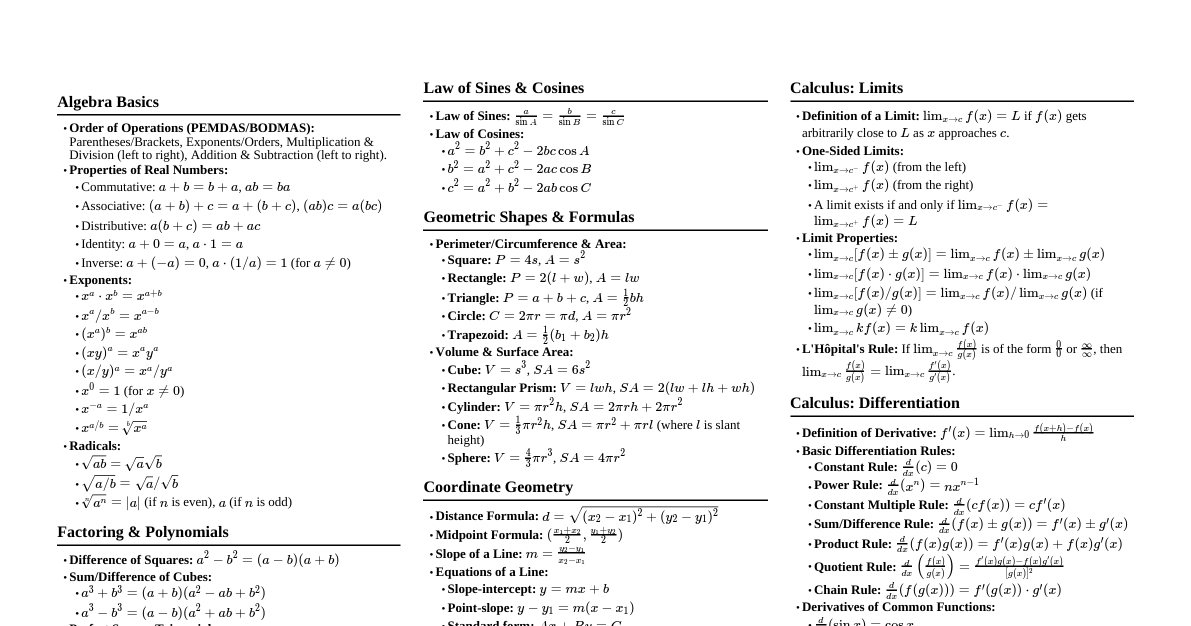
Right Circular Cone Definition: A cone whose axis is perpendicular to the base. Characteristics: A cone is formed by connecting all points on a circular base to a single point, the apex or vertex. For a right circular cone, the line segment from the vertex to the center of the base is perpendicular to the base. Key Components: Vertex (A): The pointed top of the cone. Height (AB or $h$): The perpendicular distance from the vertex to the center of the base. Radius (BC or $r$): The radius of the circular base. Slant Height (AC or $l$): The distance from the vertex to any point on the circumference of the base. Relationship between $l, r, h$: These three dimensions are related by the Pythagorean theorem: $l^2 = r^2 + h^2$. This is because the height, radius, and slant height form a right-angled triangle. Curved Surface Area (CSA): The area of the sloped surface of the cone, excluding the base. Formula: $\text{CSA} = \pi r l$ Total Surface Area (TSA): The sum of the curved surface area and the area of the circular base. Area of base = $\pi r^2$ Formula: $\text{TSA} = \pi r l + \pi r^2 = \pi r (l + r)$ Volume: The amount of space occupied by the cone. Formula: $\text{Volume} = \frac{1}{3} \pi r^2 h$ Sphere Definition: A perfectly round three-dimensional object, where every point on its surface is equidistant from its center. This distance is called the radius ($r$). Characteristics: Has no edges or vertices. Is perfectly symmetrical. Surface Area (SA): The total area of the outer surface of the sphere. Formula: $\text{SA} = 4 \pi r^2$ Volume: The amount of space enclosed by the sphere. Formula: $\text{Volume} = \frac{4}{3} \pi r^3$ Hemisphere Definition: Exactly half of a sphere. When a sphere is cut into two equal halves through its center, each half is a hemisphere. Characteristics: Consists of a curved surface and a flat circular base. The radius of the hemisphere is the same as the radius of the original sphere. Curved Surface Area (CSA): The area of the rounded part of the hemisphere. Formula: $\text{CSA} = 2 \pi r^2$ (half of a sphere's surface area) Total Surface Area (TSA): The sum of the curved surface area and the area of its flat circular base. Area of circular base = $\pi r^2$ Formula: $\text{TSA} = 2 \pi r^2 + \pi r^2 = 3 \pi r^2$ Volume: The amount of space enclosed by the hemisphere. Formula: $\text{Volume} = \frac{2}{3} \pi r^3$ (half of a sphere's volume) Summary of Formulas for Common 3D Shapes This table provides a quick reference for the surface areas and volumes of the discussed geometric shapes, where $r$ is the radius, $h$ is the height, and $l$ is the slant height. Shape Curved Surface Area (CSA) Total Surface Area (TSA) Volume Right Circular Cone $\pi r l$ $\pi r(l+r)$ $\frac{1}{3} \pi r^2 h$ Sphere $4 \pi r^2$ $4 \pi r^2$ $\frac{4}{3} \pi r^3$ Hemisphere $2 \pi r^2$ $3 \pi r^2$ $\frac{2}{3} \pi r^3$ Example Problems - Right Circular Cone Let's apply the formulas to solve some typical problems involving cones. Example 1: Calculate Curved Surface Area Problem: Find the curved surface area of a cone with a slant height $l=10$ cm and a base radius $r=7$ cm. Formula Used: CSA $= \pi r l$ Calculation: Using $\pi = \frac{22}{7}$ $\text{CSA} = \frac{22}{7} \times 7 \text{ cm} \times 10 \text{ cm}$ $\text{CSA} = 22 \times 10 = 220 \text{ cm}^2$ Answer: The curved surface area of the cone is $220 \text{ cm}^2$. Example 2: Calculate Total Surface Area Problem: A cone has a height $h=16$ cm and