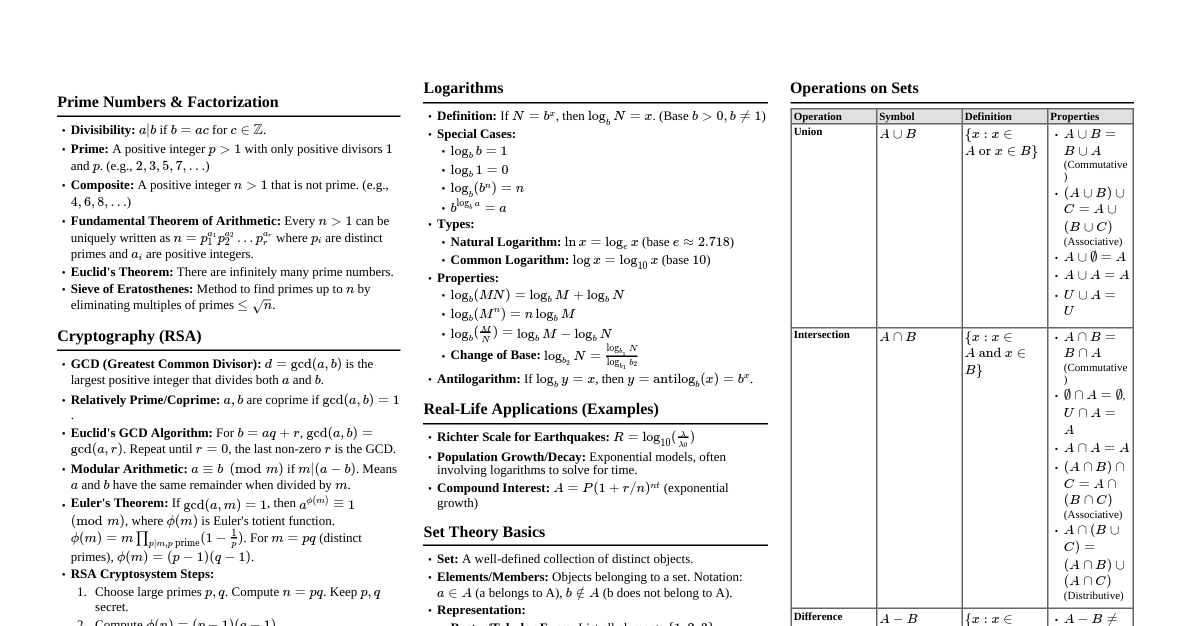
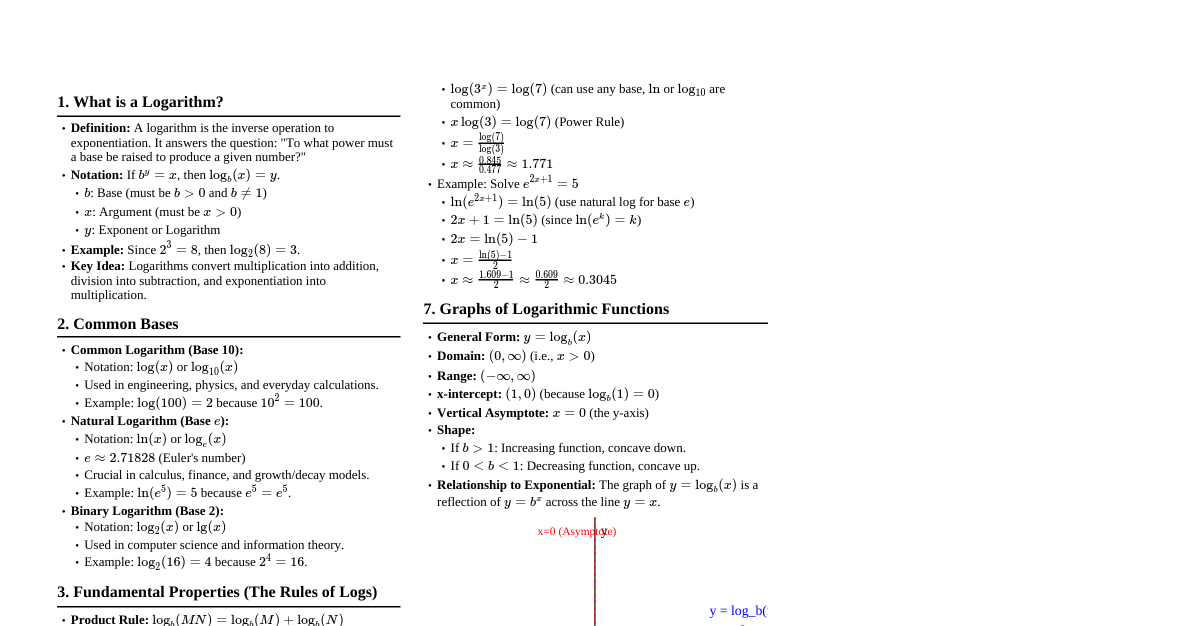
1. Number Systems & Basic Operations Natural Numbers: $N = \{1, 2, 3, ...\}$ Whole Numbers: $W = \{0, 1, 2, 3, ...\}$ Integers: $Z = \{..., -2, -1, 0, 1, 2, ...\}$ Rational Numbers: $Q = \{\frac{p}{q} \mid p, q \in Z, q \neq 0\}$ Irrational Numbers: Non-terminating, non-repeating decimals (e.g., $\sqrt{2}, \pi, e$) Real Numbers: $R = Q \cup \text{Irrational Numbers}$ Even Numbers: Numbers divisible by 2 ($2n$) Odd Numbers: Numbers not divisible by 2 ($2n+1$) Prime Numbers: Numbers greater than 1, only divisible by 1 and themselves (e.g., 2, 3, 5, 7, 11) Composite Numbers: Numbers greater than 1 that are not prime (e.g., 4, 6, 8, 9, 10) Divisibility Rules: By 2: Last digit is even. By 3: Sum of digits is divisible by 3. By 4: Last two digits are divisible by 4. By 5: Last digit is 0 or 5. By 6: Divisible by both 2 and 3. By 9: Sum of digits is divisible by 9. By 10: Last digit is 0. By 11: Difference of sum of alternate digits is 0 or divisible by 11. BODMAS/PEMDAS Rule: Brackets/Parentheses Orders/Exponents Division & Multiplication (from left to right) Addition & Subtraction (from left to right) 2. Fractions and Decimals Types of Fractions: Proper: Numerator Improper: Numerator $\ge$ Denominator (e.g., $\frac{3}{2}$) Mixed: Whole number + Proper fraction (e.g., $1\frac{1}{2}$) Addition/Subtraction: Find common denominator. $\frac{a}{b} \pm \frac{c}{d} = \frac{ad \pm bc}{bd}$ Multiplication: $\frac{a}{b} \times \frac{c}{d} = \frac{ac}{bd}$ Division: $\frac{a}{b} \div \frac{c}{d} = \frac{a}{b} \times \frac{d}{c} = \frac{ad}{bc}$ Decimal to Fraction: $0.25 = \frac{25}{100} = \frac{1}{4}$ Recurring Decimal to Fraction: $0.\overline{a} = \frac{a}{9}$ $0.\overline{ab} = \frac{ab}{99}$ $0.a\overline{b} = \frac{ab-a}{90}$ $0.ab\overline{c} = \frac{abc-ab}{900}$ 3. HCF and LCM HCF (Highest Common Factor) / GCD (Greatest Common Divisor): Largest number that divides two or more numbers exactly. LCM (Least Common Multiple): Smallest number that is a multiple of two or more numbers. Methods: Prime Factorization, Division Method. Product of two numbers: $N_1 \times N_2 = \text{HCF}(N_1, N_2) \times \text{LCM}(N_1, N_2)$ HCF of Fractions: $\frac{\text{HCF of numerators}}{\text{LCM of denominators}}$ LCM of Fractions: $\frac{\text{LCM of numerators}}{\text{HCF of denominators}}$ HCF of Decimals: Convert to fractions, then use fraction HCF. LCM of Decimals: Convert to fractions, then use fraction LCM. 4. Percentages Percentage Formula: $\text{Value} = \frac{\text{Percentage}}{100} \times \text{Whole}$ Percentage Increase: $\frac{\text{New Value} - \text{Original Value}}{\text{Original Value}} \times 100\%$ Percentage Decrease: $\frac{\text{Original Value} - \text{New Value}}{\text{Original Value}} \times 100\%$ If A is $x\%$ more than B: $A = B(1 + \frac{x}{100})$. Then B is $\frac{x}{100+x} \times 100\%$ less than A. If A is $x\%$ less than B: $A = B(1 - \frac{x}{100})$. Then B is $\frac{x}{100-x} \times 100\%$ more than A. Net Change (Successive Percentages): If an item changes by $x\%$ then by $y\%$, net change is $(x+y+\frac{xy}{100})\%$. Population Growth: $P_n = P_0(1 + \frac{R}{100})^n$ (for $n$ years) Depreciation: $V_n = V_0(1 - \frac{R}{100})^n$ (for $n$ years) 5. Profit and Loss Cost Price (CP): Price at which an article is purchased. Selling Price (SP): Price at which an article is sold. Marked Price (MP): Price listed on the article. Profit (P): $SP - CP$ (if $SP > CP$) Loss (L): $CP - SP$ (if $CP > SP$) Profit Percentage: $\frac{\text{Profit}}{CP} \times 100\%$ Loss Percentage: $\frac{\text{Loss}}{CP} \times 100\%$ SP from CP & Profit%: $SP = CP \times (1 + \frac{\text{Profit}\%}{100})$ SP from CP & Loss%: $SP = CP \times (1 - \frac{\text{Loss}\%}{100})$ CP from SP & Profit%: $CP = SP \times \frac{100}{100 + \text{Profit}\%}$ CP from SP & Loss%: $CP = SP \times \frac{100}{100 - \text{Loss}\%}$ Discount: Always calculated on Marked Price (MP). $\text{Discount} = MP - SP$ Discount Percentage: $\frac{\text{Discount}}{MP} \times 100\%$ Successive Discounts: Two successive discounts of $d_1\%$ and $d_2\%$ are equivalent to a single discount of $(d_1 + d_2 - \frac{d_1 d_2}{100})\%$. 