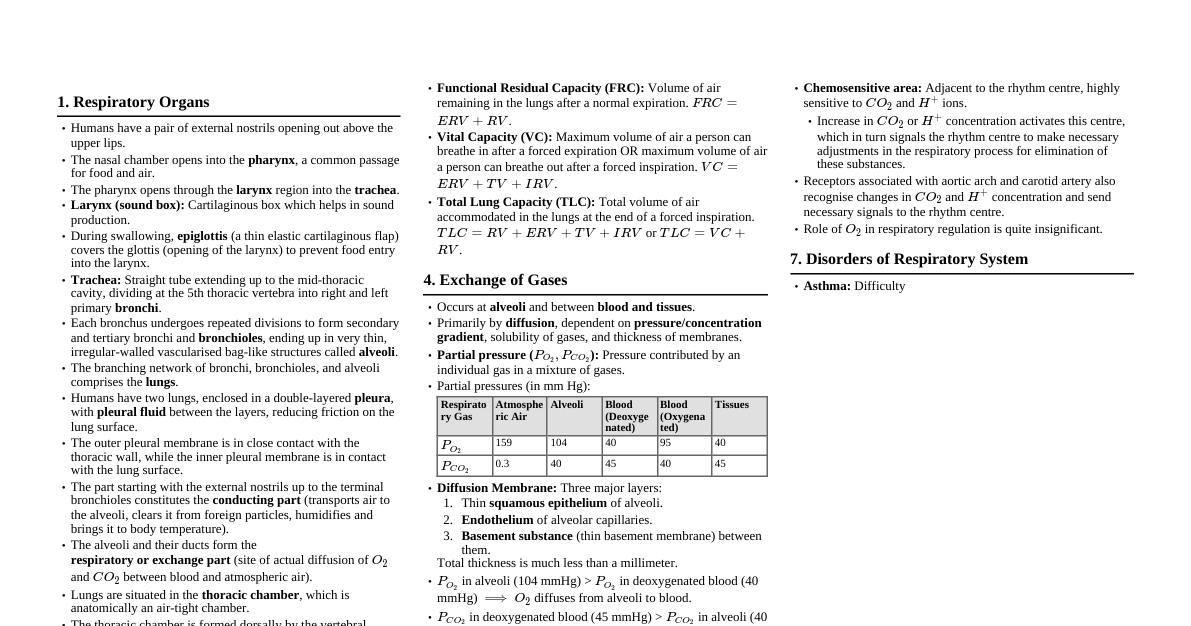
### Electrostatics #### Coulomb's Law - Force between two point charges: $F = k \frac{q_1 q_2}{r^2}$, where $k = \frac{1}{4\pi\epsilon_0} = 9 \times 10^9 \text{ Nm}^2/\text{C}^2$. - $\epsilon_0$ is permittivity of free space ($8.85 \times 10^{-12} \text{ C}^2/\text{Nm}^2$). #### Electric Field - Electric field due to a point charge $q$ at distance $r$: $E = k \frac{q}{r^2}$. - Electric field lines: originate from positive, terminate on negative charges. - Electric field due to dipole: - Axial point: $E_{axial} = \frac{2kp}{r^3}$ for $r \gg a$. - Equatorial point: $E_{equatorial} = \frac{kp}{r^3}$ for $r \gg a$. #### Electric Potential - Electric potential due to a point charge $q$ at distance $r$: $V = k \frac{q}{r}$. - Potential difference: $V_B - V_A = - \int_A^B \vec{E} \cdot d\vec{l}$. - Electric potential energy of two charges: $U = k \frac{q_1 q_2}{r}$. #### Capacitance - Capacitance of a capacitor: $C = \frac{Q}{V}$. - Parallel plate capacitor: $C = \frac{\epsilon_0 A}{d}$. - Capacitors in series: $\frac{1}{C_{eq}} = \frac{1}{C_1} + \frac{1}{C_2} + ...$ - Capacitors in parallel: $C_{eq} = C_1 + C_2 + ...$ - Energy stored in a capacitor: $U = \frac{1}{2}CV^2 = \frac{1}{2}\frac{Q^2}{C} = \frac{1}{2}QV$. ### Current Electricity #### Ohm's Law - $V = IR$, where $R$ is resistance. - Resistance: $R = \rho \frac{L}{A}$, where $\rho$ is resistivity. #### Kirchhoff's Laws - **Junction Rule (KCL):** Sum of currents entering a junction equals sum of currents leaving ($ \sum I = 0 $). - **Loop Rule (KVL):** Sum of potential changes around any closed loop is zero ($ \sum \Delta V = 0 $). #### Resistors - Resistors in series: $R_{eq} = R_1 + R_2 + ...$ - Resistors in parallel: $\frac{1}{R_{eq}} = \frac{1}{R_1} + \frac{1}{R_2} + ...$ #### Electric Power - Power dissipated: $P = VI = I^2R = \frac{V^2}{R}$. #### Cells - EMF ($\mathcal{E}$) and internal resistance ($r$): $V = \mathcal{E} - Ir$. - Cells in series: $\mathcal{E}_{eq} = \mathcal{E}_1 + \mathcal{E}_2$, $r_{eq} = r_1 + r_2$. - Cells in parallel (identical): $\mathcal{E}_{eq} = \mathcal{E}$, $\frac{1}{r_{eq}} = \frac{1}{r_1} + \frac{1}{r_2}$. ### Magnetic Effects of Current #### Biot-Savart Law - Magnetic field due to a current element $d\vec{l}$: $d\vec{B} = \frac{\mu_0}{4\pi} \frac{I d\vec{l} \times \vec{r}}{r^3}$. - $\mu_0$ is permeability of free space ($4\pi \times 10^{-7} \text{ T m/A}$). #### Magnetic Field due to Wires/Loops - Straight infinite wire: $B = \frac{\mu_0 I}{2\pi r}$. - Circular loop at center: $B = \frac{\mu_0 I}{2R}$. - Solenoid: $B = \mu_0 n I$ (inside), where $n$ is turns per unit length. - Toroid: $B = \frac{\mu_0 N I}{2\pi r}$ (inside), where $N$ is total turns. #### Ampere's Circuital Law - $\oint \vec{B} \cdot d\vec{l} = \mu_0 I_{enclosed}$. #### Force