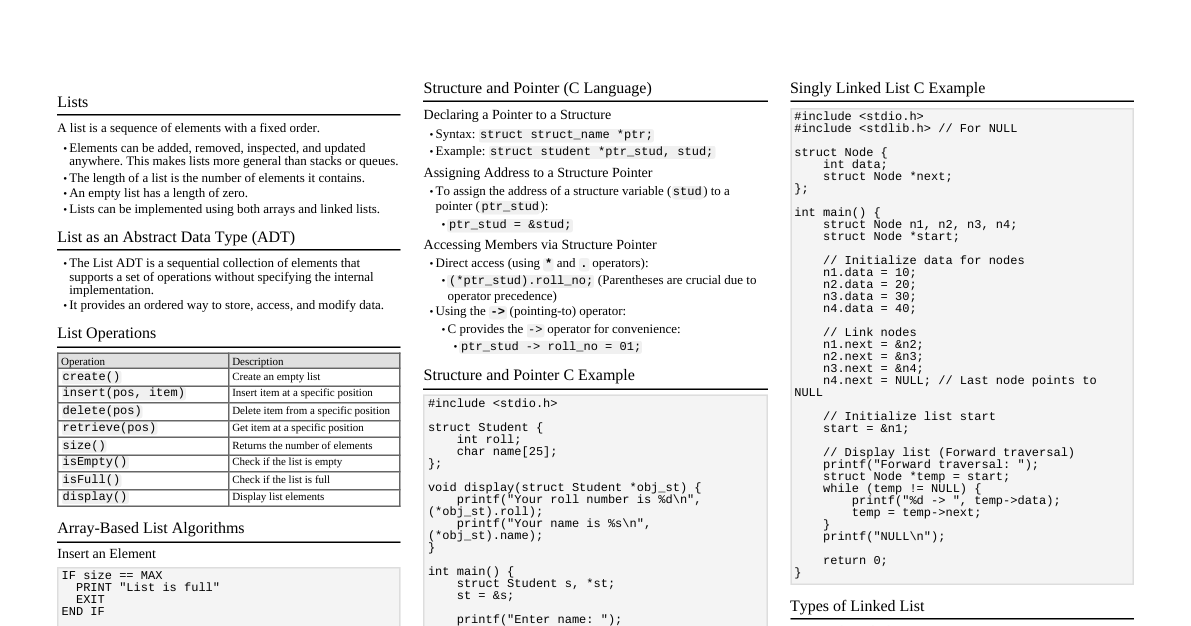
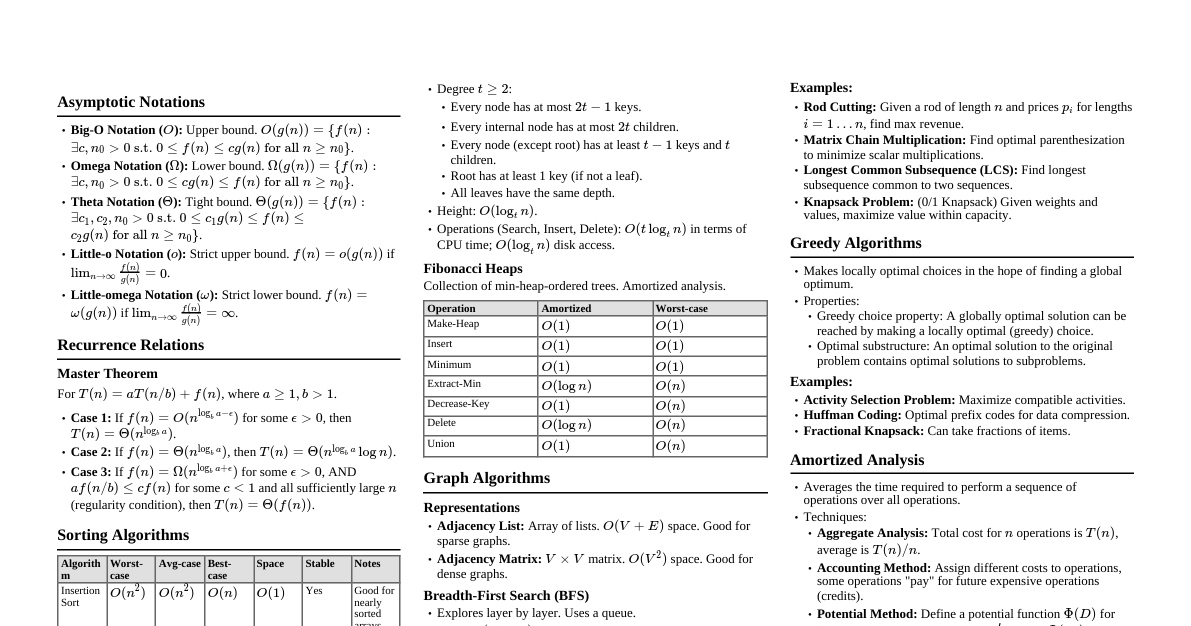
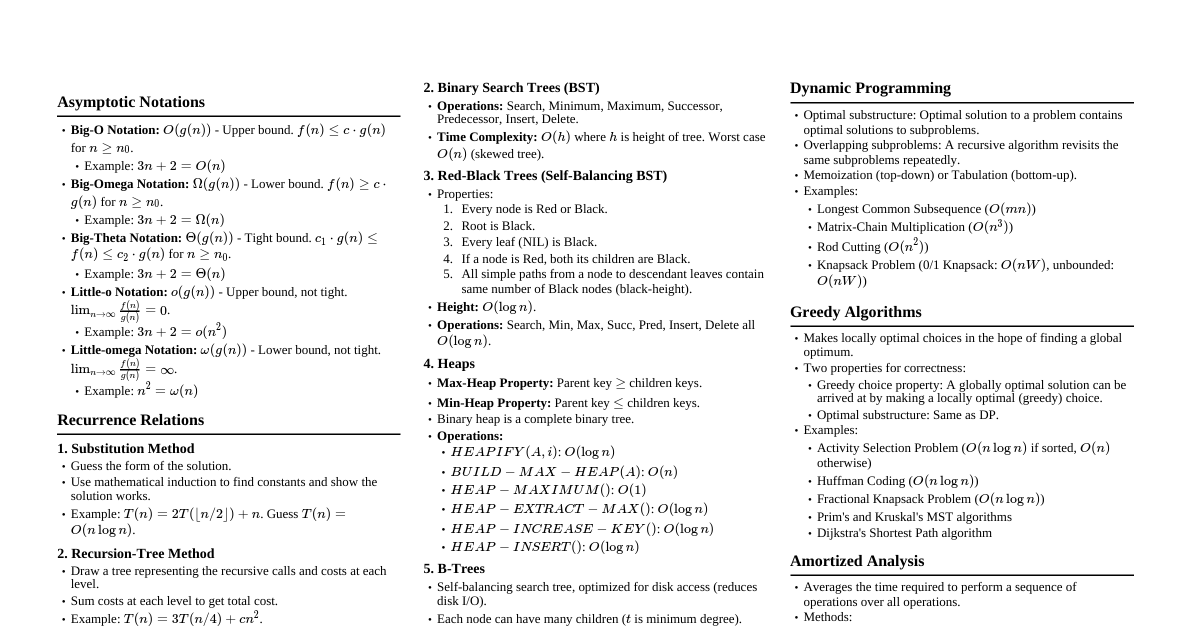
### Introduction to Algorithms & DSA - **Algorithm:** A set of well-defined instructions to solve a problem. - **Data Structure:** A particular way of organizing data in a computer to use it efficiently. - **Efficiency:** Measured by Time Complexity (how execution time grows with input size) and Space Complexity (how memory usage grows). - **Big O Notation:** Describes the upper bound of an algorithm's growth rate. - $O(1)$: Constant time - $O(\log n)$: Logarithmic time - $O(n)$: Linear time - $O(n \log n)$: Log-linear time - $O(n^2)$: Quadratic time - $O(2^n)$: Exponential time - $O(n!)$: Factorial time ### Arrays - **Definition:** A collection of items stored at contiguous memory locations. - **Characteristics:** Fixed-size (in most languages), direct access by index. - **Operations:** - Access: $O(1)$ - Search: $O(n)$ (linear), $O(\log n)$ (binary on sorted) - Insertion/Deletion: $O(n)$ (requires shifting elements) - **Use Cases:** Storing collections of same-type data, lookup tables. ### Linked Lists - **Definition:** A linear collection of data elements, called nodes, where each node points to the next. - **Types:** - **Singly Linked List:** Node has data and a pointer to the next node. - **Doubly Linked List:** Node has data and pointers to next and previous nodes. - **Circular Linked List:** Last node points back to the first node. - **Operations:** - Access: $O(n)$ - Search: $O(n)$ - Insertion/Deletion: $O(1)$ (if position is known), $O(n)$ (if search is needed) - **Use Cases:** Implementing stacks, queues, dynamic memory allocation. ### Stacks - **Definition:** LIFO (Last-In, First-Out) data structure. - **Operations:** - `push(item)`: Add an item to the top. $O(1)$ - `pop()`: Remove the top item. $O(1)$ - `peek()`: Get the top item without removing. $O(1)$ - `isEmpty()`: Check if stack is empty. $O(1)$ - **Use Cases:** Function call stack, undo/redo