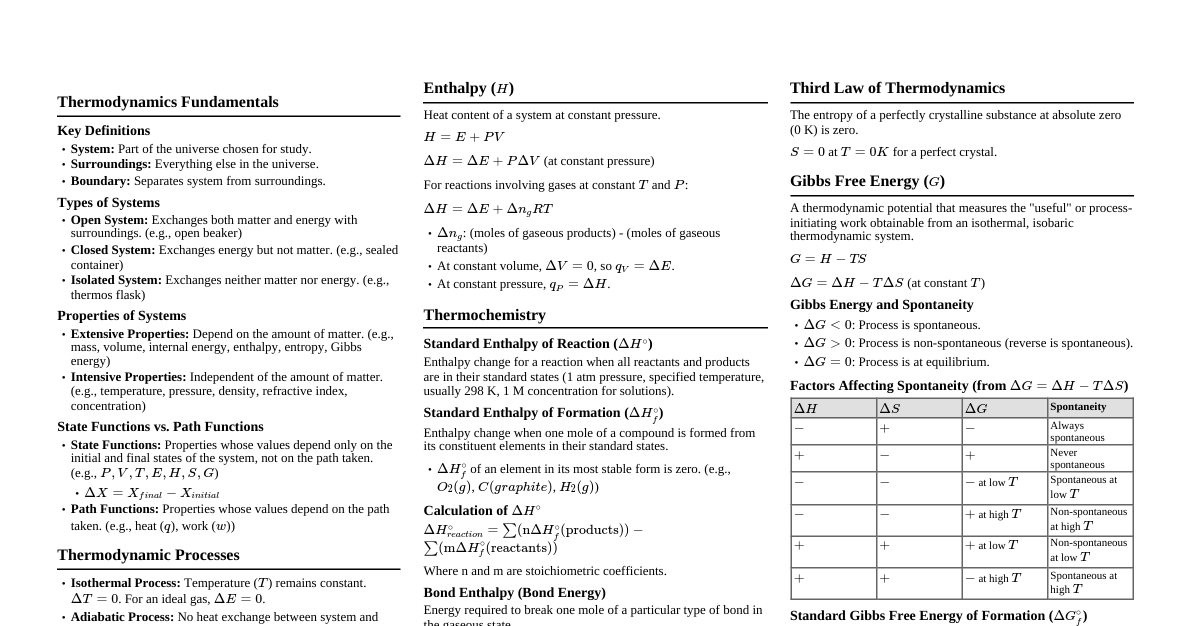
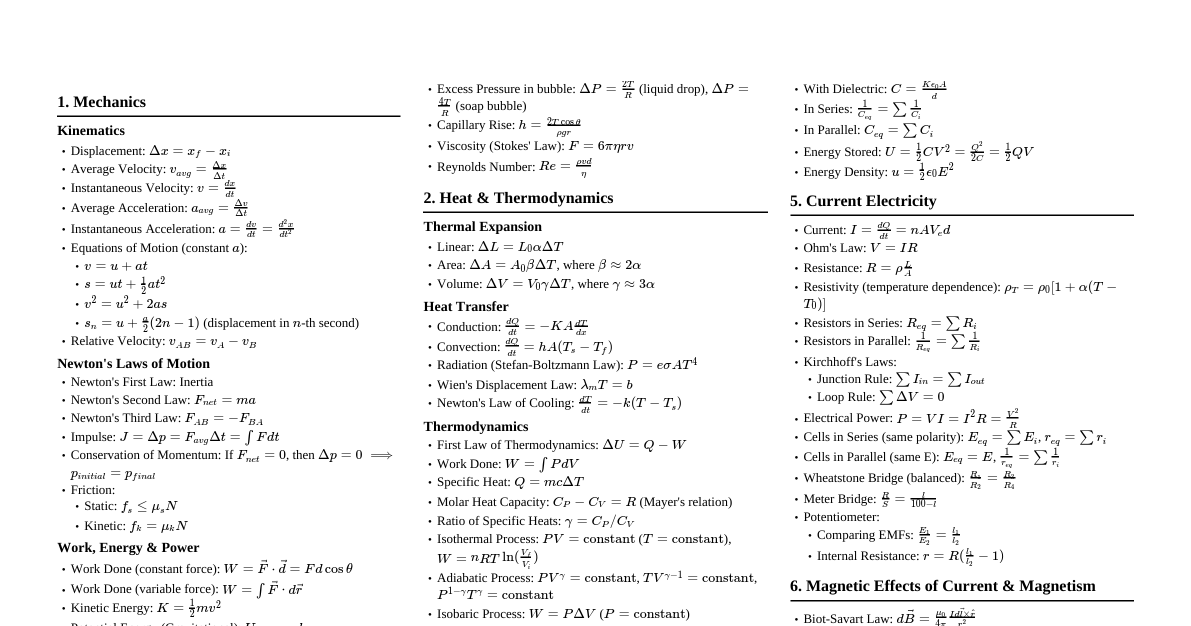
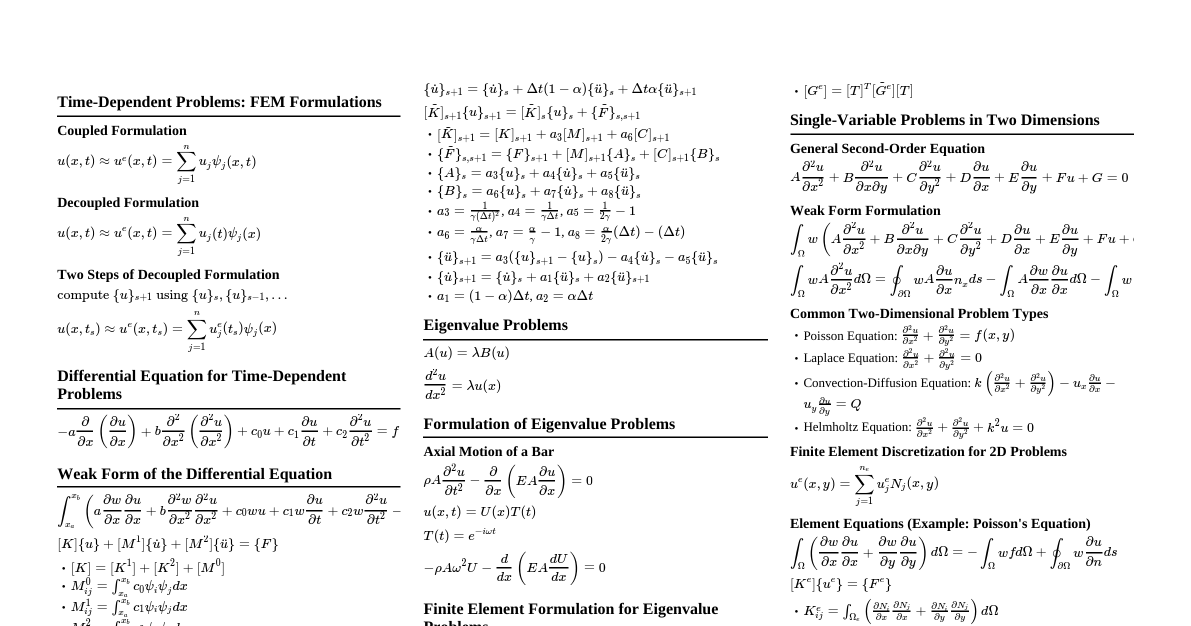
Thermodynamics Problem Solving Problem 5: Polytropic Compression of Nitrogen Given: Nitrogen ($N_2$) Mass $m = 2.2 \text{ kg}$ Initial pressure $P_1 = 100 \text{ kPa}$ Initial temperature $T_1 = 25^\circ C = 298.15 \text{ K}$ Polytropic process: $PV^{1.3} = \text{constant}$ ($n=1.3$) Volume reduced by one-half: $V_2 = 0.5 V_1$ Find: Work done $W_{12}$ and Heat transfer $Q_{12}$ Properties of Nitrogen: Gas constant $R = 0.2968 \text{ kJ/kg} \cdot \text{K}$ Specific heat at constant volume $c_v = 0.743 \text{ kJ/kg} \cdot \text{K}$ Specific heat ratio $k = 1.4$ (or $c_p = c_v + R = 1.0398 \text{ kJ/kg} \cdot \text{K}$) Calculations: Initial Volume $V_1$: $P_1 V_1 = m R T_1 \Rightarrow V_1 = \frac{m R T_1}{P_1}$ $V_1 = \frac{(2.2 \text{ kg})(0.2968 \text{ kJ/kg} \cdot \text{K})(298.15 \text{ K})}{100 \text{ kPa}} = 1.948 \text{ m}^3$ Final Volume $V_2$: $V_2 = 0.5 V_1 = 0.5 \times 1.948 \text{ m}^3 = 0.974 \text{ m}^3$ Final Pressure $P_2$: $P_1 V_1^n = P_2 V_2^n \Rightarrow P_2 = P_1 \left(\frac{V_1}{V_2}\right)^n = P_1 (2)^n$ $P_2 = 100 \text{ kPa} (2)^{1.3} = 100 \text{ kPa} \times 2.462 = 246.2 \text{ kPa}$ Final Temperature $T_2$: $\frac{P_1 V_1}{T_1} = \frac{P_2 