on a Charge/Current - Lorentz Force: $\vec{F} = q(\vec{E} + \vec{v} \times \vec{B})$. - Force on current carrying wire: $\vec{F} = I (\vec{L} \times \vec{B})$. - Force between two parallel current-carrying wires: $F/L = \frac{\mu_0 I_1 I_2}{2\pi d}$. #### Moving Coil Galvanometer - Torque: $\tau = NIAB \sin\theta$. - Current sensitivity: $\frac{\phi}{I} = \frac{NAB}{k}$. ### Electromagnetic Induction (EMI) & AC #### Faraday's Law of EMI - Induced EMF: $\mathcal{E} = - \frac{d\Phi_B}{dt}$. - Magnetic flux: $\Phi_B = \int \vec{B} \cdot d\vec{A} = BA \cos\theta$. #### Lenz's Law - The direction of induced current opposes the cause producing it. #### Motional EMF - $\mathcal{E} = Blv$. #### Self and Mutual Inductance - Self-inductance: $\Phi_B = LI$, induced EMF $\mathcal{E} = -L \frac{dI}{dt}$. - Mutual inductance: $\Phi_{B2} = MI_1$, induced EMF $\mathcal{E}_2 = -M \frac{dI_1}{dt}$. - Energy stored in an inductor: $U = \frac{1}{2}LI^2$. #### Alternating Current (AC) - RMS values: $V_{rms} = \frac{V_0}{\sqrt{2}}$, $I_{rms} = \frac{I_0}{\sqrt{2}}$. - Inductive reactance: $X_L = \omega L = 2\pi f L$. - Capacitive reactance: $X_C = \frac{1}{\omega C} = \frac{1}{2\pi f C}$. - Impedance ($Z$) for LCR series circuit: $Z = \sqrt{R^2 + (X_L - X_C)^2}$. - Phase angle: $\tan\phi = \frac{X_L - X_C}{R}$. - Power in AC circuit: $P = V_{rms}I_{rms} \cos\phi$ (where $\cos\phi$ is power factor). - Resonance condition: $X_L = X_C \implies \omega_0 = \frac{1}{\sqrt{LC}}$. #### Transformers - $\frac{V_s}{V_p} = \frac{N_s}{N_p} = \frac{I_p}{I_s}$. ### Electromagnetic Waves - Characteristics: Transverse, do not require a medium, travel at speed of light $c = \frac{1}{\sqrt{\mu_0\epsilon_0}}$. - Speed: $c = \nu \lambda$. - Energy density of electric field: $u_E = \frac{1}{2}\epsilon_0 E^2$. - Energy density of magnetic field: $u_B = \frac{1}{2\mu_0} B^2$. - Spectrum (increasing wavelength): Gamma rays ### Optics #### Reflection - Angle of incidence = Angle of reflection. - Mirror formula: $\frac{1}{f} = \frac{1}{v} + \frac{1}{u}$. - Magnification: $m = -\frac{v}{u} = \frac{h'}{h}$. - Concave mirror: $f 0$. #### Refraction - Snell's Law: $n_1 \sin i = n_2 \sin r$. - Refractive index: $n = c/v$. - Critical angle for total internal reflection: $\sin C = \frac{n_2}{n_1}$ ($n_1 > n_2$). - Lens formula: $\frac{1}{f} = \frac{1}{v} - \frac{1}{u}$. - Magnification: $m = \frac{v}{u} = \frac{h'}{h}$. - Power of a lens: $P = \frac{1}{f}$ (in dioptres, $f$ in meters). - Combination of lenses: $P_{eq} = P_1 + P_2 + ...$, $\frac{1}{f_{eq}} = \frac{1}{f_1} + \frac{1}{f_2} + ...