features, expression evaluation. ### Queues - **Definition:** FIFO (First-In, First-Out) data structure. - **Operations:** - `enqueue(item)`: Add an item to the rear. $O(1)$ - `dequeue()`: Remove the front item. $O(1)$ - `front()`: Get the front item without removing. $O(1)$ - `isEmpty()`: Check if queue is empty. $O(1)$ - **Use Cases:** Task scheduling, breadth-first search (BFS). ### Trees - **Definition:** Hierarchical data structure with a root node and subtrees of children nodes. - **Terminology:** Root, Node, Edge, Parent, Child, Sibling, Leaf, Depth, Height. - **Types:** - **Binary Tree:** Each node has at most two children. - **Binary Search Tree (BST):** Left child Root -> Right (sorted for BST) - **Pre-order:** Root -> Left -> Right (useful for copying tree) - **Post-order:** Left -> Right -> Root (useful for deleting tree) - **Use Cases:** File systems, databases, expression parsing. ### Graphs - **Definition:** A set of vertices (nodes) and edges connecting them. - **Types:** Directed/Undirected, Weighted/Unweighted, Cyclic/Acyclic. - **Representations:** - **Adjacency Matrix:** $O(V^2)$ space. $O(1)$ to check edge. - **Adjacency List:** $O(V+E)$ space. $O(deg(V))$ to check edge. - **Graph Traversal:** - **Breadth-First Search (BFS):** Uses a queue. Explores level by level. Shortest path on unweighted graphs. $O(V+E)$. - **Depth-First Search (DFS):** Uses a stack (or recursion). Explores as far as possible down each branch. $O(V+E)$. - **Use Cases:** Social networks, mapping, routing algorithms. ### Hashing - **Definition:** Mapping data of arbitrary size to fixed-size values (hash codes). - **Hash Table:** Data structure that implements an associative array abstract data type, mapping keys to values using a hash function. - **Collision Resolution:** - **Chaining:** Store multiple items in a linked list at the same hash index. - **Open Addressing:** Find another open slot (linear probing, quadratic probing, double hashing). - **Performance:** Average $O(1)$ for insert, delete, search. Worst