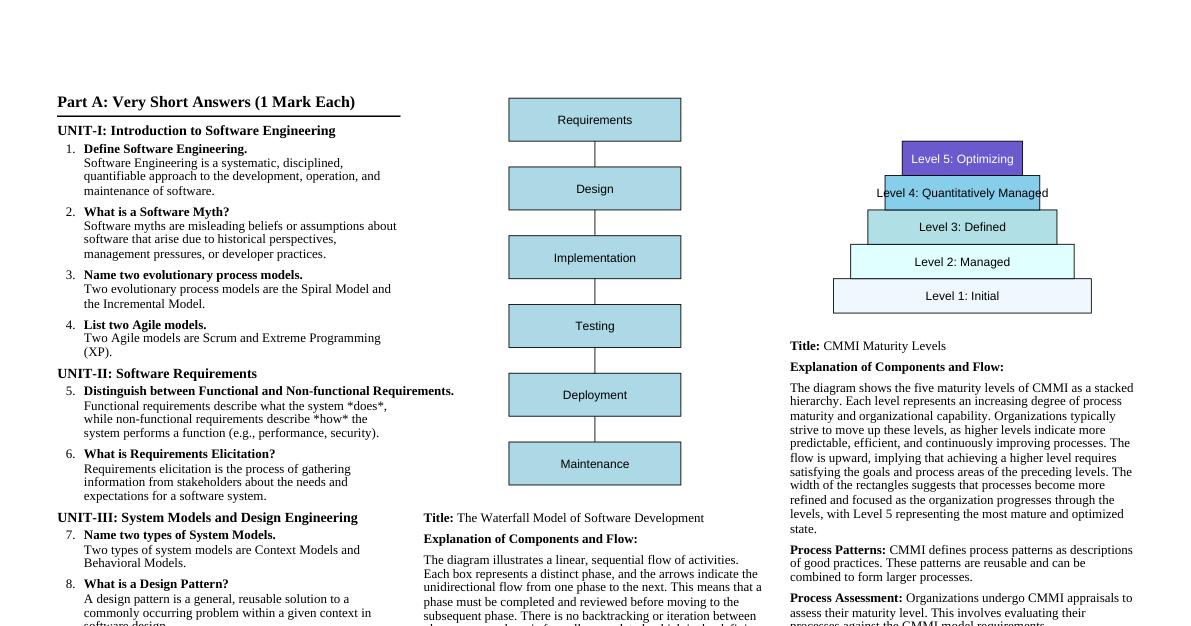
### Introduction to Software Project Management - **Definition:** Software Project Management is the discipline of planning, organizing, staffing, executing, controlling, and closing software projects. It ensures that software projects are completed on time, within budget, and according to specifications. - **Key Goals:** - Deliver high-quality software - Meet stakeholder requirements - Manage risks and changes - Optimize resource utilization - Ensure project profitability ### Software Project Lifecycle The typical phases in a software project lifecycle include: 1. **Initiation:** - Define project scope and objectives. - Identify stakeholders and their needs. - Feasibility study and business case development. 2. **Planning:** - Develop project plan (scope, schedule, budget, resources). - Risk management planning. - Quality management planning. - Communication planning. 3. **Execution:** - Team formation and task assignment. - Software development (coding, testing). - Regular progress monitoring. 4. **Monitoring & Control:** - Track project progress against the plan. - Manage changes, risks, and issues. - Report performance to stakeholders. - Quality assurance activities. 5. **Closure:** - Deliver final product. - Obtain formal acceptance. - Conduct post-project review/lessons learned. - Release resources. ### Key Planning Elements - **Scope Management:** Defining what is and is not included in the project. - Requirements gathering - Scope statement - Work Breakdown Structure (WBS) - **Time Management:** Creating and managing the project schedule. - Activity definition - Sequencing activities - Estimating durations - Developing and controlling the schedule (Gantt charts, Critical Path Method - CPM) - **Cost Management:** Estimating, budgeting, and controlling project costs. - Cost estimation techniques (e.g., COCOMO, function point analysis) - Budget formulation - Earned Value Management (EVM) - **Resource Management:** Identifying, acquiring, and managing the team and physical resources. - **Risk Management:** Identifying, assessing, and responding to project risks. - Risk identification - Risk analysis (qualitative, quantitative) - Risk response planning (avoid, mitigate, transfer, accept) - **Quality Management:** Ensuring the project meets specified quality standards. - Quality planning - Quality assurance - Quality control ### Software Project Methodologies - **Waterfall Model:** - Sequential, linear approach. - Phases completed entirely before the next begins. - Good for well-understood requirements, stable environments. - Less flexible to changes. - **Agile Methodologies (e.g., Scrum, Kanban):** - Iterative and incremental. - Focus on flexibility, collaboration, and customer feedback. - Delivers working software frequently. - **Scrum:** Sprints, daily stand-ups, product backlog, sprint backlog, Scrum Master. - **Kanban:** Visual workflow, limits Work-In-Progress (WIP), continuous flow. - **V-Model:** - Extension of Waterfall, emphasizes verification and validation at each stage. - Testing phases correspond to development phases. - **Spiral Model:** - Iterative, risk-driven approach. - Combines elements of Waterfall and prototyping. - Each cycle addresses risks and builds a more complete version. ### Project Management Tools - **Planning & Scheduling:** Microsoft Project, Jira, Asana, Trello - **Collaboration:** Slack, Microsoft Teams, Confluence - **Version Control:** Git, SVN - **Testing:** Selenium, JUnit, TestRail - **Requirements Management:** Jira, Azure DevOps, IBM DOORS