search input, often displays a magnifier symbol. 17.16 Image <input type="image" src="img.png" alt="image_name" height="50px" width="50px"/> An image that acts as a submit button. Requires src and alt . 17.17 Week <input type="week" /> Control for entering a week-year number. Browser support dependent. 17.18 Url <input type="url" name="Homepage"> Input field for URL addresses, automatically validated. 17.19 DateTime-Local <input type="datetime-local" /> Date and time picker. Browser support dependent. 17.20 Month <input type="month" /> Control to pick a month. Browser support dependent. 17.21 Time <input type="time" /> Input for time, format defined in RFC 3339. 17.22 DateTime (Global) <input type=datetime name="meeting.start"> Control for setting global date and time with timezone info. 17.23 Date <input type="date" /> Date picker. Not supported in Firefox or IE. Chapter 20: Sectioning Elements 20.1 Nav Element Primarily for main navigation blocks (links to other pages or parts of the same page). Inline items: <nav><a href="...">Google</a><a href="...">Yahoo!</a></nav> Using list items: <nav role="navigation"><ul><li><a href="...">Google</a></li></ul></nav> Recommended for lists of items to enhance user experience. Adding role="navigation" is advised. Avoid unnecessary usage: $<footer>$ elements with links do not need an additional $<nav>$ element. 20.2 Article Element Contains self-contained content (articles, blog posts, comments, widgets) that could be distributed independently. Nested $<article>$ elements imply content of inner relates to outer. Example structure for a blog post with comments: <section><article><header>... <p>... <section><h2>Comments <article>... </section></article></section> 20.3 Main Element Contains the unique main content of a web page. Should be used at most once per page. Must not be a descendant of $<article>, <aside>, <footer>, <header>$, or $<nav>$ elements. Example: <body><header>... <main><h1>Individual Blog Post <p>... <article>... </main><footer>... </body> 20.4 Header Element Represents introductory content or navigational aids for its nearest ancestor sectioning content or root element. Not a sectioning content itself. Example: <header><p>Welcome to... <h1>Voidwars! </header> 20.5 Footer Element Contains the footer part of the page. Example: <footer><p>All rights reserved </footer> 20.6 Section Element Represents a generic section to thematically group content. Should have a heading element as a child. Can be nested within $<article>$ and vice-versa. Do not use for general styling; use $<div>$ for that purpose. Chapter 22: Label Element Attribute Description for References the ID of the target element. E.g., for="surname" . form HTML5 [Obsolete]: References the form containing the target element. Allows placing the label anywhere in the document. 22.1 About Label Used to reference a form action element, easing target/selection for input types like radio or checkbox. As wrapper: <label><input type="checkbox" name="Cats"> I like Cats!</label> Clicking text toggles input. As reference (using for ): <input id="cats" type="checkbox" name="Cats"><label for="cats">I like Cats!</label> for value must match target's ID. Note: Do not use more than one control element within a $<label>$ element. 22.2 Basic Use Simple form with labels: <form action="/login" method="POST"><label for="username">Username:</label><input id="username" type="text" name="username" /></form> Chapter 23: Output Element Attribute Description name String representing the name of an output. Used for collecting values on form submit. for Space-separated list of form element IDs whose values the output displays calculations for. form String representing the ID of the associated form. The $<output>$ element needs JavaScript to function. Input values from fields are text, so they must be converted to numbers (e.g., parseInt(), parseFloat(), Number() ) for calculations. Chapter 24: Void Elements HTML elements that do not have a closing tag and do not contain any content. HTML 4.01/XHTML 1.0 Strict void elements: area, base, br, col, hr, img, input, link, meta, param . HTML5 additions (non-deprecated): source . Example with void elements: <img src="..." /><br><hr><input type="number" placeholder="Enter your favorite number"> It is best practice to have a space before the slash for self-closing tags (e.g., $<img />$). Chapter 25: Media Elements Attribute Details width Sets the element's width in pixels. height Sets the element's height in pixels. <source> Defines resources of the audio or video files. track Defines the text track for media elements. controls Displays controls. autoplay Automatically starts playing the media. loop Plays the media in a repeated cycle. muted Plays the media without sound. poster Assigns an image to display until a video is loaded. 