case $O(n)$ if many collisions. - **Use Cases:** Dictionaries, caches, unique data identification. ### Sorting Algorithms - **Comparison-based Sorts:** - **Bubble Sort:** Repeatedly steps through the list, compares adjacent elements and swaps them if they are in the wrong order. $O(n^2)$. - **Selection Sort:** Divides the list into a sorted and unsorted part. Selects smallest element from unsorted part and moves to sorted. $O(n^2)$. - **Insertion Sort:** Builds the final sorted array (or list) one item at a time. $O(n^2)$, good for nearly sorted data. - **Merge Sort:** Divide and conquer. Divides array in half, sorts each half, then merges. Stable. $O(n \log n)$. - **Quick Sort:** Divide and conquer. Picks an element as pivot and partitions the array around the pivot. In-place. $O(n \log n)$ average, $O(n^2)$ worst. - **Heap Sort:** Uses a binary heap data structure. In-place. $O(n \log n)$. - **Non-Comparison Sorts:** - **Counting Sort:** For integers with small range. Counts frequency of each item. $O(n+k)$ where $k$ is range. - **Radix Sort:** Sorts integers by processing individual digits. $O(nk)$ where $k$ is number of digits. - **Stability:** A sort is stable if it preserves the relative order of equal elements. (Merge Sort, Insertion Sort, Bubble Sort, Counting Sort, Radix Sort are stable). ### Searching Algorithms - **Linear Search:** Checks each element sequentially until a match is found or end of list. $O(n)$. - **Binary Search:** For sorted arrays. Repeatedly divides the search interval in half. $O(\log n)$. ```python def binary_search(arr, target): low, high = 0, len(arr) - 1 while low ### Recursion & Dynamic Programming - **Recursion:** A function that calls itself to solve a smaller instance of the same problem. - **Base Case:** Condition to stop recursion. - **Recursive Step:** Calls itself with modified input. - **Dynamic Programming:** Technique to solve complex problems by breaking them into simpler subproblems. - **Overlapping Subproblems:** Subproblems are solved