$ #### Optical Instruments - **Compound Microscope:** $M = m_o m_e = (\frac{v_o}{u_o})(1 + \frac{D}{f_e})$ (for final image at D). - **Astronomical Telescope:** $M = -\frac{f_o}{f_e}$ (normal adjustment). Length $L = f_o + f_e$. #### Wave Optics - **Huygens' Principle:** Every point on a wavefront is a source of secondary wavelets. - **Interference (Young's Double Slit Experiment):** - Path difference: $\Delta x = d \sin\theta$. - Constructive interference (bright fringe): $\Delta x = n\lambda$. - Destructive interference (dark fringe): $\Delta x = (n + \frac{1}{2})\lambda$. - Fringe width: $\beta = \frac{\lambda D}{d}$. - **Diffraction (Single Slit):** - Condition for minima: $a \sin\theta = n\lambda$. - Width of central maximum: $2\theta = \frac{2\lambda}{a}$. - **Polarization:** Malus' Law: $I = I_0 \cos^2\theta$. ### Dual Nature of Radiation and Matter #### Photoelectric Effect - Einstein's Photoelectric Equation: $h\nu = \phi_0 + K_{max}$, where $\phi_0$ is work function and $K_{max}$ is maximum kinetic energy. - Threshold frequency $\nu_0$: $h\nu_0 = \phi_0$. - Stopping potential $V_0$: $K_{max} = eV_0$. #### De Broglie Wavelength - $\lambda = \frac{h}{p} = \frac{h}{mv}$. - For an electron accelerated through potential $V$: $\lambda = \frac{1.227}{\sqrt{V}} \text{ nm}$. ### Atoms and Nuclei #### Bohr's Model of Hydrogen Atom - Quantization of angular momentum: $L = mvr = \frac{nh}{2\pi}$. - Radius of $n^{th}$ orbit: $r_n \propto n^2$. - Energy of $n^{th}$ orbit: $E_n = -\frac{13.6}{n^2} \text{ eV}$. - Energy difference for transitions: $\Delta E = E_f - E_i = h\nu$. #### Nuclear Structure - Mass defect: $\Delta m = [Z m_p + (A-Z) m_n] - M_{nucleus}$. - Binding energy: $E_b = \Delta m c^2$. - Nuclear density is nearly constant. #### Radioactivity - Law of radioactive decay: $N = N_0 e^{-\lambda t}$. - Half-life: $T_{1/2} = \frac{\ln 2}{\lambda} = \frac{0.693}{\lambda}$. - Mean life: $\tau = \frac{1}{\lambda}$. ### Semiconductor Electronics #### Types of Semiconductors - Intrinsic: Pure Si, Ge. - Extrinsic: - n-type: Doping with pentavalent impurities (P, As). Majority carriers: electrons. - p-type: Doping with trivalent impurities (Al, B). Majority carriers: holes. #### PN Junction Diode - Forward bias: Current flows easily. - Reverse bias: Small leakage current. - Zener diode: Used for voltage regulation (operates in reverse breakdown). #### Rectifiers - Half-wave rectifier: Output frequency = input frequency. - Full-wave rectifier: Output frequency = $2 \times$ input frequency. #### Transistors (BJT) - Current relations: $I_E = I_B + I_C$. - Current gain: - $\alpha = \frac{I_C}{I_E}$ (common base). - $\beta = \frac{I_C}{I_B}$ (common emitter). - Relation between $\alpha$ and $\beta$: $\beta = \frac{\alpha}{1-\alpha}$. #### Logic Gates - **AND Gate:** $Y = A \cdot B$ - **OR Gate:** $Y = A + B$ - **NOT Gate:** $Y = \bar{A}$ - **NAND Gate:** $Y = \overline{A \cdot B}$ (Universal gate) - **NOR Gate:** $Y = \overline{A + B}$ (Universal gate) - **XOR Gate:** $Y = A \oplus B = A\bar{B} + \bar{A}B$