25.1 Audio <audio controls><source src="file.mp3" type="audio/mpeg">Your browser does not support the audio element.</audio> Embeds an audio file. 25.2 Video <video width="500" height="700" controls><source src="video.mp4" type="video/mp4">Your browser does not support the video tag.</video> Embeds a video file. 25.3 Using $<video>$ and $<audio>$ element to display audio/video content Use $src$ attribute or $<source>$ elements; browser chooses most suitable. Audio example with fallback: <audio src="audio.ogg">Your browser does not support the <code>audio element.</audio> Video example with fallback: <video src="videofile.webm">Sorry, your browser doesn't support embedded videos,but don't worry, you can <a href="videofile.webm">download it</a>and watch it with your favorite video player!</video> 25.4 Video header or background Video that autoplay, loops, and is muted, without controls. Example: <video width="1280" height="720" autoplay muted loop poster="video.jpg" id="videobg"><source src="video.mp4" type="video/mp4"></video> CSS fallback for $#videobg$: #videobg { background: url(video.jpg) no-repeat; background-size: cover; } Chapter 26: Progress Element Parameter Value max Total work required for the task. value Amount of work accomplished. position Current position of the $<progress>$ element. labels List of $<progress>$ element labels. 26.1 Progress Represents the progress of a task. Example: <progress value="22" max="100"></progress> (22% filled bar). 26.2 Changing the color of a progress bar Can be styled using the progress[value] selector. Chrome/Safari/Opera: Use -webkit-appearance: none; to reset, then style progress[value]::-webkit-progress-bar . Firefox: Use -moz-appearance: none; and border: none; to reset, then style it directly. IE 10+: Supports progress element but not background-color ; use color instead. 26.3 HTML Fallback For browsers not supporting $<progress>$, use a $<div>$ nested inside as a workaround. <progress max="100" value="20"><div class="progress-bar"><span style="width: 20%;">Progress: 20%</span></div></progress> Supported browsers ignore the nested $<div>$. Chapter 27: Selection Menu Controls 27.1 Select Menu Generates a drop-down menu for user options. Example: <select name=""><option value="1">One</option><option value="2">Two</option></select> Changing the Size: Use size attribute. size="0" or "1" for drop-down, greater than 1 for a box with scrollbar. Multi-option Selection: Add multiple attribute to allow selecting multiple options. 27.2 Options Options inside a select menu are user selections. Syntax: <option>Some Option</option> Attributes: value (sent on form submission) and label (displayed text). Selecting by default: Add selected attribute to an $<option>$. 27.3 Option Groups Groups options within a selection menu for structured layout using $<optgroup>$. Syntax: <optgroup label="Fruits"><option value="banana">Bananas</option></optgroup> Disabling an $<optgroup>$ disables all options within it. 27.4 Datalist Specifies a list of predefined options for an $<input>$ element, providing autocomplete. Example: <input list="Languages"><datalist id="Languages"><option value="PHP"><option value="Perl"></datalist> Chapter 28: Embed Parameters Details src Address of the resource. type Type of embedded resource. width Horizontal dimension. height Vertical dimension. 28.1 Basic usage New in HTML5. Integration point for external (typically non-HTML) application or interactive content. Example: <embed src="myflash.swf"> 28.2 Defining the MIME type Use the type attribute to define the MIME type. Example: <embed type="video/mp4" src="video.mp4" width="640" height="480"> Chapter 29: IFrames Attribute Details name Element's name, used with an $<a>$ tag to change the iframe's $src$. width Element's width in pixels. height Element's height in pixels. src Page to be displayed in the frame. srcdoc Content to be displayed in the frame (must be valid HTML). Takes precedence over $src$. sandbox When set, iframe content is treated as unique origin; features like scripts, plugins, forms, popups disabled. Restrictions can be relaxed. allowfullscreen Allows iframe content to use requestFullscreen() . 