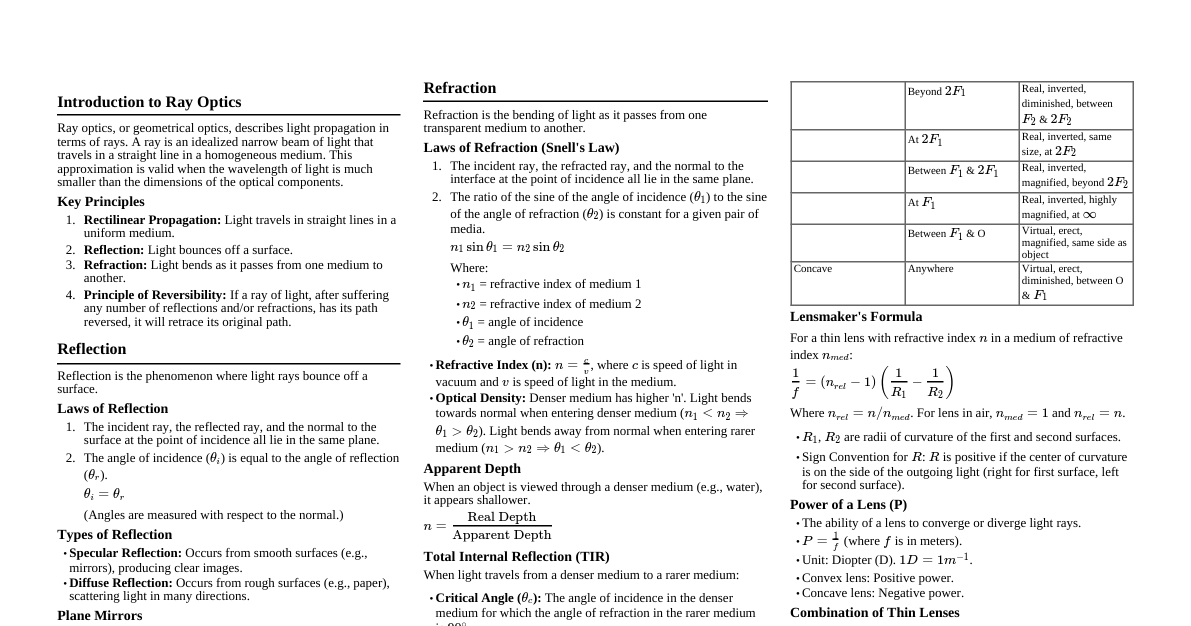
Spherical Mirrors: Overview Definition: A mirror that forms part of the surface of a sphere. Types: Concave Mirror: Reflecting surface is curved inward (like a spoon). Converging mirror. Convex Mirror: Reflecting surface is curved outward. Diverging mirror. Key Terms: Pole (P): Geometric center of the mirror's reflecting surface. Center of Curvature (C): Center of the sphere from which the mirror is a part. Radius of Curvature (R): Distance between P and C. ($R = PC$) Principal Axis: Line passing through P and C. Focus (F): Point on the principal axis where parallel rays converge (concave) or appear to diverge from (convex) after reflection. Focal Length (f): Distance between P and F. ($f = PF$) Relation between R and f For spherical mirrors with small apertures, the focal length is half the radius of curvature: $$ f = \frac{R}{2} $$ For concave mirrors, $R$ and $f$ are positive. For convex mirrors, $R$ and $f$ are negative. Mirror Formula and Magnification Mirror Formula Relates object distance ($u$), image distance ($v$), and focal length ($f$): $$ \frac{1}{f} = \frac{1}{u} + \frac{1}{v} $$ $u$: Object distance from the pole. $v$: Image distance from the pole. $f$: Focal length of the mirror. Linear Magnification (m) Ratio of image height ($h_i$) to object height ($h_o$), also related to $u$ and $v$: $$ m = \frac{h_i}{h_o} = -\frac{v}{u} $$ $m > 0$: Image is erect (virtual). $m $|m| > 1$: Image is magnified. $|m| $|m| = 1$: Image is same size. Sign Convention (New Cartesian Sign Convention) Origin: Pole (P) of the mirror. Principal Axis: X-axis. Incident Light: Travels from left to right. Distances: Measured from the pole. Measured in the direction of incident light are positive. Measured opposite to the direction of incident light are negative. Heights: Measured upwards (perpendicular to principal axis) are positive. Measured downwards (perpendicular to principal axis) are negative. Quantity Concave Mirror Convex Mirror Focal Length ($f$) Negative Positive Radius of Curvature ($R$) Negative Positive Object Distance ($u$) Always Negative Always Negative Image Distance ($v$) Can be positive or negative Always Positive Image Formation by Concave Mirror Nature, position, and size of the image depend on the object's position. Object Position Image Position Nature Size At infinity At F Real & Inverted Highly Diminished Beyond C Between F & C Real & Inverted Diminished At C At C Real & Inverted Same Size Between C & F Beyond C Real & Inverted Magnified At F At infinity Real & Inverted Highly Magnified Between F & P Behind the mirror Virtual & Erect Magnified Image Formation by Convex Mirror Convex mirrors always form virtual, erect, and diminished images. Object Position Image Position Nature Size At infinity At F (behind mirror) Virtual & Erect Highly Diminished Between infinity & P Between P & F (behind mirror) Virtual & Erect Diminished Uses of Spherical Mirrors Concave Mirrors: Shaving mirrors (magnified, erect image when face is between F and P). Dentist's mirrors (magnified image of teeth). Headlights of cars, searchlights (produce parallel beam when bulb is at F). Solar furnaces (concentrate sunlight at F). Convex Mirrors: Rear-view mirrors in vehicles (wide field of view, diminished image). Security mirrors in shops. Street light reflectors.