V_2}{T_2} \Rightarrow T_2 = T_1 \frac{P_2 V_2}{P_1 V_1} = T_1 \frac{P_2}{P_1} \frac{V_2}{V_1}$ $T_2 = 298.15 \text{ K} \frac{246.2 \text{ kPa}}{100 \text{ kPa}} \frac{0.974 \text{ m}^3}{1.948 \text{ m}^3} = 298.15 \text{ K} \times 2.462 \times 0.5 = 367.0 \text{ K}$ Alternatively: $T_2 = T_1 \left(\frac{V_1}{V_2}\right)^{n-1} = 298.15 \text{ K} (2)^{1.3-1} = 298.15 \text{ K} (2)^{0.3} = 298.15 \times 1.231 = 367.0 \text{ K}$ Work Done $W_{12}$ (Polytropic Process): $W_{12} = \frac{P_2 V_2 - P_1 V_1}{1-n} = \frac{m R (T_2 - T_1)}{1-n}$ $W_{12} = \frac{(2.2 \text{ kg})(0.2968 \text{ kJ/kg} \cdot \text{K})(367.0 - 298.15) \text{ K}}{1-1.3}$ $W_{12} = \frac{2.2 \times 0.2968 \times 68.85}{-0.3} = \frac{44.97}{-0.3} = -149.9 \text{ kJ}$ Work is done on the system, so $W_{12} = -149.9 \text{ kJ}$ (or $149.9 \text{ kJ}$ input). Heat Transfer $Q_{12}$ (First Law of Thermodynamics): $Q_{12} - W_{12} = \Delta U = m c_v (T_2 - T_1)$ $Q_{12} = W_{12} + m c_v (T_2 - T_1)$ $Q_{12} = -149.9 \text{ kJ} + (2.2 \text{ kg})(0.743 \text{ kJ/kg} \cdot \text{K})(367.0 - 298.15) \text{ K}$ $Q_{12} = -149.9 \text{ kJ} + 2.2 \times 0.743 \times 68.85 \text{ kJ}$ $Q_{12} = -149.9 \text{ kJ} + 112.7 \text{ kJ} = -37.2 \text{ kJ}$ Heat is transferred from the system ($37.2 \text{ kJ}$ rejected). Answers: Work Done $= -149.9 \text{ kJ}$, Heat Transfer $= -37.2 \text{ kJ}$ Problem 6: Multi-stage Process for Air with Stops Given: Air Mass $m = 3 \text{ kg}$ Initial pressure $P_1 = 200 \text{ kPa}$ Initial temperature $T_1 = 27^\circ C = 300.15 \text{ K}$ Stops: $V_2 = 2 V_1$ Final state: $P_3 = 2 P_1$ Specific heat at constant volume $c_v = 0.800 \text{ kJ/kg} \cdot \text{K}$ Find: Work done $W_{13}$ and Heat transfer $Q_{13}$ Properties of Air: Gas constant $R = 0.287 \text{ kJ/kg} \cdot \text{K}$ Calculations: Initial Volume $V_1$: $P_1 V_1 = m R T_1 \Rightarrow V_1 = \frac{m R T_1}{P_1}$ $V_1 = \frac{(3 \text{ kg})(0.287 \text{ kJ/kg} \cdot \text{K})(300.15 \text{ K})}{200 \text{ kPa}} = 1.292 \text{ m}^3$ Process 1-2 (Constant Pressure, Piston Rises to Stops): $P_2 = P_1 = 200 \text{ kPa}$ $V_2 = 2 V_1 = 2 \times 1.292 \text{ m}^3 = 2.584 \text{ m}^3$ Temperature $T_2$: $\frac{V_1}{T_1} = \frac{V_2}{T_2} \Rightarrow T_2 = T_1 \frac{V_2}{V_1} = T_1 (2) = 300.15 \text{ K} \times 2 = 600.3 \text{ K}$ Work Done $W_{12}$: $W_{12} = P_1 (V_2 - V_1) = 200 \text{ kPa} (2.584 - 1.292) \text{ m}^3$ $W_{12} = 200 \times 1.292 = 258.4 \text{ kJ}$ Heat Transfer $Q_{12}$: $Q_{12} - W_{12} = m c_v (T_2 - T_1)$ $Q_{12} = W_{12} + m c_v (T_2 - T_1)$ $Q_{12} = 258.4 \text{ kJ} + (3 \text{ kg})(0.800 \text{ kJ/kg} \cdot \text{K})(600.3 - 300.15) \text{ K}$ $Q_{12} = 258.4 \text{ kJ} + 3 \times 0.800 \times 300.15 \text{ kJ}$ $Q_{12} = 258.4 \text{ kJ} + 720.36 \text{ kJ} = 978.76 \text{ kJ}$ Process 2-3 (Constant Volume, Heating to Final Pressure): $V_3 = V_2 = 2.584 \text{ m}^3$ (Piston against stops) $P_3 = 2 P_1 = 2 \times 200 \text{ kPa} = 400 \text{ kPa}$ Temperature $T_3$: $\frac{P_2}{T_2} = \frac{P_3}{T_3} \Rightarrow T_3 = T_2 \frac{P_3}{P_2} = T_2 \frac{2 P_1}{P_1} = T_2 (2)$ $T_3 = 600.3 \text{ K} \times 2 = 1200.6 \text{ K}$ Work Done $W_{23}$: $W_{23} = 0 \text{ kJ}$ (Constant volume process) Heat Transfer $Q_{23}$: $Q_{23} - W_{23} = m c_v (T_3 - T_2)$ $Q_{23} = 0 + (3 \text{ kg})(0.800 \text{ kJ/kg} \cdot \text{K})(1200.6 - 600.3) \text{ K}$ $Q_{23} = 3 \times 0.800 \times 600.3 \text{ kJ} = 1440.72 \text{ kJ}$ Total Work Done $W_{13}$: $W_{13} = W_{12} + W_{23} = 258.4 \text{ kJ} + 0 \text{ kJ} = 258.4 \text{ kJ}$ Total Heat Transfer $Q_{13}$: $Q_{13} = Q_{12} + Q_{23} = 978.76 \text{ kJ} + 1440.72 \text{ kJ} = 2419.48 \text{ kJ}$ Answers: Work Done $= 258.4 \text{ kJ}$, Heat Transfer $= 2419.5 \text{ kJ}$ P-v Diagram for Problem 6 P v 1 $(P_1, v_1)$ 2 $(P_1, v_2=2v_1)$ 3 $(P_3=2P_1, v_2)$ P=const v=const $P_1$ $P_3=2P_1$ $v_1$ $v_2=2v_1$