29.1 Basics of an Inline Frame Used to include another page within your page. Example: <iframe src="base.html"></iframe> 29.2 Sandboxing Embeds untrusted web pages with restrictions. Example: <iframe sandbox src="http://example.com/"></iframe> To allow scripts/forms: add allow-scripts allow-forms to sandbox attribute. 29.3 Setting the Frame Size Use width and height attributes (values in pixels). Example: <iframe src="base.html" width="800" height="600"></iframe> 29.4 Using the "srcdoc" Attribute Specifies exact HTML content for the iframe. Example: <iframe srcdoc="<p>IFrames are cool!</p>"></iframe> Falls back to src if srcdoc not supported. 29.5 Using Anchors with IFrames Change iframe content from outside by setting anchor's href to URL and target to iframe's name . Example: <iframe src="webpage.html" name="myIframe"></iframe><a href="different_webpage.html" target="myIframe">Change the Iframe content</a> Chapter 30: Content Languages 30.1 Base Document Language Declare primary language in the $<html>$ element: <html lang="en"> Other languages in document should have their own lang attributes. 30.2 Element Language Use lang attribute for element-specific language. Example: <p lang="en">The content of this element is in English.</p> Language declaration is inherited by child elements. 30.3 Elements with Multiple Languages Can "overwrite" a language declaration for specific parts. Example: <p lang="en">This English sentence contains the German word <span lang="de">Hallo</span>.</p> 30.4 Regional URLs Use hreflang attribute on $<a>$ and $<area>$ elements to specify linked resource language (valid BCP 47 tag). Example: <a href="example.org" hreflang="en">example.org</a> 30.5 Handling Attributes with Different Languages Any element (except a few HTML 4.0 elements) can have its own lang attribute to override parent's declaration. Example: <p lang="en" title="An English paragraph"><span lang="de" title="A German sentence">Hallo Welt!</span></p> Chapter 31: SVG SVG (Scalable Vector Graphics) defines graphics for the web. The HTML $<svg>$ element is a container for SVG graphics. 31.1 Inline SVG SVG can be written directly into HTML, styled with CSS, and manipulated with JavaScript. Example path definition: <svg class="attention" xmlns="..." viewBox="0 0 1000 1000"><path id="attention" d="..." /></svg> CSS styling example: .attention { fill: red; width: 50px; height: 50px; } 31.2 Embedding external SVG files in HTML Use $<img>$ or $<object>$ elements. Using $<img>$: <img src="attention.svg" width="50" height="50"> Cannot style or manipulate with CSS/JS. Using $<object>$: <object type="image/svg+xml" data="attention.svg" width="50" height="50"> Directly imports SVG, allowing JS/CSS manipulation. 31.3 Embedding SVG using CSS Use background-image property. Example with external SVG: .attention { background-image: url(attention.svg); background-size: 100% 100%; width: 50px; height: 50px; } Can embed directly using a data URL in CSS. Chapter 32: Canvas Attribute Description height Specifies the canvas height. width Specifies the canvas width. 32.1 Basic Example HTML5 element for drawing graphics. Example: <canvas id="myCanvas">Cannot display graphic. Canvas not supported.</canvas> (300x150 px transparent canvas) Use JavaScript with .getContext("2d") method for drawing. var ctx = document.getElementById("myCanvas").getContext("2d");ctx.fillStyle = "#f00";ctx.fillRect(0, 0, ctx.canvas.width, ctx.canvas.height); 32.2 Drawing two rectangles on a $<canvas>$ Example HTML: <canvas width="300" height="200">Your browser does not support canvas.</canvas> Example JS: function init(){ var canvas = document.querySelector('canvas'); var ctx = canvas.getContext('2d'); ctx.fillStyle = 'red'; ctx.fillRect(0,0, 100, 100); ctx.fillStyle = 'green'; ctx.fillRect(25,25,50,50); } Chapter 33: Meta Information 33.1 Page Information Application Name: <meta name="application-name" content="OpenStreetMap"> (Name of web app). Author: <meta name="author" content="Your Name"> (Author of the page, only one name). Description: <meta name="description" content="Page Description"> (Short summary for search engines). Generator: <meta name="generator" content="HTML Generator 1.42"> (Software used to generate document). Keywords: <meta name="keywords" content="Keyword1, Keyword2"> (Comma-separated keywords for search engines). 