6. Simple and Compound Interest Principal (P): Initial amount. Rate (R): Interest rate per annum (in %). Time (T): Time period in years. Simple Interest (SI): $SI = \frac{P \times R \times T}{100}$ Amount (A) for SI: $A = P + SI = P(1 + \frac{RT}{100})$ Compound Interest (CI): Amount (A) compounded annually: $A = P(1 + \frac{R}{100})^T$ CI: $CI = A - P$ Compounded Half-yearly: $A = P(1 + \frac{R/2}{100})^{2T}$ Compounded Quarterly: $A = P(1 + \frac{R/4}{100})^{4T}$ Compounded Monthly: $A = P(1 + \frac{R/12}{100})^{12T}$ Compounded Annually, different rates: $A = P(1 + \frac{R_1}{100})(1 + \frac{R_2}{100})...$ Difference between CI and SI for 2 years: $P(\frac{R}{100})^2$ Difference between CI and SI for 3 years: $P(\frac{R}{100})^2(3 + \frac{R}{100})$ 7. Ratio and Proportion Ratio: $a:b$ or $\frac{a}{b}$. Order matters. Proportion: $a:b :: c:d \implies \frac{a}{b} = \frac{c}{d} \implies ad = bc$ (Product of Extremes = Product of Means) Compound Ratio: $(a:b)$ and $(c:d)$ is $ac:bd$. Duplicate Ratio: Of $a:b$ is $a^2:b^2$. Sub-duplicate Ratio: Of $a:b$ is $\sqrt{a}:\sqrt{b}$. Triplicate Ratio: Of $a:b$ is $a^3:b^3$. Sub-triplicate Ratio: Of $a:b$ is $\sqrt[3]{a}:\sqrt[3]{b}$. Mean Proportional: Between $a$ and $b$ is $\sqrt{ab}$ ($a:x :: x:b$). Third Proportional: To $a$ and $b$ is $\frac{b^2}{a}$ ($a:b :: b:x$). Fourth Proportional: To $a, b, c$ is $\frac{bc}{a}$ ($a:b :: c:x$). Componendo: If $\frac{a}{b} = \frac{c}{d}$, then $\frac{a+b}{b} = \frac{c+d}{d}$ Dividendo: If $\frac{a}{b} = \frac{c}{d}$, then $\frac{a-b}{b} = \frac{c-d}{d}$ Componendo & Dividendo: If $\frac{a}{b} = \frac{c}{d}$, then $\frac{a+b}{a-b} = \frac{c+d}{c-d}$ 8. Averages Average (Mean): $\text{Average} = \frac{\text{Sum of all observations}}{\text{Number of observations}}$ Weighted Average: $\frac{w_1x_1 + w_2x_2 + \dots + w_nx_n}{w_1 + w_2 + \dots + w_n}$ Average Speed: $\frac{\text{Total Distance}}{\text{Total Time}}$. Not $\frac{v_1+v_2}{2}$. If a person travels distance D at speed $v_1$ and returns at speed $v_2$: Average speed = $\frac{2v_1v_2}{v_1+v_2}$ If a person travels 3 equal distances at speeds $v_1, v_2, v_3$: Average speed = $\frac{3}{\frac{1}{v_1} + \frac{1}{v_2} + \frac{1}{v_3}}$ Average of first 'n' natural numbers: $\frac{n+1}{2}$ Average of first 'n' even numbers: $n+1$ Average of first 'n' odd numbers: $n$ 9. Time and Work Work Rate: If a person can do a piece of work in $n$ days, then in one day, the person does $\frac{1}{n}$ of the work. Combined Work: If A does work in $x$ days and B in $y$ days, together they do it in $\frac{xy}{x+y}$ days. Men, Days, Work: $\frac{M_1 D_1 H_1}{W_1} = \frac{M_2 D_2 H_2}{W_2}$ (where H is hours per day) Efficiency: Work done per unit time. Efficiency $\propto \frac{1}{\text{Time taken}}$. Pipes and Cisterns: (Similar to Time and Work) Inlet pipe fills a tank in $x$ hours, fills $\frac{1}{x}$ of tank in 1 hour. Outlet pipe empties a tank in $y$ hours, empties $\frac{1}{y}$ of tank in 1 hour. Net part filled in 1 hour (if both open): $\frac{1}{x} - \frac{1}{y}$ (if $y>x$, tank fills; if $x>y$, tank empties) If multiple inlets and outlets: $\frac{1}{T} = \sum \frac{1}{T_{inlets}} - \sum \frac{1}{T_{outlets}}$ 10. Time, Speed and Distance Speed: $\text{Speed} = \frac{\text{Distance}}{\text{Time}}$ Distance: $\text{Distance} = \text{Speed} \times \text{Time}$ Time: $\text{Time} = \frac{\text{Distance}}{\text{Speed}}$ Conversion: $1 \text{ km/hr} = \frac{5}{18} \text{ m/s}$; $1 \text{ m/s} = \frac{18}{5} \text{ km/hr}$ Relative Speed: Same direction: $|v_1 - v_2|$ Opposite direction: $v_1 + v_2$ Trains: Time taken by a train of length $L$ to pass a pole/man: $\frac{L}{\text{Speed}}$ Time taken by a train of length $L_T$ to pass a platform/bridge of length $L_P$: $\frac{L_T + L_P}{\text{Speed}}$ Time taken by two trains of length $L_1, L_2$ and speeds $v_1, v_2$ to pass each other: Same direction: $\frac{L_1 + L_2}{|v_1 - v_2|}$ Opposite direction: $\frac{L_1 + L_2}{v_1 + v_2}$ Boats and Streams: Speed of boat in still water = $u$ Speed of stream = $v$ Downstream Speed: $S_D = u+v$ Upstream Speed: $S_U = u-v$ $u = \frac{S_D + S_U}{2}$ $v = \frac{S_D - S_U}{2}$ 11. Area and Perimeter (Basic 2D Shapes) Rectangle: Area: $L \times W$ Perimeter: $2(L+W)$ Diagonal: $\sqrt{L^2 + W^2}$ Square: Area: $s^2$ or $\frac{1}{2}d^2$ (where $d$ is diagonal) Perimeter: $4s$ Diagonal: $s\sqrt{2}$ Triangle: Area: $\frac{1}{2} \times \text{base} \times \text{height}$ Area (Heron's Formula): $\sqrt{s(s-a)(s-b)(s-c)}$, where $s = \frac{a+b+c}{2}$ (semi-perimeter) Perimeter: $a+b+c$ Equilateral Triangle (side $a$): Area = $\frac{\sqrt{3}}{4}a^2$, Height = $\frac{\sqrt{3}}{2}a$ Circle: Area: $\pi r^2$ Circumference: $2\pi r$ or $\pi d$ Area of Sector (angle $\theta$ in