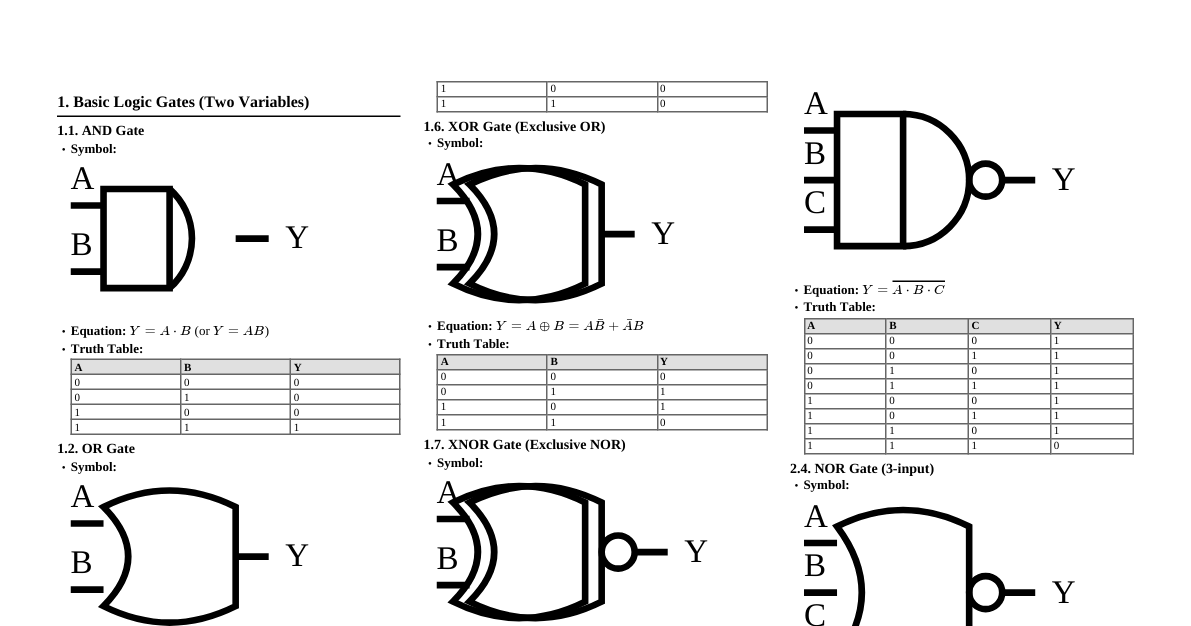
### Set Theory - **Definition:** A collection of distinct objects. - $A = \{1, 2, 3\}$ - $x \in A$ (x is an element of A) - $x \notin A$ (x is not an element of A) - **Subsets:** $A \subseteq B$ if every element of A is also in B. - Proper subset: $A \subset B$ if $A \subseteq B$ and $A \neq B$. - **Cardinality:** $|A|$ is the number of elements in set A. - **Power Set:** $P(A)$ is the set of all subsets of A. $|P(A)| = 2^{|A|}$. - **Set Operations:** - **Union:** $A \cup B = \{x \mid x \in A \text{ or } x \in B\}$ - **Intersection:** $A \cap B = \{x \mid x \in A \text{ and } x \in B\}$ - **Difference:** $A - B = \{x \mid x \in A \text{ and } x \notin B\}$ - **Complement:** $\bar{A} = U - A$ (where U is the universal set) - **Cartesian Product:** $A \times B = \{(a, b) \mid a \in A \text{ and } b \in B\}$ - **De Morgan's Laws:** - $\overline{A \cup B} = \bar{A} \cap \bar{B}$ - $\overline{A \cap B} = \bar{A} \cup \bar{B}$ ### Logic - **Propositions:** Statements that are either true (T) or false (F). - $p \land q$ (p AND q) - $p \lor q$ (p OR q) - $\neg p$ (NOT p) - $p \rightarrow q$ (p IMPLIES q, if p then q) - $p \leftrightarrow q$ (p IFF q, p if and only if q) - **Truth Table:** Evaluates the truth value of compound propositions. - **Tautology:** A proposition that is always true. - **Contradiction:** A proposition that is always false. - **Logical Equivalence:** $p \equiv q$ if $p \leftrightarrow q$ is a tautology. - De Morgan's Laws: $\neg(p \land q) \equiv \neg p \lor \neg q$, $\neg(p \lor q) \equiv \neg p \land \neg q$ - **Quantifiers:** - $\forall x$ (for all x, universal quantifier) - $\exists x$ (there exists an x, existential quantifier) - **Rules of Inference:** - **Modus Ponens:** $((p \rightarrow q) \land p) \rightarrow q$ - **Modus Tollens:** $((p \rightarrow q) \land \neg q) \rightarrow \neg p$ - **Hypothetical Syllogism:** $((p \rightarrow q) \land (q \rightarrow r)) \rightarrow (p \rightarrow r)$ ### Relations - **Definition:** A relation R from set A to set B is a subset of $A \times B$. - Binary relation on A is a subset of $A \times A$. - **Properties of Relations (on a set A):** - **Reflexive:** $(a, a) \in R$ for all $a \in A$. - **Symmetric:** If $(a, b) \in R$, then $(b, a) \in R$. - **Antisymmetric:** If $(a, b) \in R$ and $(b, a) \in R$, then $a = b$. - **Transitive:** If $(a, b) \in R$ and $(b, c) \in R$, then $(a, c) \in R$. - **Equivalence Relation:** A relation that is reflexive, symmetric, and transitive. - Partitions the