33.2 Character Encoding Specifies character encoding for HTML document. HTML5: <meta charset="UTF-8"> (UTF-8 is widely used and recommended). HTML 4.01 (alternative): <meta http-equiv="content-type" content="text/html; charset=UTF-8"> 33.3 Robots Controls whether search engines index a page or follow links. <meta name="robots" content="noindex"> (Instructs not to show page in search results). Values/Directives: all, noindex, nofollow, follow, none, noarchive, nocache, nosnippet, noodp, notranslate, noimageindex, unavailable_after . 33.4 Social Media Open Graph (Facebook): Extends metadata for richer social media display. <meta property="og:title" content="Content Title"><meta property="og:image" content="https://example.com/image.jpg"> Twitter Cards: Metadata for controlling how tweets with links are displayed. <meta name="twitter:card" content="summary"><meta name="twitter:title" content="Content Title"> Google+ / Schema.org: <meta itemprop="name" content="Content Title"><meta itemprop="description" content="Content description less than 200 characters"> 33.5 Mobile Layout Control Commonly uses $<meta name="viewport">$ tag. Example: <meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1"> Sets viewport width to device width and initial zoom to 1. Attributes: width, height, initial-scale, minimum-scale, maximum-scale, user-scalable . 33.6 Automatic Refresh Refreshes page after a specified time. Example: <meta http-equiv="refresh" content="5"> (refreshes every 5 seconds). Caution: Not recommended due to negative user experience. 33.7 Phone Number Recognition Mobile platforms automatically recognize phone numbers. To disable for WebKit-based browsers: <meta name="format-detection" content="telephone=no"> 33.8 Automatic redirect Redirects to another URL after a specified time. Example: <meta http-equiv="refresh" content="5;url=https://www.example.com/"> 33.9 Web App Sets up web app shortcut icon/full-screen mode. Android Chrome: <meta name="mobile-web-app-capable" content="yes"> iOS: <meta name="apple-mobile-web-app-capable" content="yes"> Set status bar color: Android Chrome: <meta name="theme-color" content="black"> iOS: <meta name="apple-mobile-web-app-status-bar-style" content="black"> Chapter 34: Marking up computer code 34.1 Block with $<pre>$ and $<code>$ For code where formatting (whitespace, new lines, indentation) matters. Example: <pre><code>x = 42if x == 42: print "x is 42"</code></pre> Escape special HTML characters (e.g., $<$ as $<$). 34.2 Inline with $<code>$ For computer code within a sentence. Example: <p>The <code>a element creates a hyperlink.</p> Chapter 35: Marking-up Quotes 35.1 Inline with $<q>$ Used for quotes that are part of a sentence. Example: <p>She wrote <q>The answer is 42.</q> and everyone agreed.</p> Browsers automatically render quotation marks. Source URL (cite attribute): <q cite="http://example.com/blog/hello-world">The answer is 42.</q> (browsers typically don't show this URL). 35.2 Block with $<blockquote>$ Used for block-level quotes. Example: <blockquote><p>The answer is 42.</p></blockquote> Source URL (cite attribute): <blockquote cite="http://example.com/blog/hello-world"><p>The answer is 42.</p></blockquote> Citation/Attribution (HTML 4.01): Not part of blockquote; use $<p>Source: <cite><a href="...">Hello World</a></cite></p>$. HTML5: Citation can be inside blockquote within a $<cite>$ element or $<footer>$. Chapter 36: Tabindex Value Meaning Negative Element is focusable but not reachable via sequential keyboard navigation. 0 Element is focusable and reachable via keyboard, order defined by platform. Positive Element is focusable and reachable via keyboard, order defined by attribute value (increasing number). 