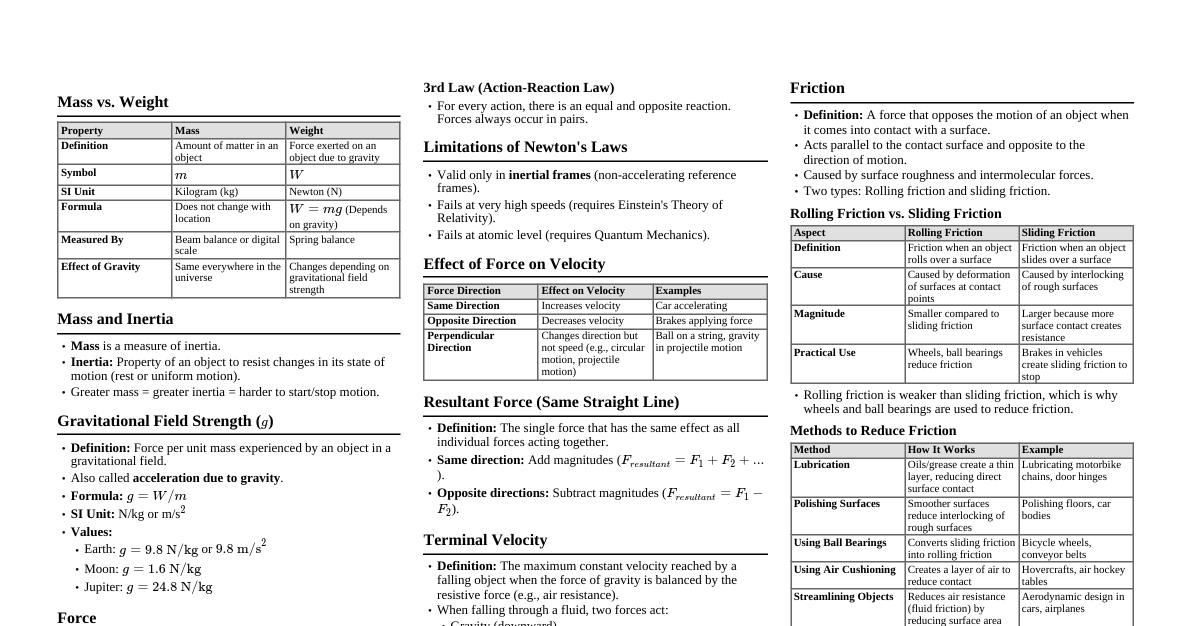
### Arithmetic Basics - **Numbers:** - **Natural Numbers:** $\{1, 2, 3, ...\}$ - **Whole Numbers:** $\{0, 1, 2, 3, ...\}$ - **Integers:** $\{..., -2, -1, 0, 1, 2, ...\}$ - **Rational Numbers:** Numbers that can be written as a fraction $\frac{a}{b}$ where $a, b$ are integers and $b \neq 0$. E.g., $\frac{1}{2}, -3, 0.75$. - **Irrational Numbers:** Numbers that cannot be written as a simple fraction. E.g., $\pi, \sqrt{2}$. - **Real Numbers:** All rational and irrational numbers. - **Operations:** - **Addition (+):** Combining quantities. - **Subtraction (-):** Finding the difference. - **Multiplication (× or *):** Repeated addition. - **Division (÷ or /):** Splitting into equal parts. - **Order of Operations (PEMDAS/BODMAS):** 1. **P**arentheses / **B**rackets 2. **E**xponents / **O**rders 3. **M**ultiplication and **D**ivision (from left to right) 4. **A**ddition and **S**ubtraction (from left to right) ### Fractions, Decimals, & Percentages - **Fractions:** Represent parts of a whole. - **Numerator:** Top number (parts you have). - **Denominator:** Bottom number (total parts). - **Equivalent Fractions:** $\frac{1}{2} = \frac{2}{4}$ - **Adding/Subtracting:** Find a common denominator. - **Multiplying:** Multiply numerators, multiply denominators. $\frac{a}{b} \times \frac{c}{d} = \frac{ac}{bd}$ - **Dividing:** Multiply by the reciprocal of the second fraction. $\frac{a}{b} \div \frac{c}{d} = \frac{a}{b} \times \frac{d}{c}$ - **Decimals:** Another way to represent parts of a whole, based on powers of 10. - **Conversion:** Fraction to decimal: Divide numerator by denominator. Decimal to fraction: Place digits over power of 10 and simplify. - **Percentages:** Parts per hundred. - **Conversion:** Decimal to percent: Multiply by 100 and add % sign. Percent to decimal: Divide by 100. - **Calculating Percentages:** "What is 20% of 50?" $\rightarrow 0.20 \times 50 = 10$. ### Exponents & Roots - **Exponents:** $a^n = a \times a \times ... \times a$ (n times) - **Product Rule:** $a^m \times a^n = a^{m+n}$ - **Quotient Rule:** $\frac{a^m}{a^n} = a^{m-n}$ - **Power Rule:** $(a^m)^n = a^{mn}$ - **Zero Exponent:** $a^0 = 1$ (for $a \neq 0$) - **Negative Exponent:** $a^{-n} = \frac{1}{a^n}$ - **Fractional Exponent:** $a^{m/n} = \sqrt[n]{a^m}$ - **Roots:** The inverse of exponents. - **Square Root:** $\sqrt{x}$ (finds a number that, when multiplied by itself, equals $x$) - **Cube Root:** $\sqrt[3]{x}$ - **Properties:** $\sqrt{ab} = \sqrt{a}\sqrt{b}$, $\sqrt{\frac{a}{b}} = \frac{\sqrt{a}}{\sqrt{b}}$ ### Algebra Basics - **Variables:** Letters representing unknown values (e.g., $x, y, a$). - **Expressions:** Combinations of variables, numbers, and operations (e.g., $3x + 5$). - **Equations:** Statements that two expressions are equal (e.g., $3x + 5 = 11$). - **Solving Linear Equations:** Isolate the variable using inverse operations. - Example: $2x - 3 = 7$ 1. Add 3 to both sides: $2x = 10$ 2. Divide by 2: $x = 5$ - **Inequalities:** Comparisons between expressions ($ , \le, \ge$). - Solving: Similar to equations, but flip the inequality sign if multiplying or dividing by a negative number. - Example: $-2x > 6 \rightarrow x ### Functions - **Definition:** A relation where each input (domain) has exactly one output (range). - Represented as $y = f(x)$. - **Types of Functions:** - **Linear:** $f(x) = mx + b$ (straight line) - $m$: slope (rate of change) - $b$: y-intercept (where line crosses y-axis) - **Quadratic:** $f(x) = ax^2 + bx + c$ (parabola) - Vertex: turning point. - **Exponential:** $f(x) = a \cdot b^x$ (rapid growth/decay) - **Absolute Value:** $f(x) = |x|$ (V-shape) - **Rational:** $f(x) = \frac{P(x)}{Q(x)}$ (fraction of polynomials) - **Graphing Functions:** Plotting input-output pairs on a coordinate plane $(x, y)$. - **Domain & Range:** - **Domain:** All possible input values ($x$). - **Range:** All possible output values ($y$). ### Geometry - **Basic Shapes:** - **Perimeter:** Distance around a 2D shape. - **Area:** Space inside a 2D shape. - **Volume:** Space inside a 3D shape. - **Formulas:** - **Square:** Perimeter $P=4s$, Area $A=s^2$ - **Rectangle:** Perimeter $P=2l+2w$, Area $A=lw$ - **Triangle:** Perimeter $P=a+b+c$, Area $A=\frac{1}{2}bh$ - **Circle:** Circumference $C=2\pi r$ or $C=\pi d$, Area $A=\pi r^2$ - **Cube:** Volume $V=s^3$ - **Rectangular Prism:** Volume $V=lwh$ - **Cylinder:** Volume $V=\pi r^2 h$ - **Cone:** Volume $V=\frac{1}{3}\pi r^2 h$ - **Sphere:** Volume $V=\frac{4}{3}\pi r^3$, Surface Area $A=4\pi r^2$ - **Angles:** - **Acute:** $ 90^\circ$ - **Straight:** $=180^\circ$ - **Complementary:** Sum to $90^\circ$ - **Supplementary:** Sum to $180^\circ$ - **Pythagorean Theorem:** For a right triangle with legs $a, b$ and hypotenuse $c$: $a^2 + b^2 = c^2$. - **Transformations:** - **Translation:** Sliding a shape. - **Rotation:** Turning a shape. - **Reflection:** Flipping a shape. - **Dilation:** Resizing a shape. ### Trigonometry - **Right Triangle Ratios (SOH CAH TOA):** - $\sin(\theta) = \frac{\text{Opposite}}{\text{Hypotenuse}}$ - $\cos(\theta) = \frac{\text{Adjacent}}{\text{Hypotenuse}}$ - $\tan(\theta) = \frac{\text{Opposite}}{\text{Adjacent}}$ - **Reciprocal Identities:** - $\csc(\theta) = \frac{1}{\sin(\theta)}$ - $\sec(\theta) = \frac{1}{\cos(\theta)}$ - $\cot(\theta) = \frac{1}{\tan(\theta)}$ - **Unit Circle:** A circle with radius 1 centered at the origin, used to define trig functions for all angles. - A point $(x,y)$ on the unit circle corresponds to $(\cos\theta, \sin\theta)$. - **Trigonometric Graphs:** Sine, Cosine, Tangent waves. - **Amplitude:** Height of the wave. - **Period:** Length of one full cycle. - **Phase Shift:** Horizontal shift. - **Vertical Shift:** Vertical shift. ### Statistics & Probability - **Statistics:** The study of collecting, analyzing, interpreting, presenting, and organizing data. - **Measures of Central Tendency:** - **Mean:** Average (sum of values / count of values). - **Median:** Middle value when data is ordered. - **Mode:** Most frequent value. - **Measures of Spread:** - **Range:** Max value - Min value. - **Quartiles:** Divide data into four equal parts. - **Interquartile Range (IQR):** $Q_3 - Q_1$. - **Types of Graphs:** Bar graphs, histograms, pie charts, line graphs, scatter plots. - **Probability:** The likelihood of an event occurring. - **Formula:** $P(\text{Event}) = \frac{\text{Number of favorable outcomes}}{\text{Total number of possible outcomes}}$ - **Independent Events:** Outcome of one does not affect the other. $P(A \text{ and } B) = P(A) \times P(B)$ - **Dependent Events:** Outcome of one affects the other. - **Mutually Exclusive Events:** Cannot happen at the same time. $P(A \text{ or } B) = P(A) + P(B)$