set into equivalence classes. - **Partial Order Relation:** A relation that is reflexive, antisymmetric, and transitive. - e.g., "less than or equal to" ($\le$) on integers. ### Functions - **Definition:** A relation $f: A \rightarrow B$ where every element in A maps to exactly one element in B. - Domain: A, Codomain: B, Range: $\{f(a) \mid a \in A\}$. - **Types of Functions:** - **Injective (One-to-one):** If $f(a) = f(b)$ implies $a = b$. - **Surjective (Onto):** For every $b \in B$, there exists an $a \in A$ such that $f(a) = b$. - **Bijective (One-to-one correspondence):** Both injective and surjective. - **Inverse Function:** If $f$ is bijective, $f^{-1}: B \rightarrow A$ exists. - **Composition of Functions:** $(g \circ f)(x) = g(f(x))$. ### Counting & Combinatorics - **Product Rule:** If there are $n_1$ ways for event 1 and $n_2$ ways for event 2, there are $n_1 n_2$ ways for both. - **Sum Rule:** If there are $n_1$ ways for event 1 OR $n_2$ ways for event 2 (mutually exclusive), there are $n_1 + n_2$ ways. - **Permutations:** Order matters. - $P(n, k) = \frac{n!}{(n-k)!}$ (number of ways to arrange k items from n) - With repetition: $n^k$ - **Combinations:** Order does not matter. - $C(n, k) = \binom{n}{k} = \frac{n!}{k!(n-k)!}$ (number of ways to choose k items from n) - With repetition allowed (stars and bars): $\binom{n+k-1}{k}$ - **Pigeonhole Principle:** If $k+1$ or more items are placed into $k$ bins, then at least one bin contains two or more items. ### Graph Theory - **Definition:** A graph $G = (V, E)$ consists of a set of vertices V and a set of edges E. - **Directed Graph:** Edges have direction (ordered pairs). - **Undirected Graph:** Edges have no direction (unordered pairs). - **Terminology:** - **Degree of a vertex:** Number of edges incident to it. - **Path:** Sequence of distinct vertices connected by edges. - **Cycle:** Path that starts and ends at the same vertex. - **Connected Graph:** A path exists between every pair of vertices. - **Special Graphs:** - **Complete Graph ($K_n$):** Every pair of distinct vertices is connected by a unique edge. - **Bipartite Graph:** Vertices can be divided into two disjoint sets U and V such that every edge connects a vertex in U to one in V. - **Tree:** A connected undirected graph with no simple circuits. A tree with n vertices has $n-1$ edges. - **Graph Traversal:** - **Breadth-First Search (BFS):** Explores neighbor nodes first. - **Depth-First Search (DFS):** Explores as far as possible along each branch before backtracking.