36.1 Add an element to the tabbing order Example: <div tabindex="0">Some button</div> Note: Prefer native HTML $<button>$ or $<a>$ tags. 36.2 Remove an element from the tabbing order Example: <button tabindex="-1">This button will not be reachable by tab</button> Element is still focusable, just not via tab key. 36.3 Define a custom tabbing order (not recommended) Positive tabindex values define a custom order. Example: <div tabindex="2">Second</div><div tabindex="1">First</div> Not recommended as it can confuse screen reader users; rearrange DOM structure instead. Chapter 37: Global Attributes Attribute Description class Defines one or more class names for an element. contenteditable Sets whether the content of an element can be edited. contextmenu Defines a context menu shown when a user right-clicks an element. dir Sets the text direction for text within an element. draggable Sets whether an element can be dragged. hidden Hides an element not currently in use on the page. id Defines a unique identifier for an element. lang Defines the language of an element's content. spellcheck Sets whether to spell/grammar check the content of an element. style Defines a set of inline CSS styles for an element. tabindex Sets the order in which elements on a page are navigated by the tab keyboard shortcut. title Defines additional information about an element, generally tooltip text on mouseover. translate Defines whether to translate the content of an element. 37.1 Contenteditable Attribute Makes content editable. Example: <p contenteditable>This is an editable paragraph.</p> Child elements inherit contenteditable from parent. Can be turned off for specific text: <span contenteditable="false">But not this.</span> Chapter 38: HTML 5 Cache 38.1 Basic Example of HTML5 cache HTML5 cache uses a manifest file to specify resources for offline use. HTML file links to manifest: <html manifest="index.appcache"> Manifest file (e.g., index.appcache ): CACHE MANIFESTindex.html Files listed in manifest are cached. HTML and manifest files must be in the same folder. Chapter 39: HTML Event Attributes 39.1 HTML Form Events Attribute Description onblur Fires when element loses focus. onchange Fires when element's value changes. oncontextmenu Script to run when a context menu is triggered. onfocus Fires when element gets focus. oninput Script to run when element gets user input. oninvalid Script to run when element is invalid. onreset Fires when Reset button in form is clicked. onsearch Fires when user writes in a search field. onselect Fires after some text has been selected. onsubmit Fires when a form is submitted. 39.2 Keyboard Events Attribute Description onkeydown Fires when user presses a key. onkeypress Fires when user presses a key (deprecated). onkeyup Fires when user releases a key. Chapter 40: Character Entities 40.1 Character Entities in HTML Used for symbols/special characters not available on keyboard or reserved in HTML. Syntax: &entity_name; or &#entity_number; . Example: <input type="text" placeholder=" 🔍 Search"/> (magnifying glass icon). 40.2 Common Special Characters Character Description Entity Name Entity Number non-breaking space   $ less than < < $>$ greater than > > & ampersand & & — em dash — — – en dash – – © copyright © © ® registered trademark ® ® ™ trademark ™ ™ ☎ phone ☎ ☎ Chapter 41: ARIA (Accessible Rich Internet Applications) 41.1 role="presentation" Removes implicit native role semantics from the accessibility API. Example for clearing floats: <div role="presentation" style="clear:both;"></div> 41.2 role="alert" For important, time-sensitive information. Example: <div role="alert" aria-live="assertive">Your session will expire in 60 seconds.</div> Use both role="alert" and aria-live="assertive" for broader screen reader support. 41.3 role="alertdialog" A dialog that contains an alert message, with initial focus on an element within the dialog. Example: <div role="alertdialog"><h1>Warning <div role="alert">Your session will expire in 60 seconds.</div></div> 41.4 role="application" Declares a region as a web application, not a document. Example: <div role="application"><h1>Calculator <input id="num1" type="text"> + <input id="num2" type="text"> = <span id="result"></span></div> 41.5 role="article" A section of a page that is an independent composition (e.g., blog post). Example: <article><h1>My first article <p>Lorem ipsum...</p></article> Setting ARIA role matching default implicit semantics is unnecessary. 41.6 role="banner" A region with site-oriented content (e.g., logo, site title, main navigation). Example: <div role="banner"><h1>My Site <ul><li><a href="/">Home</a></li></ul></div> 41.7 role="button" Input for user-triggered actions. Example: <button role="button">Add</button> 41.8 role="cell" A cell in a tabular container. Example: <td role="cell">95</td> 41.9 role="checkbox" A checkable input with three values: true, false, or mixed. Example: <input type="checkbox" role="checkbox" aria-checked="false">I agree to the terms 41.10 role="columnheader" A cell containing header information for a column. Example: <th role="columnheader">Day 1</th> 41.11 role="combobox" Presentation of a select element, typically a textbox with type-ahead functionality. Example: <input type="text" role="combobox" aria-expanded="false"> 41.12 role="complementary" Supporting section of the document, meaningful even when separated from main content. Example: <div role="complementary"><h2>More Articles <ul>...