degrees): $\frac{\theta}{360} \times \pi r^2$ Length of Arc (angle $\theta$ in degrees): $\frac{\theta}{360} \times 2\pi r$ Parallelogram: Area: $\text{base} \times \text{height}$ Perimeter: $2(\text{side}_1 + \text{side}_2)$ Rhombus: Area: $\frac{1}{2} d_1 d_2$ (where $d_1, d_2$ are diagonals) Perimeter: $4 \times \text{side}$ Trapezoid: Area: $\frac{1}{2} \times (\text{sum of parallel sides}) \times \text{height}$ 12. Volume and Surface Area (Basic 3D Shapes) Cube (side $a$): Volume: $a^3$ Lateral Surface Area: $4a^2$ Total Surface Area: $6a^2$ Diagonal: $a\sqrt{3}$ Cuboid (L, W, H): Volume: $L \times W \times H$ Lateral Surface Area: $2H(L+W)$ Total Surface Area: $2(LW + LH + WH)$ Diagonal: $\sqrt{L^2 + W^2 + H^2}$ Cylinder (radius $r$, height $h$): Volume: $\pi r^2 h$ Curved Surface Area: $2\pi rh$ Total Surface Area: $2\pi r(r+h)$ Cone (radius $r$, height $h$, slant height $l = \sqrt{r^2+h^2}$): Volume: $\frac{1}{3}\pi r^2 h$ Curved Surface Area: $\pi r l$ Total Surface Area: $\pi r (r+l)$ Sphere (radius $r$): Volume: $\frac{4}{3}\pi r^3$ Surface Area: $4\pi r^2$ Hemisphere (radius $r$): Volume: $\frac{2}{3}\pi r^3$ Curved Surface Area: $2\pi r^2$ Total Surface Area: $3\pi r^2$ 13. Algebra Basics (Relevant to Arithmetic) Basic Identities: $(a+b)^2 = a^2 + 2ab + b^2$ $(a-b)^2 = a^2 - 2ab + b^2$ $(a+b)(a-b) = a^2 - b^2$ $(a+b)^3 = a^3 + b^3 + 3ab(a+b)$ $(a-b)^3 = a^3 - b^3 - 3ab(a-b)$ $a^3 + b^3 = (a+b)(a^2 - ab + b^2)$ $a^3 - b^3 = (a-b)(a^2 + ab + b^2)$ Exponents: $a^m \times a^n = a^{m+n}$ $\frac{a^m}{a^n} = a^{m-n}$ $(a^m)^n = a^{mn}$ $(ab)^m = a^m b^m$ $(\frac{a}{b})^m = \frac{a^m}{b^m}$ $a^0 = 1$ (for $a \neq 0$) $a^{-m} = \frac{1}{a^m}$ Surds (Roots): $\sqrt{ab} = \sqrt{a} \times \sqrt{b}$ $\sqrt{\frac{a}{b}} = \frac{\sqrt{a}}{\sqrt{b}}$ $(\sqrt{a})^2 = a$ $\sqrt[n]{a} = a^{1/n}$ 14. Series and Progressions Arithmetic Progression (AP): $a, a+d, a+2d, ...$ $n^{th}$ term: $a_n = a + (n-1)d$ Sum of $n$ terms: $S_n = \frac{n}{2}(2a + (n-1)d)$ or $S_n = \frac{n}{2}(a + a_n)$ Geometric Progression (GP): $a, ar, ar^2, ...$ $n^{th}$ term: $a_n = ar^{n-1}$ Sum of $n$ terms: $S_n = \frac{a(r^n - 1)}{r-1}$ (if $r > 1$) or $S_n = \frac{a(1 - r^n)}{1-r}$ (if $r Sum of infinite GP: $S_\infty = \frac{a}{1-r}$ (if $|r|