multiple times. - **Optimal Substructure:** Optimal solution to problem can be constructed from optimal solutions of its subproblems. - **Memoization:** Storing results of expensive function calls and returning the cached result when the same inputs occur again (top-down DP). - **Tabulation:** Solving subproblems iteratively and storing results in a table (bottom-up DP). - **Use Cases:** Fibonacci sequence, factorial, shortest path problems, knapsack problem. ### Greedy Algorithms - **Definition:** Makes the locally optimal choice at each step with the hope of finding a global optimum. - **Characteristics:** - **Greedy Choice Property:** A global optimal solution can be reached by making locally optimal choices. - **Optimal Substructure:** The optimal solution to the problem contains optimal solutions to subproblems. - **Use Cases:** Dijkstra's algorithm (shortest path), Prim's/Kruskal's algorithm (minimum spanning tree), Activity Selection Problem. ### Backtracking - **Definition:** A general algorithmic technique for finding all (or some) solutions to computational problems, notably constraint satisfaction problems, that incrementally builds candidates to the solutions, and abandons a candidate ("backtracks") as soon as it determines that the candidate cannot possibly be completed to a valid solution. - **Characteristics:** Often implemented with recursion. Explores all possible paths until a solution is found or a path is invalid. - **Use Cases:** N-Queens problem, Sudoku solver, Hamiltonian cycle, subset sum. ### Common Algorithm Paradigms - **Divide and Conquer:** Break problem into smaller subproblems, solve them, and combine solutions (e.g., Merge Sort, Quick Sort). - **Dynamic Programming:** Solve overlapping subproblems and store results (e.g., Fibonacci, Knapsack). - **Greedy:** Make locally optimal choices (e.g., Dijkstra's, MST). - **Backtracking:** Explore all paths, prune invalid ones (e.g., N-Queens, Sudoku). - **Brute Force:** Try all possible solutions (often inefficient).