</ul></div> 41.13 role="contentinfo" Large perceivable region with information about the parent document (e.g., author, publication date). Example: <p role="contentinfo">Author: Albert Einstein<br>Published: August 15, 1940</p> 41.14 role="definition" A definition of a term or concept. Example: <span id="def1" role="definition">an intense feeling of deep affection.</span> 41.15 role="dialog" An application window interrupting current processing to prompt user for info or response. Example: <div role="dialog"><p>Are you sure? <button role="button">Yes</button></div> 41.16 role="directory" A list of references to members of a group, like a static table of contents. Example: <ul role="directory"><li><a href="/chapter-1">Chapter 1</a></li></ul> 41.17 role="document" A region containing related information declared as document content. Example: <div role="document"><h1>The Life of Albert Einstein <p>Lorem ipsum...</p></div> 41.18 role="form" A landmark region containing elements that combine to create a form. Using $<form>$ element implies default ARIA semantics, so role="form" is not required. Example: <form action=""><fieldset><legend>Login form</legend><div><label for="username">Your username</label><input type="text" id="username" aria-describedby="username-tip" required /></div></fieldset></form> 41.19 role="grid" Interactive control with tabular data arranged in rows and columns. Example: <table role="grid"><thead>...</thead><tbody>...</tbody></table> 41.20 role="gridcell" A cell in a grid or treegrid. Example: <td role="gridcell">17</td> 41.21 role="group" Set of UI objects not intended for page summary/table of contents by assistive technologies. Example: <div role="group"><button role="button">Previous</button></div> 41.22 role="heading" A heading for a section of the page. Example: <h1 role="heading">Introduction 41.23 role="img" A container for elements that form an image. Example: <figure role="img"><img alt="A cute cat." src="albert.jpg"><figcaption>This is my cat, Albert.</figcaption></figure> 41.24 role="link" An interactive reference to a resource, causing navigation when activated. Setting ARIA role matching default implicit semantics is unnecessary. 41.25 role="list" A group of non-interactive list items. Example: <ul role="list"><li role="listitem">One</li></ul> 41.26 role="listbox" A widget allowing user to select one or more items from a list of choices. Example: <ul role="listbox"><li>One</li></ul> 41.27 role="listitem" A single item in a list or directory. Example: <li role="listitem">One</li> 41.28 role="log" A live region where new information is added in meaningful order and old information may disappear. Example: <ul role="log"><li>User 1 logged in.</li></ul> 41.29 role="main" The main content of a document. Example: <div role="main"><p>Lorem ipsum...</p></div> 41.30 role="marquee" A live region where non-essential information changes frequently. Example: <ul role="marquee"><li>Dow +0.26%</li></ul> 41.31 role="math" Content representing a mathematical expression. Example: <img role="math" alt="y=mx+b" src="slope.png"> 41.32 role="menu" A widget offering a list of choices. Example: <ul role="menu"><li role="menuitem">New</li></ul> 41.33 role="menubar" A presentation of a menu that remains visible and is presented horizontally. Example: <ul role="menubar"><li role="menuitem">File</li></ul> 41.34 role="menuitem" An option in a group of choices contained by a menu or menubar. Example: <li role="menuitem">Help</li> 41.35 role="menuitemcheckbox" A checkable menuitem with three values: true, false, or mixed. Example: <li role="menuitemcheckbox" aria-checked="true">Word wrap</li> 41.36 role="menuitemradio" A checkable menuitem in a group of menuitemradio roles, where only one can be checked. Example: <li role="menuitemradio" aria-checked="true">Left</li> 41.37 role="navigation" A collection of navigational elements (links). Example: <ul role="navigation"><li><a href="/">Home</a></li></ul> 41.38 role="note" A section whose content is parenthetic or ancillary to the main content. Example: <p role="note">Lorem ipsum...