a base radius $r=12$ cm. Calculate its total surface area. Step 1: Find the slant height ($l$). We know $l^2 = r^2 + h^2$ $l^2 = (12 \text{ cm})^2 + (16 \text{ cm})^2 = 144 + 256 = 400$ $l = \sqrt{400} = 20 \text{ cm}$ Step 2: Calculate Curved Surface Area (CSA). $\text{CSA} = \pi r l = 3.14 \times 12 \text{ cm} \times 20 \text{ cm} = 753.6 \text{ cm}^2$ Step 3: Calculate Total Surface Area (TSA). $\text{TSA} = \pi r (l+r) = 3.14 \times 12 \text{ cm} \times (20 \text{ cm} + 12 \text{ cm})$ $\text{TSA} = 3.14 \times 12 \times 32 = 1205.76 \text{ cm}^2$ Answer: The total surface area of the cone is $1205.76 \text{ cm}^2$. Example 3: Calculate Volume of a Cone Problem: A conical tent has a height of $9$ m and a base diameter of $24$ m. Find the volume of air it can hold. Given: Height $h=9$ m. Diameter $D=24$ m, so radius $r = D/2 = 12$ m. Formula Used: Volume $= \frac{1}{3} \pi r^2 h$ Calculation: Using $\pi \approx 3.14$ $\text{Volume} = \frac{1}{3} \times 3.14 \times (12 \text{ m})^2 \times 9 \text{ m}$ $\text{Volume} = \frac{1}{3} \times 3.14 \times 144 \times 9$ $\text{Volume} = 3.14 \times 48 \times 9 = 1356.48 \text{ m}^3$ Answer: The conical tent can hold $1356.48 \text{ m}^3$ of air. Example Problems - Sphere and Hemisphere Here are some problems demonstrating the use of sphere and hemisphere formulas. Example 4: Calculate Surface Area of a Sphere Problem: Find the surface area of a sphere whose radius $r=7$ cm. Formula Used: SA $= 4 \pi r^2$ Calculation: Using $\pi = \frac{22}{7}$ $\text{SA} = 4 \times \frac{22}{7} \times (7 \text{ cm})^2$ $\text{SA} = 4 \times \frac{22}{7} \times 49 = 4 \times 22 \times 7 = 616 \text{ cm}^2$ Answer: The surface area of the sphere is $616 \text{ cm}^2$. Example 5: Calculate Areas of a Hemisphere Problem: A hemispherical bowl has a radius $r=21$ cm. Calculate its curved surface area and total surface area. Step 1: Calculate Curved Surface Area (CSA). Formula: $\text{CSA} = 2 \pi r^2$ $\text{CSA} = 2 \times \frac{22}{7} \times (21 \text{ cm})^2 = 2 \times \frac{22}{7} \times 441$ $\text{CSA} = 2 \times 22 \times 63 = 2772 \text{ cm}^2$ Step 2: Calculate Total Surface Area (TSA). Formula: $\text{TSA} = 3 \pi r^2$ $\text{TSA} = 3 \times \frac{22}{7} \times (21 \text{ cm})^2 = 3 \times \frac{22}{7} \times 441$ $\text{TSA} = 3 \times 22 \times 63 = 4158 \text{ cm}^2$ Answer: The curved surface area is $2772 \text{ cm}^2$ and the total surface area is $4158 \text{ cm}^2$. Example 6: Calculate Volume of a Sphere Problem: A spherical ball has a radius $r=11.2$ cm. Find its volume. Formula Used: Volume $= \frac{4}{3} \pi r^3$ Calculation: Using $\pi \approx 3.14$ $\text{Volume} = \frac{4}{3} \times 3.14 \times (11.2 \text{ cm})^3$ $\text{Volume} = \frac{4}{3} \times 3.14 \times 1404.928 \approx 5887.32 \text{ cm}^3$ Answer: The volume of the spherical ball is approximately $5887.32 \text{ cm}^3$. Example 7: Calculate Volume of a Hemispherical Bowl Problem: A hemispherical bowl has a radius $r=3.5$ cm. Find the volume of liquid it can hold. Formula Used: Volume $= \frac{2}{3} \pi r^3$ Calculation: Using $\pi = \frac{22}{7}$ $\text{Volume} = \frac{2}{3} \times \frac{22}{7} \times (3.5 \text{ cm})^3$ $\text{Volume} = \frac{2}{3} \times \frac{22}{7} \times 3.5 \times 3.5 \times 3.5$ $\text{Volume} = \frac{2}{3} \times 22 \times 0.5 \times 3.5 \times 3.5$ $\text{Volume} = \frac{2}{3} \times 22 \times 6.125 \approx 89.83 \text{ cm}^3$ Answer: The hemispherical bowl can hold approximately $89.83 \text{ cm}^3$ of liquid.