</p> 41.39 role="option" A selectable item in a select list. Example: <li role="option">Option 1</li> 41.40 role="progressbar" An element displaying the progress status for tasks. Example: <progress role="progressbar" value="25" max="100">25%</progress> 41.41 role="radio" A checkable input in a group of radio roles, only one of which can be checked. Example: <div role="radiogroup"><input role="radio" type="radio" aria-checked="true"> One</div> 41.42 role="region" A large perceivable section of a web page or document that is important enough to be included in a page summary. Example: <div role="region">Home team: 4<br>Away team: 2</div> 41.43 role="radiogroup" A group of radio buttons. Example: <div role="radiogroup"><input role="radio" type="radio" aria-checked="true"> One</div> 41.44 role="row" A row of cells in a tabular container. Example: <tr role="row">...</tr> 41.45 role="rowgroup" A group containing one or more row elements in a grid. Example: <thead role="rowgroup">...</thead> 41.46 role="rowheader" A cell containing header information for a row in a grid. Example: <th role="rowheader">Day 1</th> 41.47 role="scrollbar" A graphical object that controls the scrolling of content within a viewing area. Example: <div role="scrollbar" aria-controls="content1" aria-orientation="vertical" aria-valuemax="100" aria-valuemin="0" aria-valuenow="25"><div class="scrollhandle"></div></div> 41.48 role="search" A landmark region that contains a collection of items to create a search facility. Example: <div role="search"><input role="searchbox" type="text"><button role="button">Search</button></div> 41.49 role="searchbox" A textbox intended for specifying search criteria. Example: <input role="searchbox" type="text"> 41.50 role="separator" A divider that separates content sections or menu items. Example: <hr role="separator"> 41.51 role="slider" A user input where the user selects a value from within a given range. Example: <div role="slider" aria-valuemax="100" aria-valuemin="0" aria-valuenow="25"><div class="sliderhandle"></div></div> 41.52 role="spinbutton" A form of range that expects the user to select from among discrete choices. Example: <input role="spinbutton" aria-valuemax="100" aria-valuemin="0" aria-valuenow="25" type="number" value="25"> 41.53 role="status" A container whose content is advisory information, not important enough for an alert. Example: <div role="status">Online</div> 41.54 role="switch" A type of checkbox representing on/off values. Example: <select role="switch" aria-checked="false"><option>On</option><option selected>Off</option></select> 41.55 role="tab" A grouping label providing a mechanism for selecting tab content. Example: <li role="tab">Introduction</li> 41.56 role="table" A section containing data arranged in rows and columns, for tabular containers that are not interactive. Example: <table role="table"><thead>...</thead><tbody>...</tbody></table> 41.57 role="tablist" A list of tab elements, referencing tabpanel elements. Example: <ul role="tablist"><li role="tab">Introduction</li></ul> 41.58 role="tabpanel" A container for resources associated with a tab. Example: <div role="tabpanel">...</div> 41.59 role="textbox" Input that allows free-form text as its value. Example: <textarea role="textbox"></textarea> 41.60 role="timer" A live region containing a numerical counter for elapsed or remaining time. Example: <p><span role="timer">60 seconds remaining.</p> 41.61 role="toolbar" A collection of commonly used function buttons in compact visual form. Example: <ul role="toolbar"><li><img alt="New" src="new.png"></li></ul> 41.62 role="tooltip" A contextual popup displaying a description for an element. Example: <span aria-describedby="slopedesc">Slope</span><div role="tooltip" id="slopedesc">y=mx+b</div> 41.63 role="tree" A list that may contain sub-level nested groups that can be collapsed and expanded. Example: <ul role="tree"><li role="treeitem">Part 1<ul><li role="treeitem">Chapter 1</li></ul></li></ul> 41.64 role="treegrid" A grid whose rows can be expanded and collapsed like a tree. 41.65 role="treeitem" An option item of a tree, expandable/collapsible if it contains sub-level treeitems. Example: (see 41.63 role="tree" for example code)